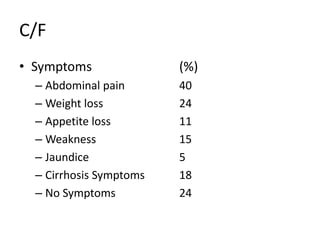
Hepatocellular carcinoma is one of the most common malignancies worldwide, with over 1 million new cases annually. Risk factors include cirrhosis from hepatitis B or C, alcohol consumption, and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Symptoms vary and include abdominal pain, weight loss, jaundice, and cirrhosis symptoms. Staging systems include Okuda and CLIP classifications which consider tumor extent, ascites, bilirubin and albumin levels, and portal vein thrombosis. Treatment depends on staging and liver function but may include surgical resection, ablation, transarterial chemoembolization, radiation, chemotherapy, or liver transplant. Early stage 1-2 HCC is typically treated