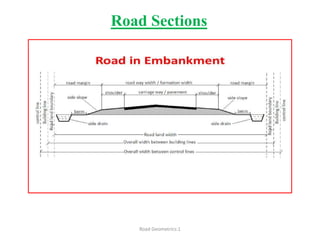
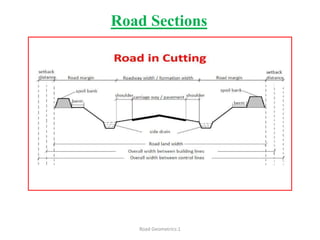
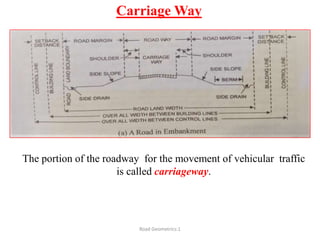
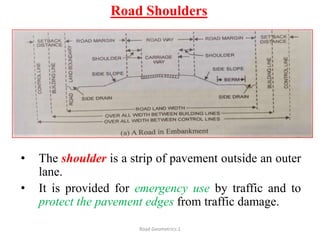
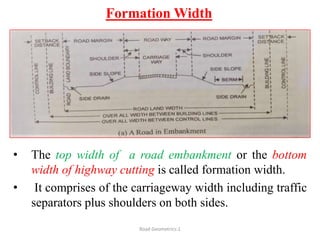
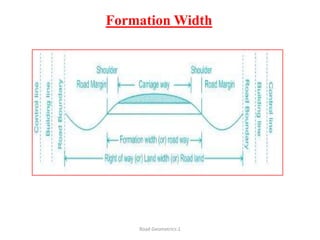
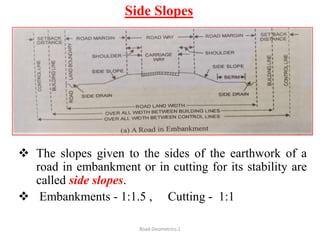
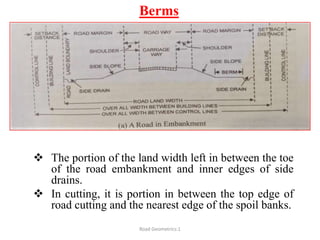
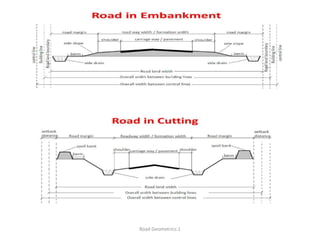
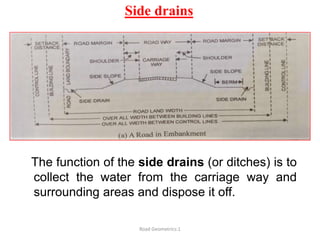
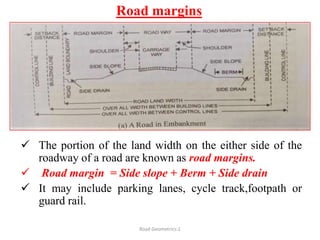
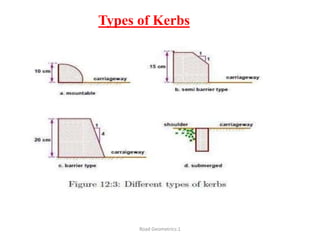
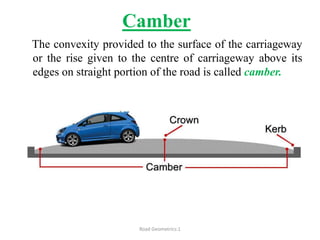
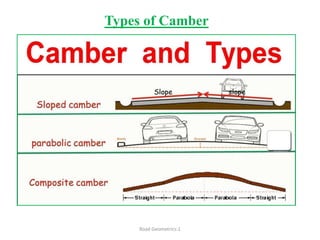
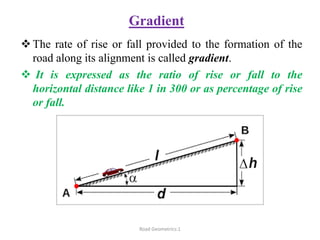
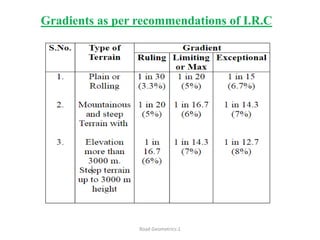
This document defines key terms related to road geometrics and cross sections. It discusses the carriageway as the portion for vehicular traffic, road shoulders for emergency use and protecting edges, and formation width as the road embankment width including carriageway and shoulders. It also covers side slopes for embankment/cutting stability, berms between embankments and drains, road margins as land widths with possible inclusions, right of way as acquired land area, and camber and gradients as providing drainage and vehicle regulation.