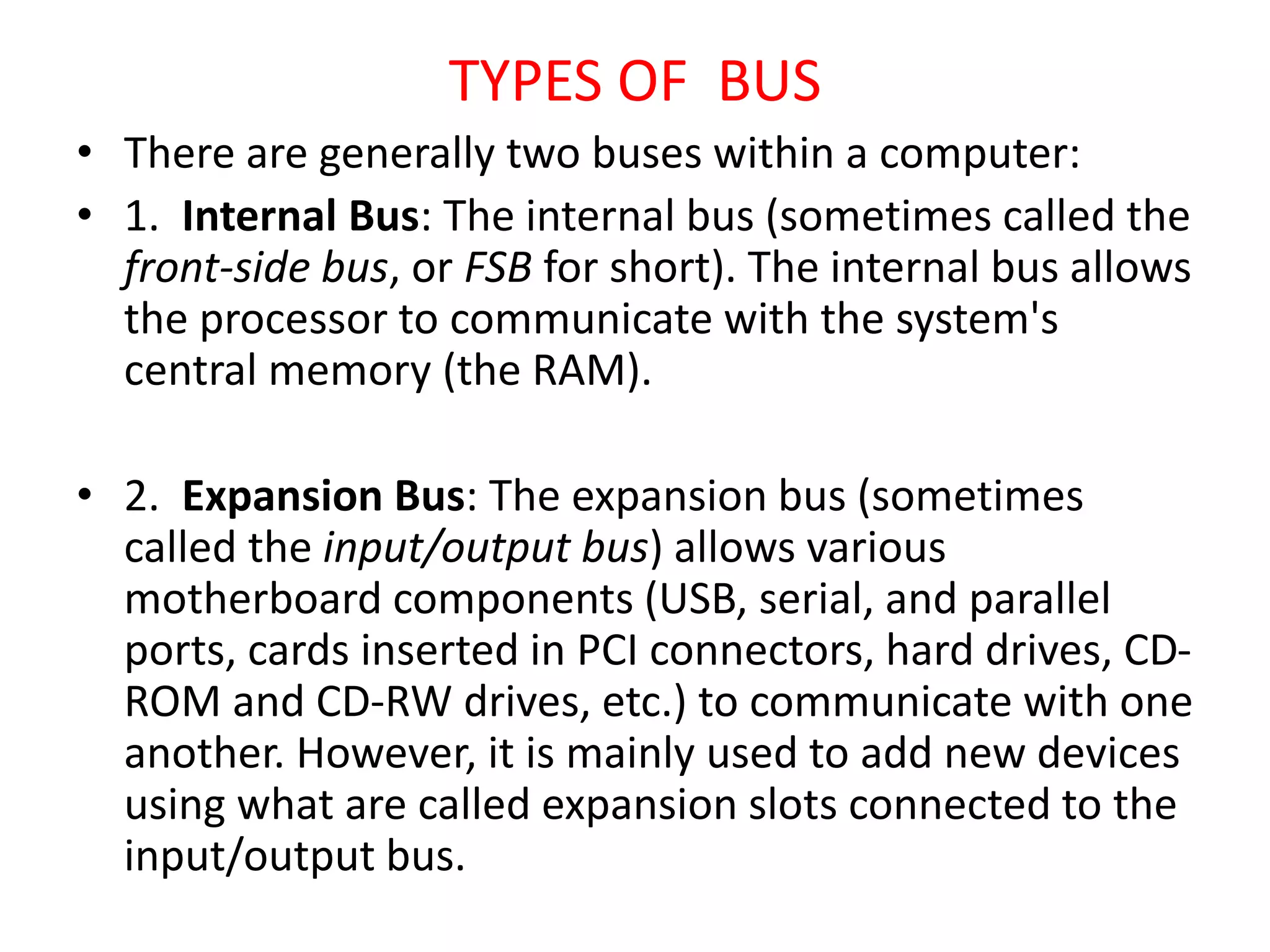
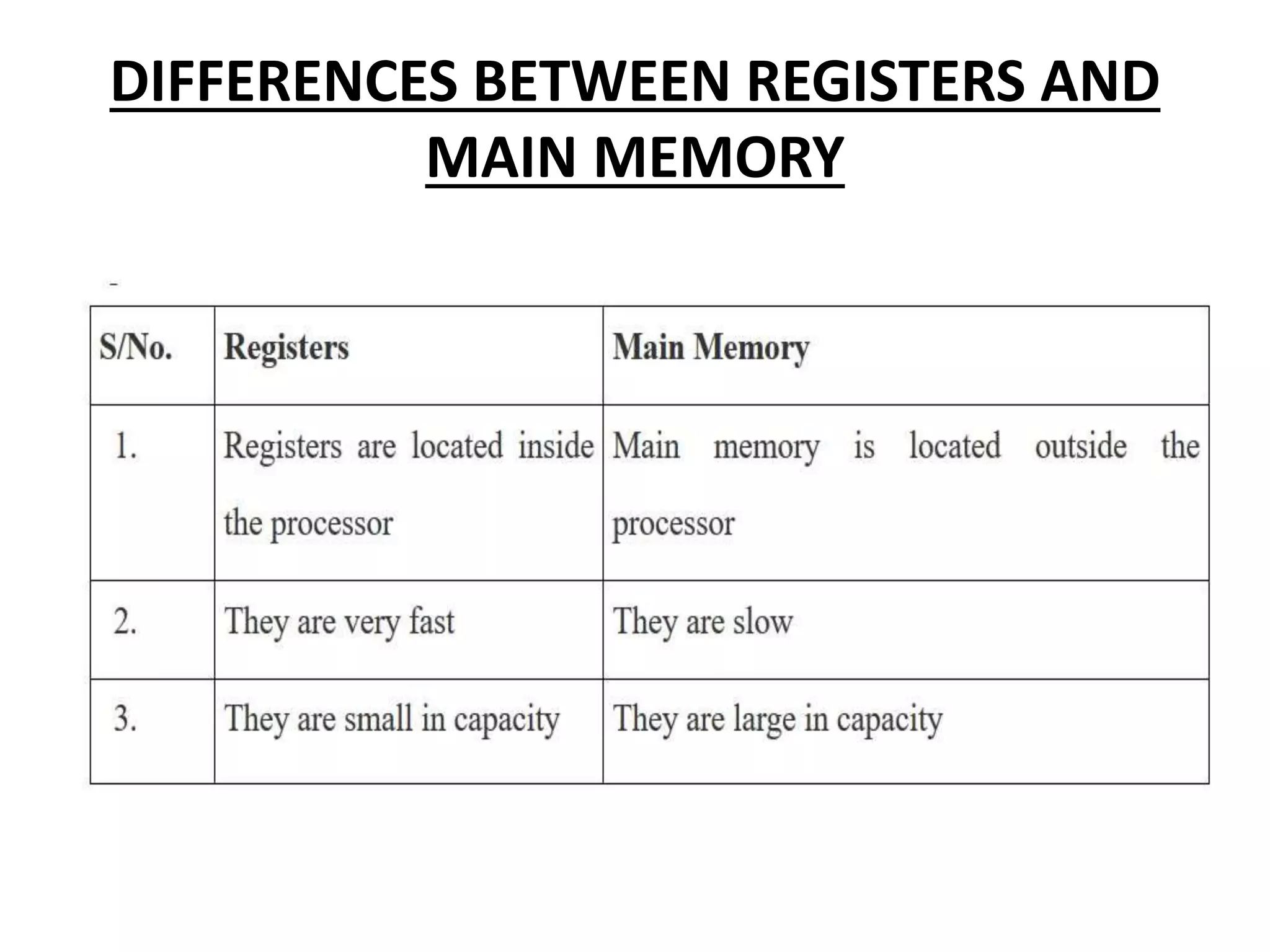
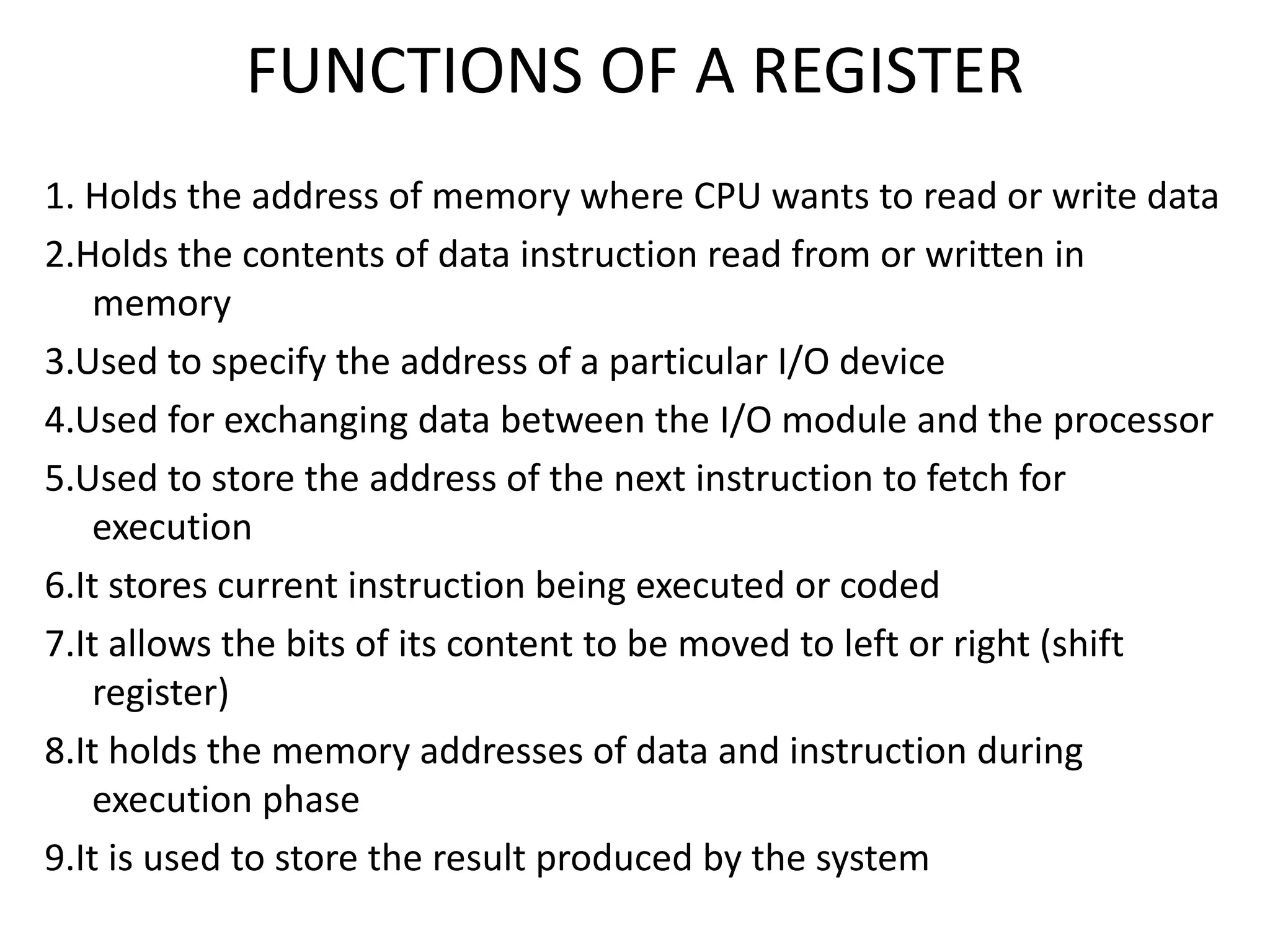
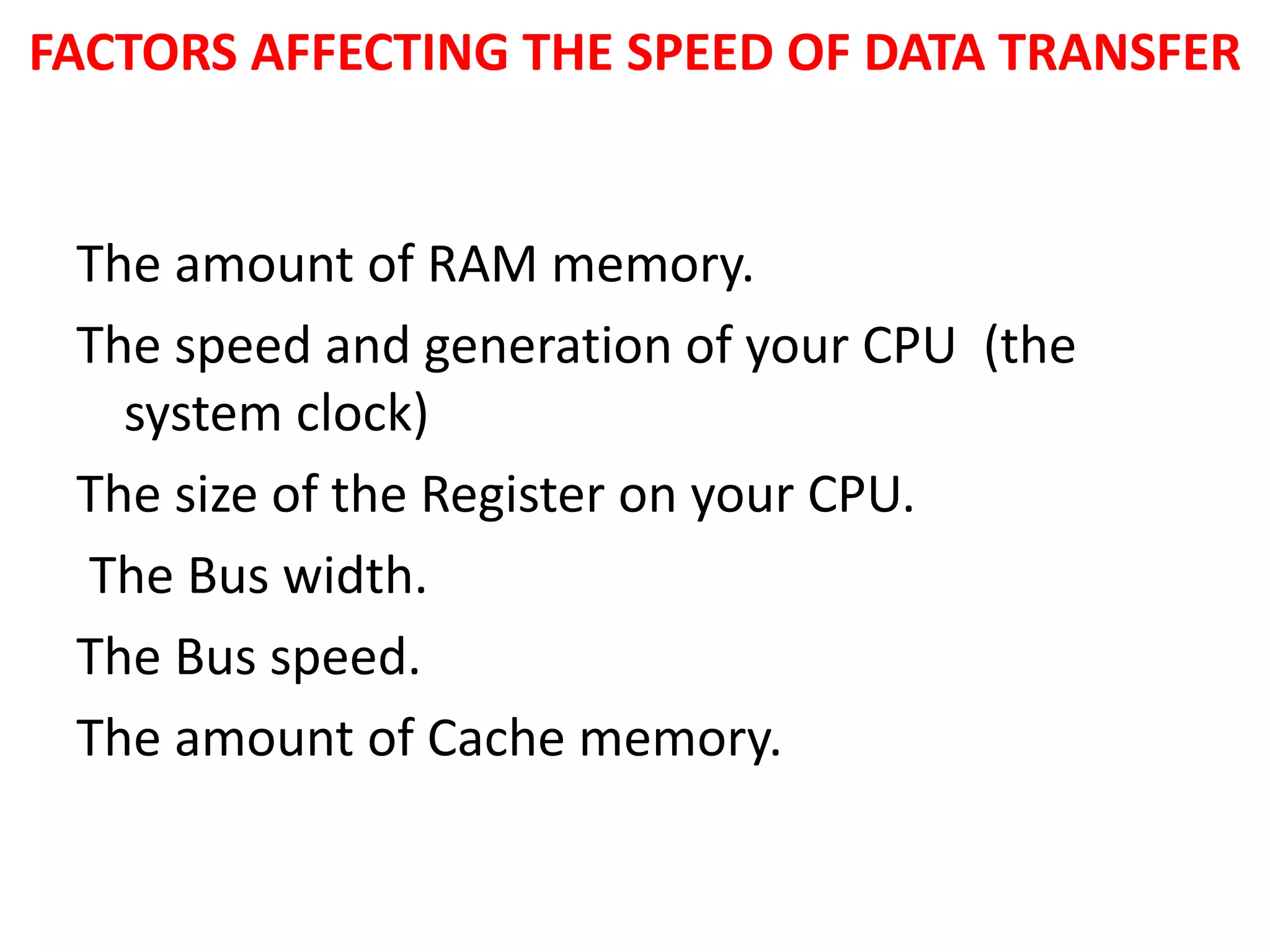
