The document discusses various cross-sectional elements of highways including:
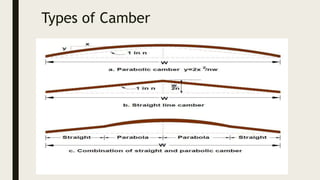
1) Cross-slope or camber which slopes the road surface transversely to drain water, with types including rolling and plane camber.
2) Width of pavement or carriageway which depends on traffic lanes and vehicle width, with recommended widths by road class.
3) Medians which divide opposite traffic, and serve functions like channelizing intersections and protecting pedestrians.
4) Other elements like kerbs, shoulders, guard rails, footpaths, driveways, cycle tracks, bus bays, parking lanes, and service roads.