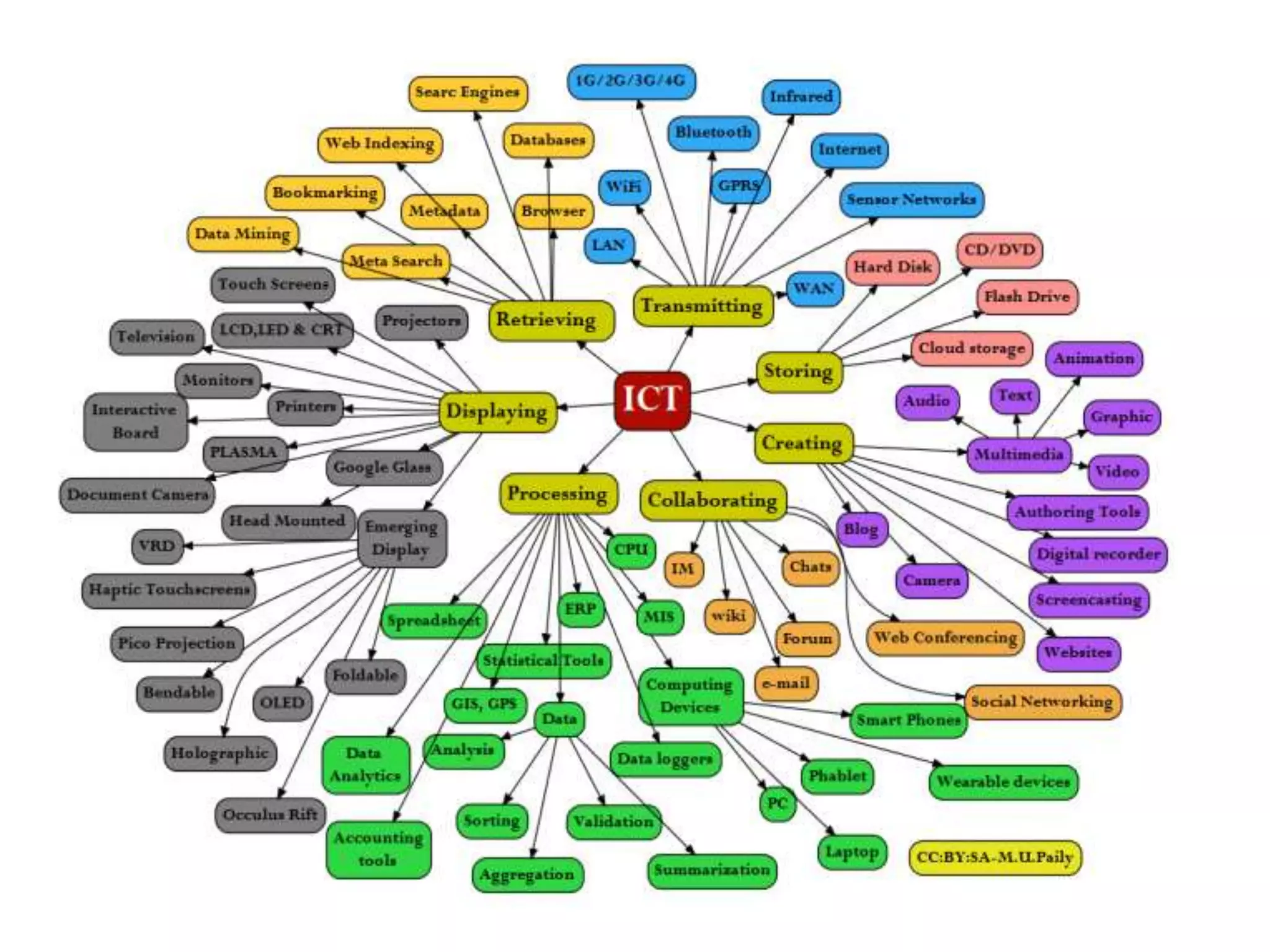
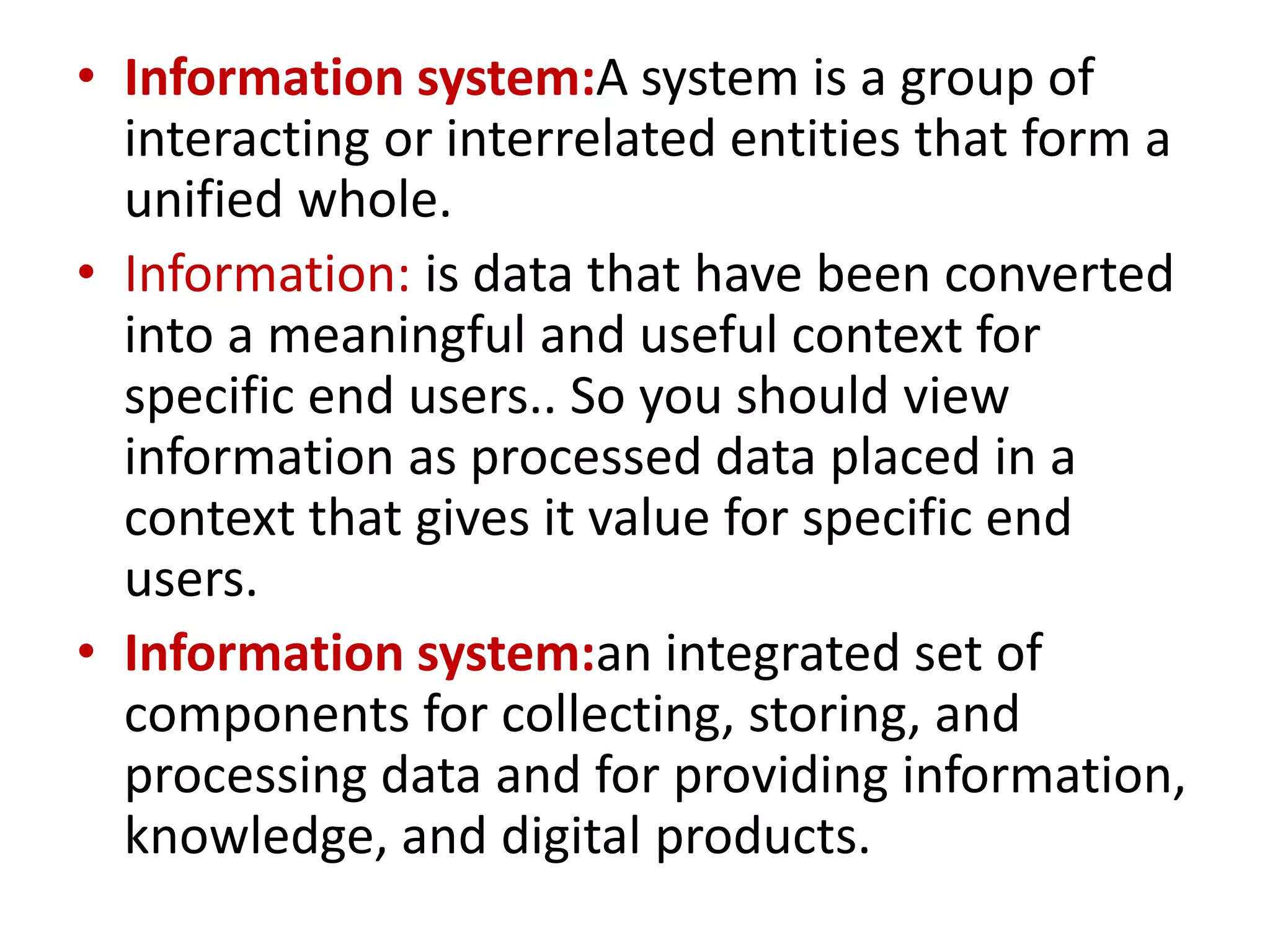
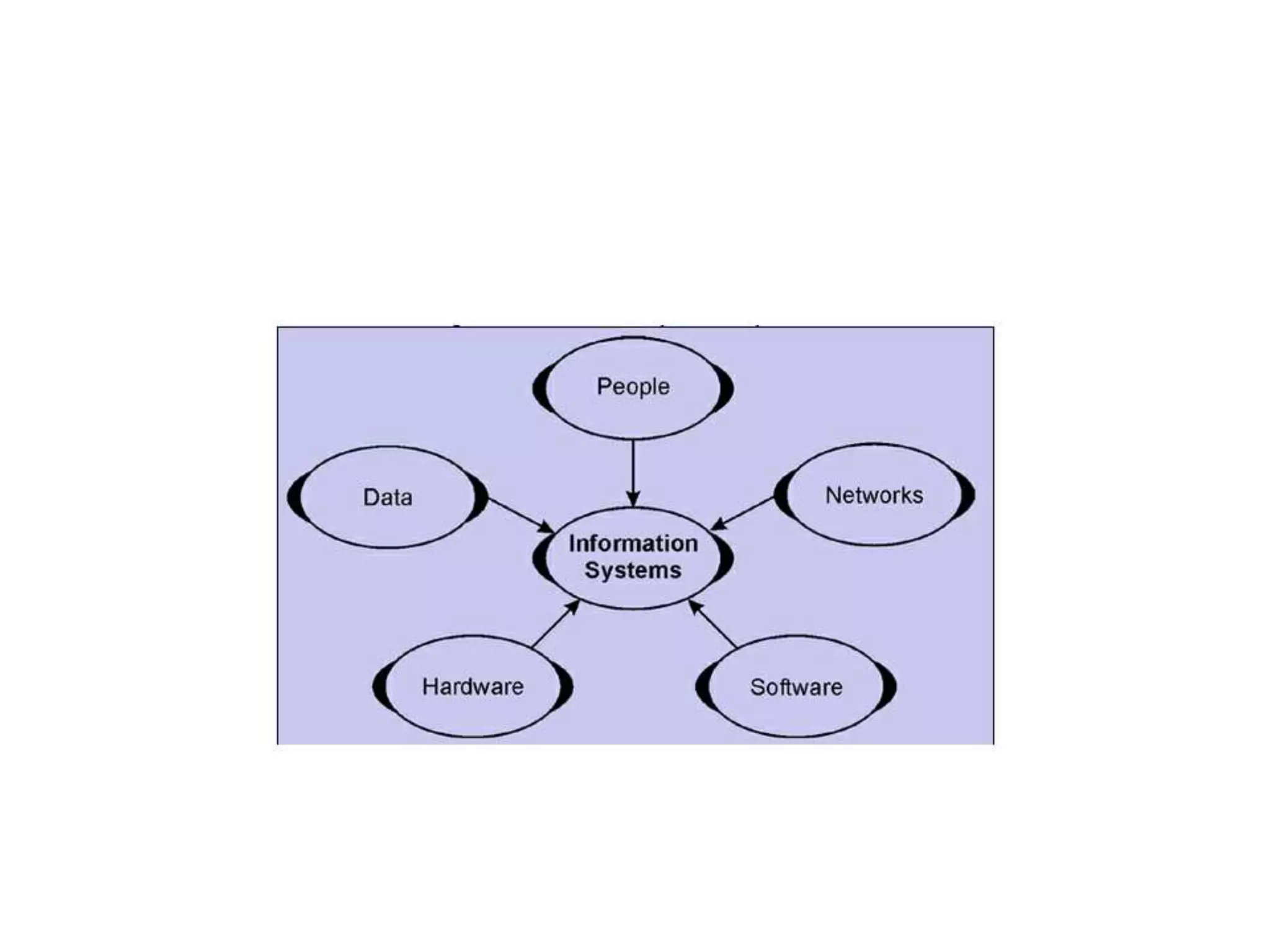
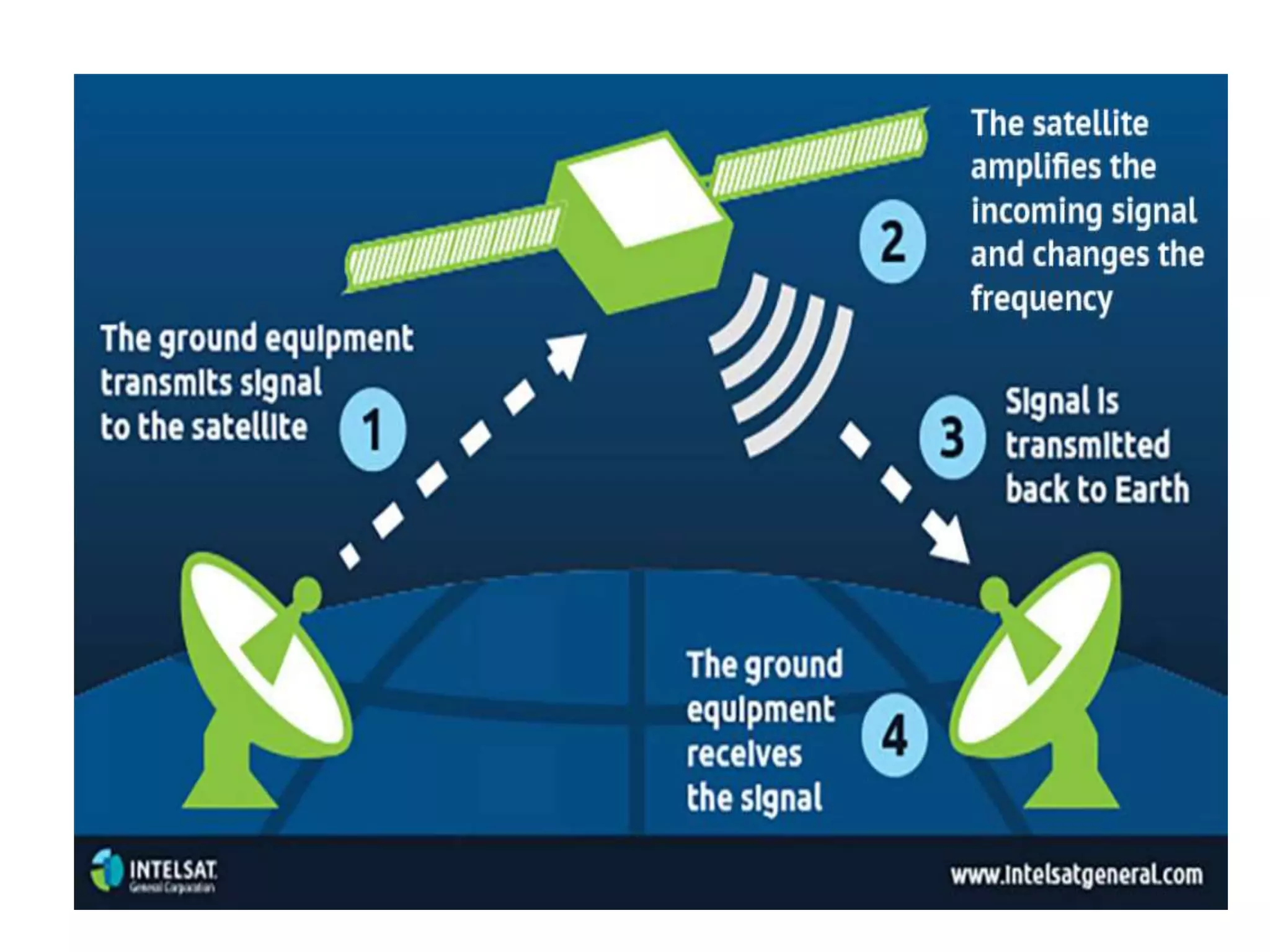
