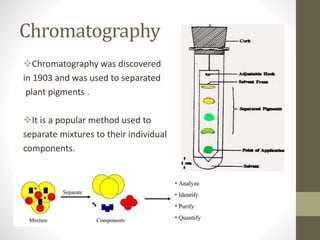
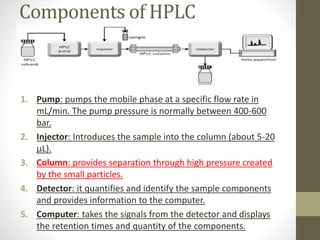
High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) is a popular analytical technique used to separate, identify, and quantify mixtures into their individual components. HPLC uses high pressure pumps to push a pressurized mobile phase through a column packed with adsorbent particles. Sample components interact differently with the stationary phase based on their properties and are eluted from the column at different retention times, allowing for separation. The separated components are then detected and quantified to analyze the sample. HPLC provides high-speed, efficient, and sensitive separation compared to traditional liquid chromatography.