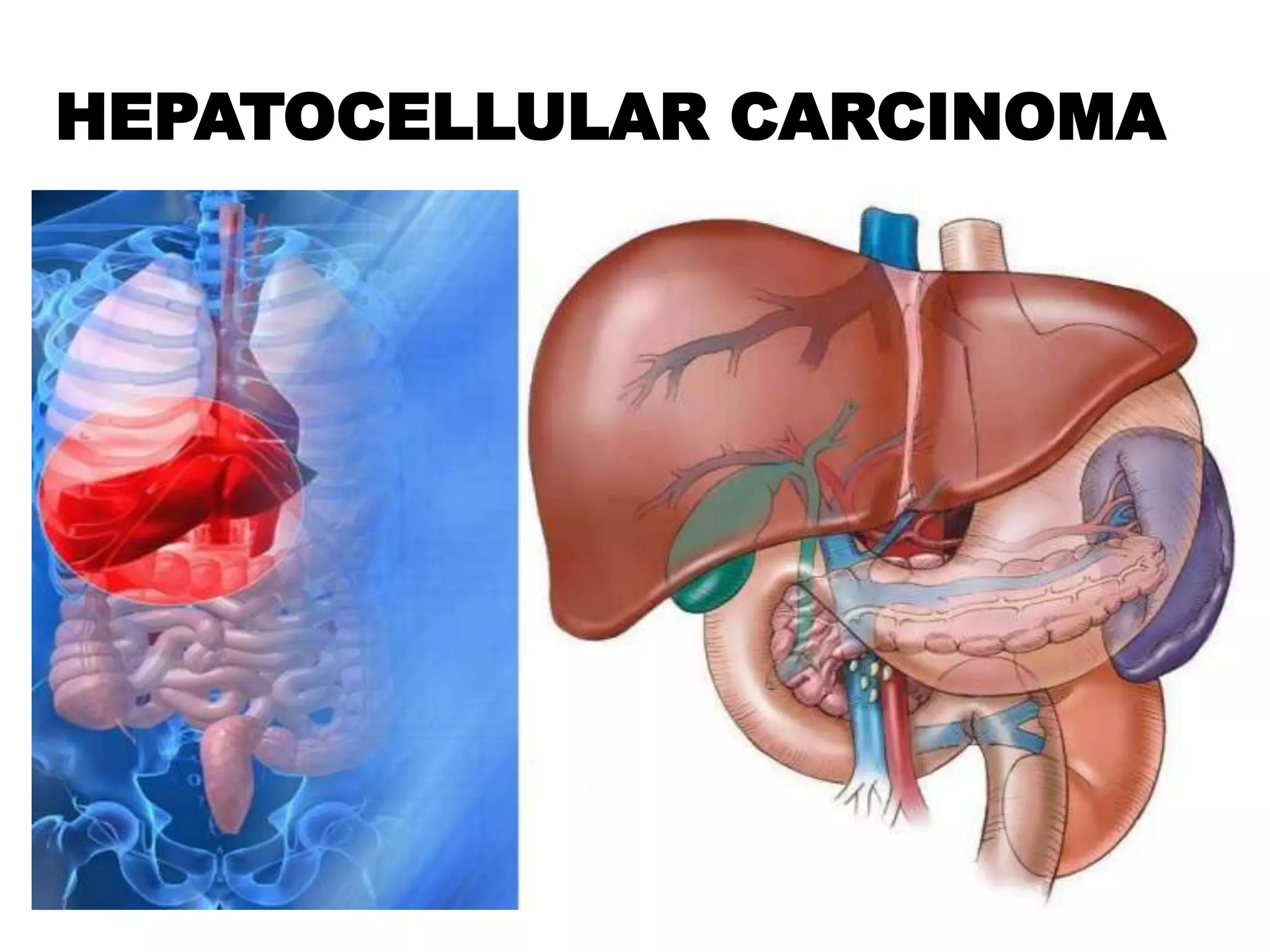
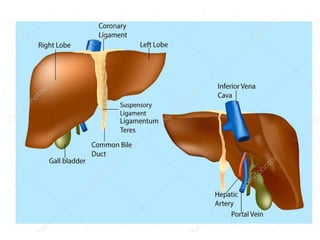
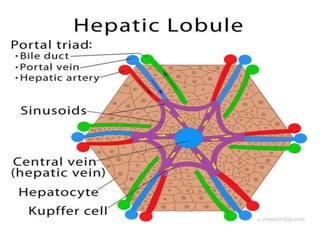
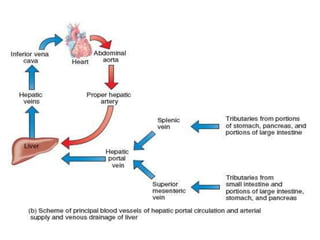
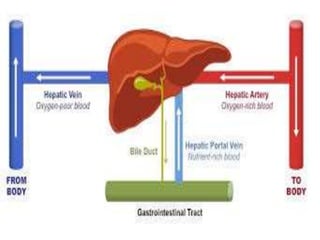
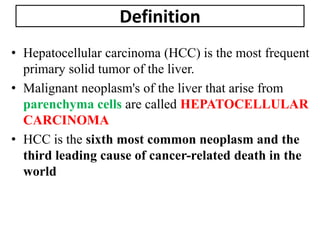
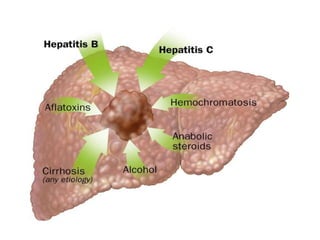
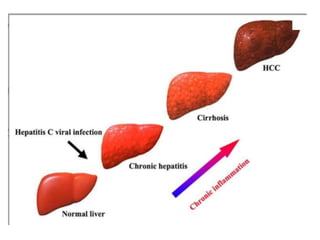
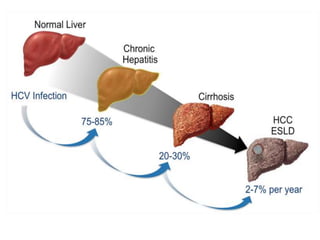
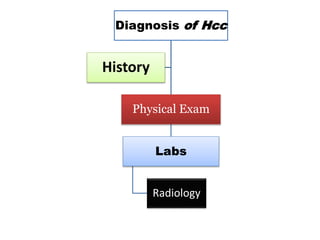
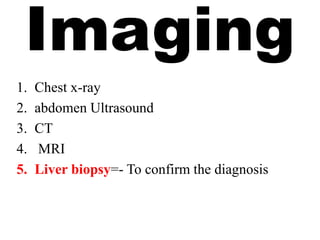
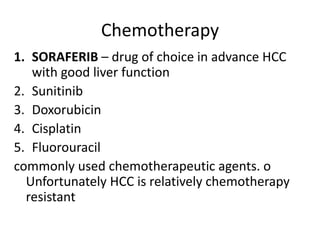
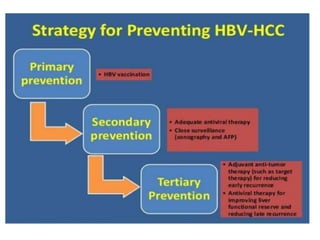
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common type of liver cancer. It is usually caused by chronic hepatitis B or C infections or cirrhosis from excessive alcohol use. The cancer develops through a multi-stage process where chronic liver injury leads to cell death, regeneration, and eventual mutations in hepatocytes. Diagnosis involves blood tests, imaging like ultrasound or CT scan, and sometimes a biopsy. Treatment depends on the size and spread of the tumor and may include surgical resection, liver transplantation, ablation, embolization, or chemotherapy. Prognosis varies but resection or transplantation can offer 5-year survival rates of 30-40% or 75%, respectively, while embolization provides around a 60%