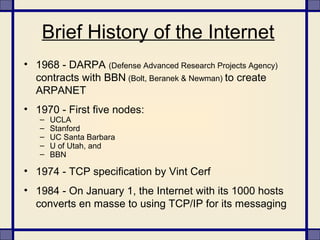
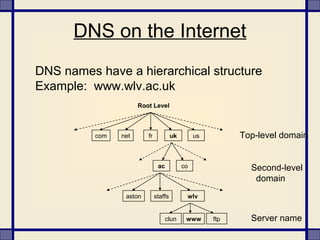
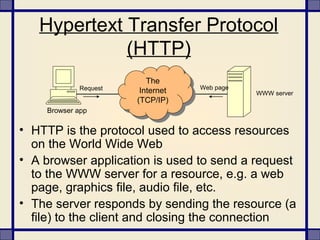
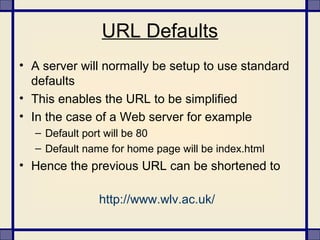
The document provides information about what constitutes cybercrime and the types of criminal activities that fall under this category. It discusses how cybercrime involves illegal activities that are committed online using computers and networks. Some examples of cybercrime variants mentioned include hacking, cyber squatting, phishing, cyber stalking, and vishing - which aim to illegally access systems, steal personal and financial information, or harass individuals over the internet. The document also notes how cybercriminals can include children, dissatisfied employees, professional hackers, and crackers.