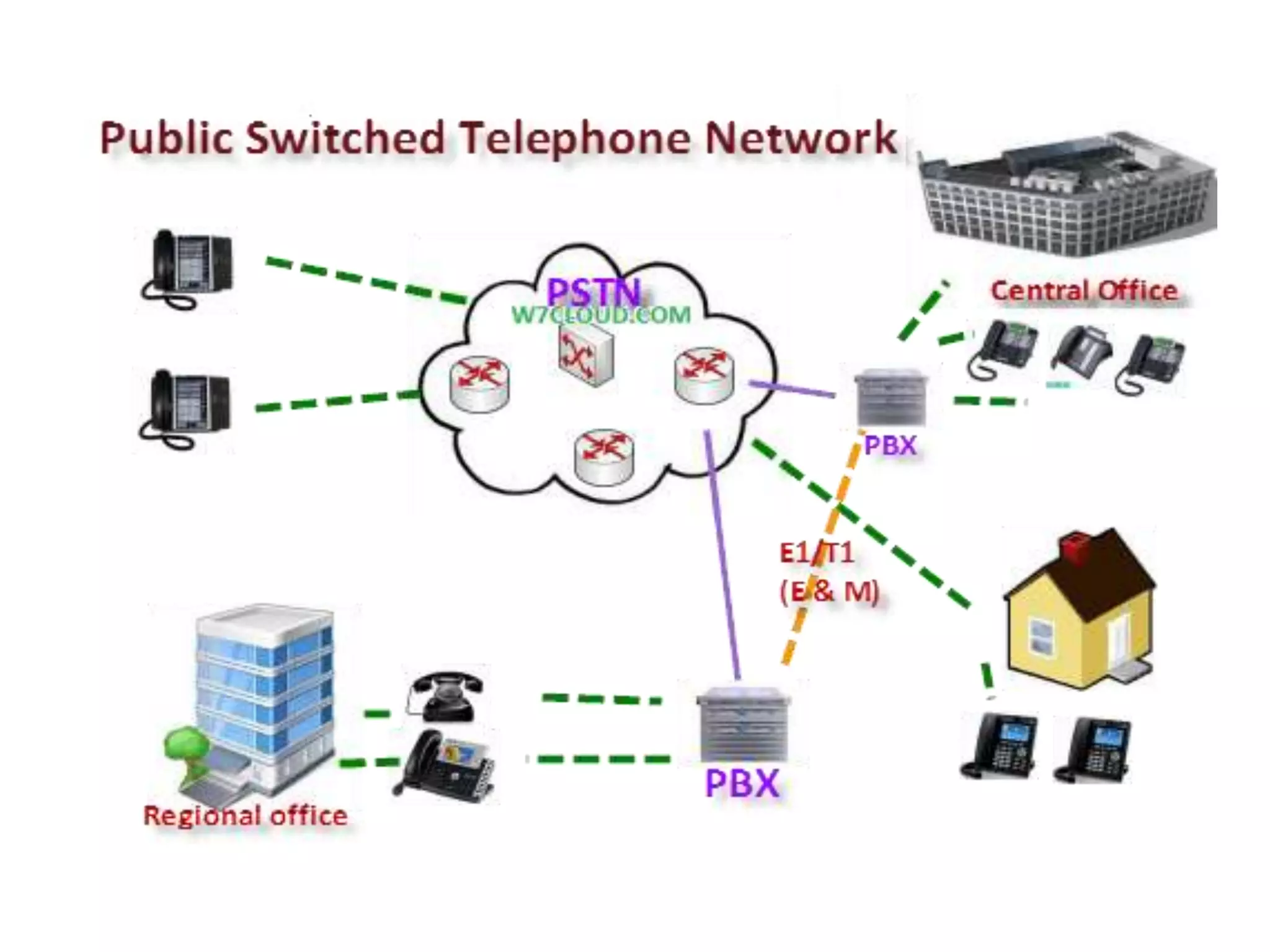
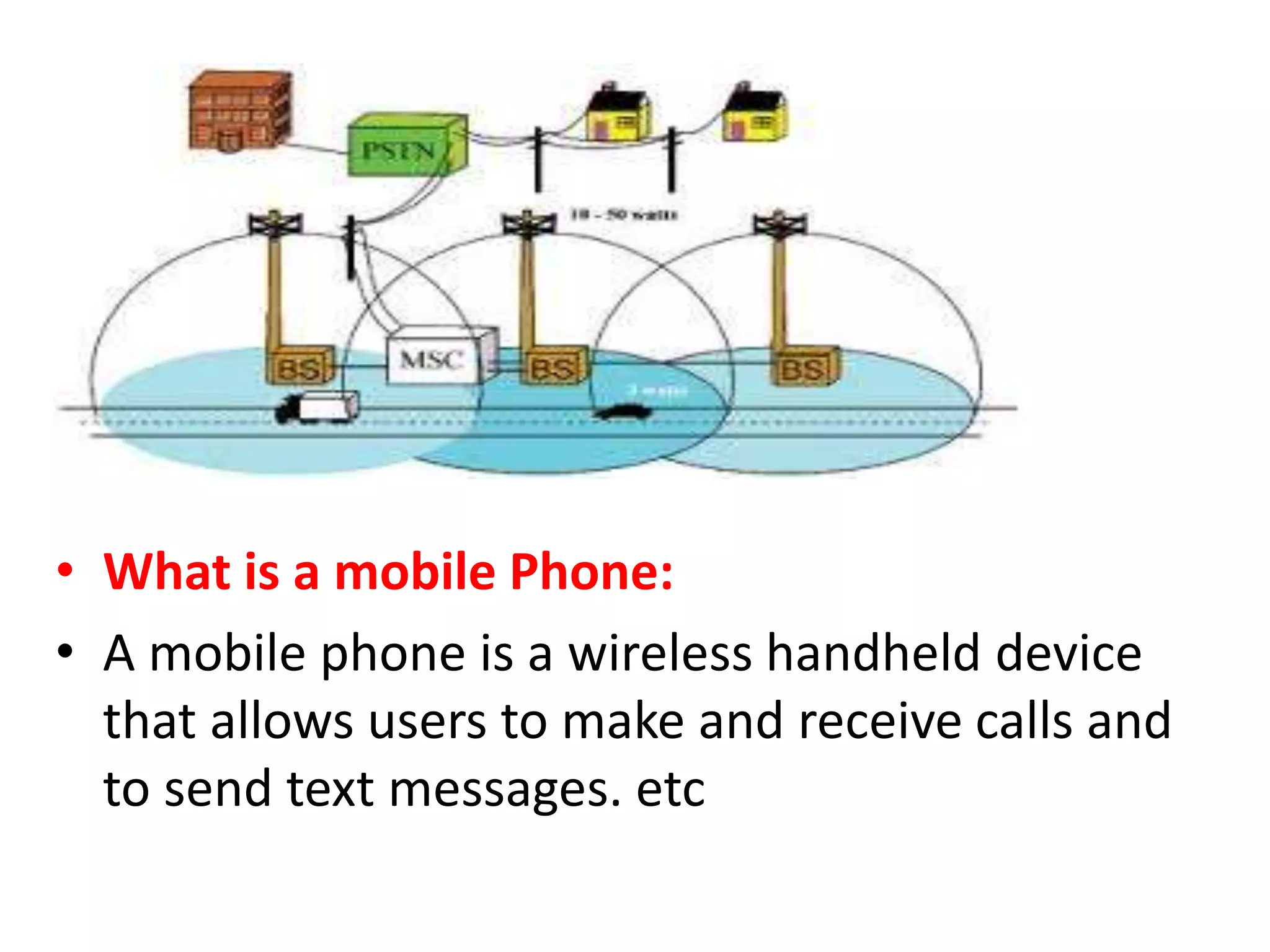
This document defines and describes various information and communication technologies (ICT). It discusses broadcasting systems like radio and television broadcasting which transmit audio/video signals to a wide audience. It also describes telecommunications as the exchange of information via electronic means like phones, internet, satellites. Other ICTs discussed include data networks to share information between connected computers, information systems to collect and process data, and satellite communications to provide links between locations on Earth. Mobile phone systems across generations are also summarized.