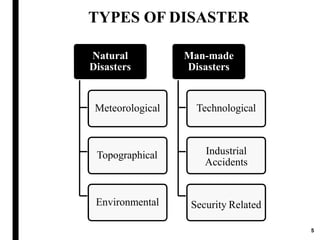
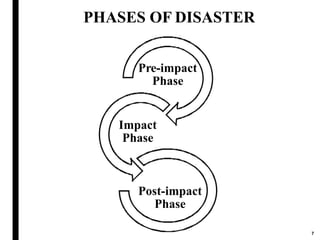
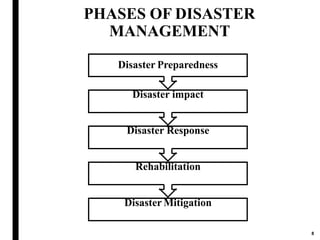
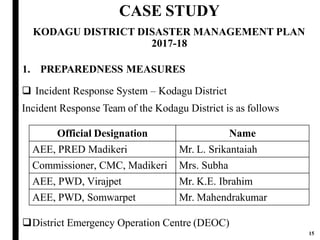
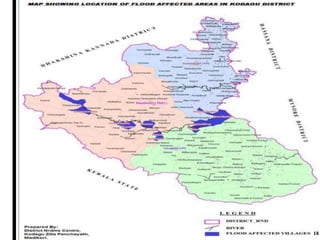
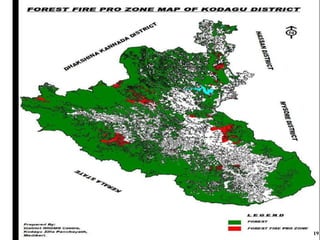
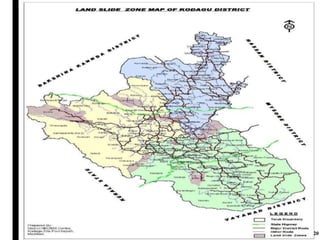
The document outlines disaster management, which involves organizing resources for preparedness, response, recovery, and mitigation to alleviate the impact of disasters. It categorizes disasters into natural and man-made types and details the phases and necessary actions before, during, and after such events. The document also highlights the advantages and disadvantages of disaster management, exemplified by the Kodagu district disaster management plan.