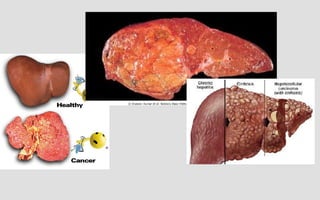
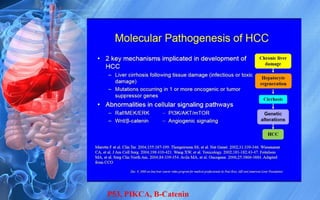
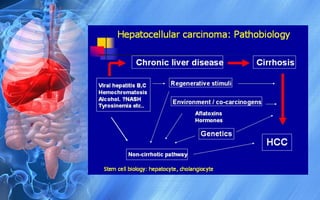
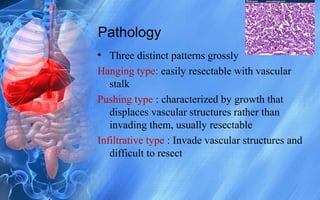
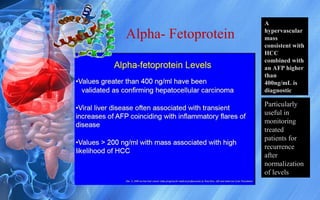
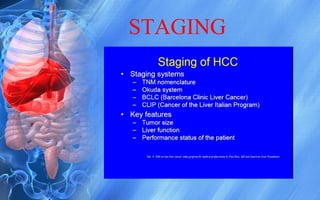
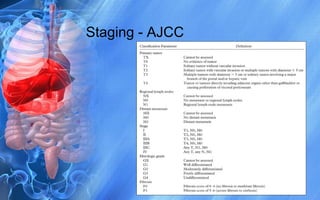
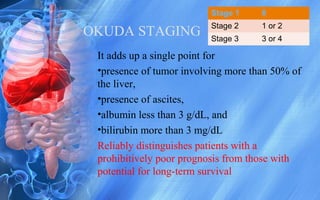
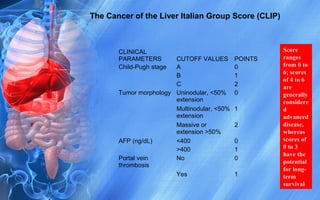
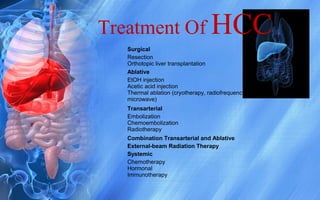
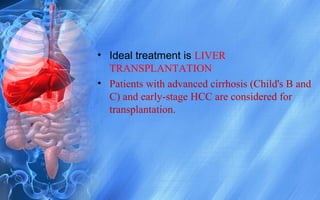
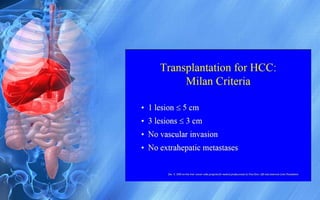
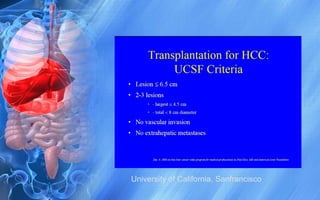
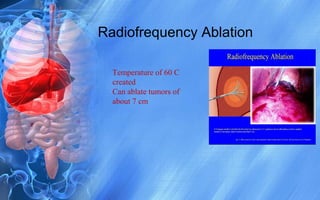
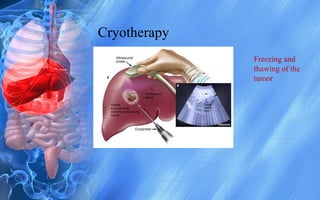
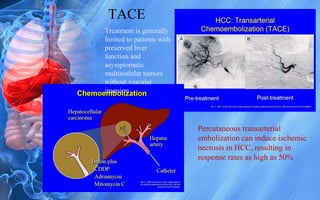
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common type of liver cancer. It has a high worldwide incidence, especially in areas where hepatitis B is prevalent like Southeast Asia. Major risk factors for HCC include hepatitis B and C infections, cirrhosis of the liver from any cause, and alcohol abuse. The disease progresses as hepatocytes undergo repeated cycles of cell death and regeneration due to chronic inflammation and cirrhosis, accumulating mutations over time that can lead to cancer. Diagnosis involves blood tests, imaging like ultrasound or CT scan, and often a biopsy. Staging systems evaluate tumor characteristics, liver function, and physical status to determine prognosis and treatment options. Treatment may include surgical resection, liver transplantation, ablation