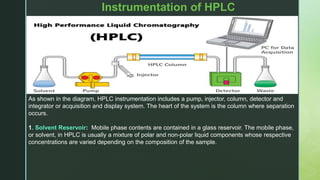
The document discusses High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC), including its principles, types of separations, instrumentation, applications in fields like food and pharmaceuticals, and advantages like speed and accuracy over traditional chromatography techniques. HPLC uses high pressure to pass samples in liquid mobile phases through stationary phases in columns to separate mixtures based on properties like polarity, size, or ionic charge.