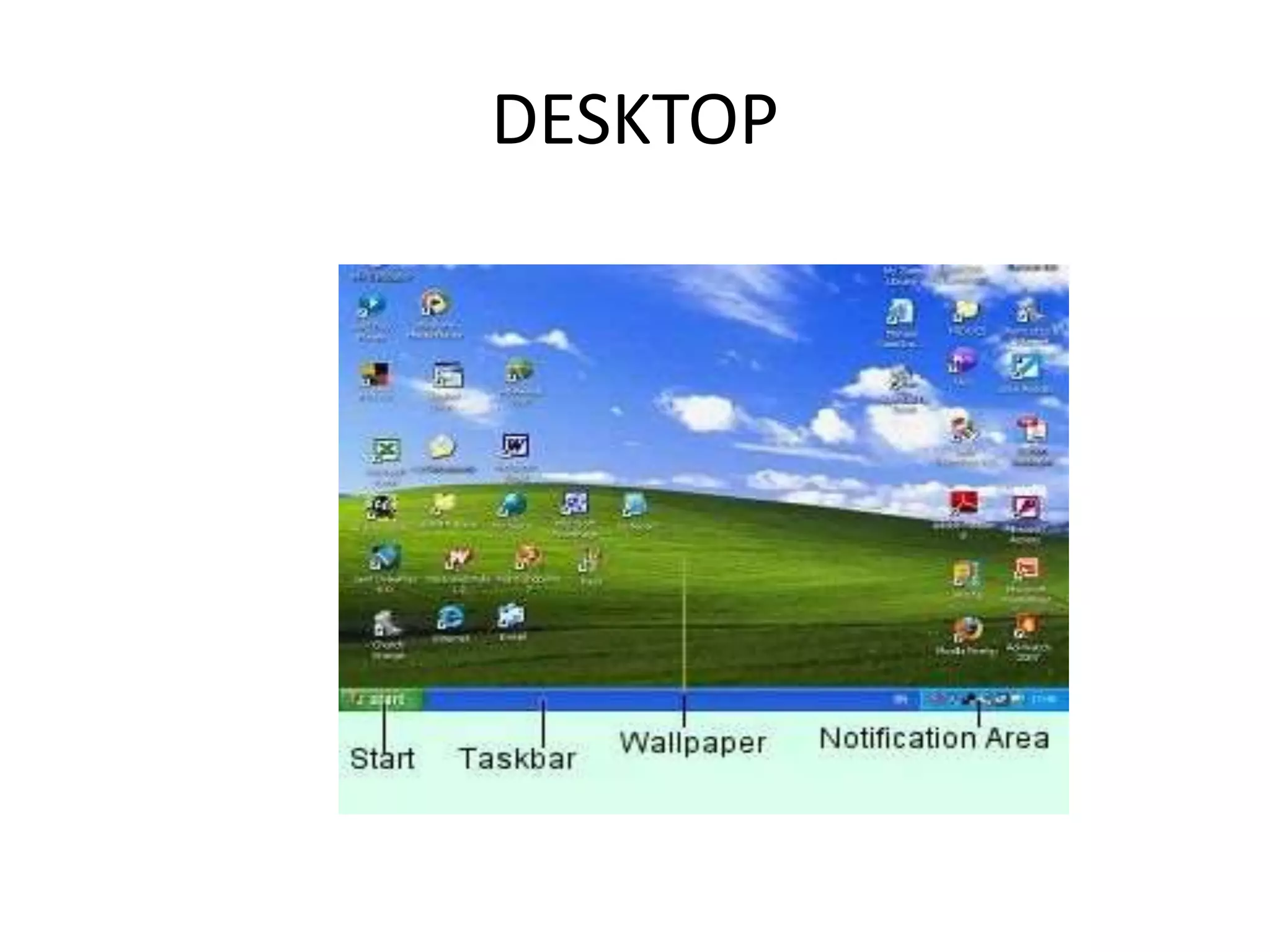
Registers are temporary storage areas within the CPU that can hold instructions and data during processing. They are faster than main memory. An address identifies the location of data in memory. A bus is a communication pathway that allows different computer components to transfer data. There are internal and expansion buses. Registers include the memory data register, current instruction register, and program counter. Booting loads an operating system from secondary storage into RAM to start a computer, while shutting down closes programs to turn off power in an orderly fashion.