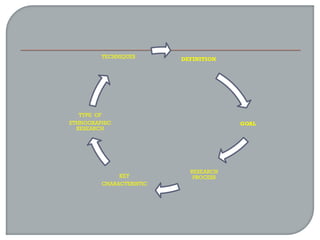
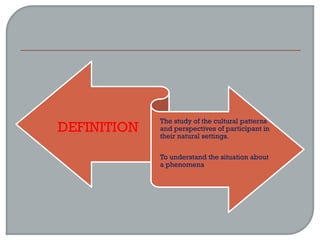
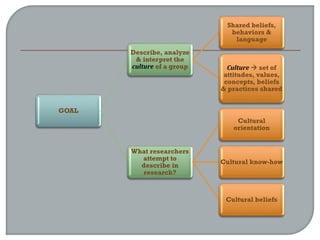
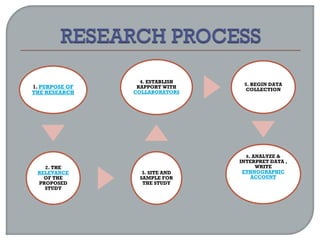
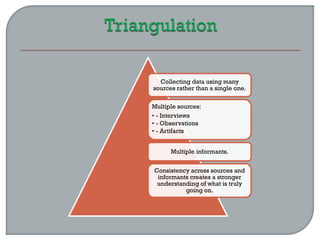
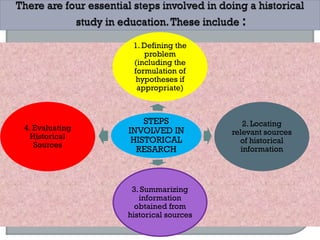
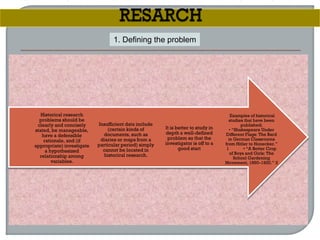
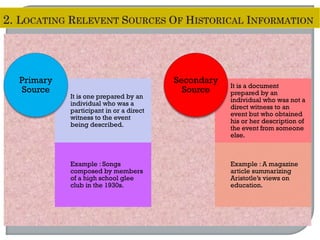
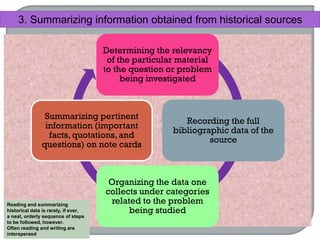
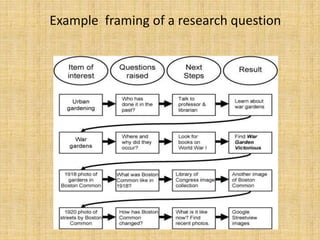
This document defines ethnographic research and outlines the ethnographic research process. It discusses key characteristics of ethnographic research such as being conducted in a natural context and emphasizing everyday experiences through observation and interviews. The document also describes common ethnographic research techniques like triangulation, participant observation, and taking field notes. It provides examples of historical research studies and outlines the steps involved in historical research, including defining the problem, locating sources, summarizing information, and evaluating sources. Limitations of historical research discussed include relying on limited surviving records and not ensuring a representative sample.