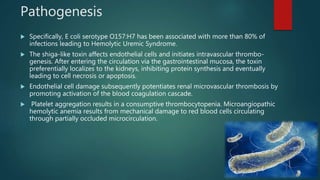
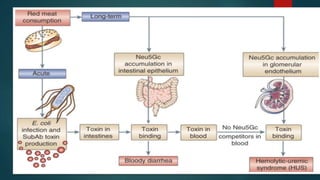
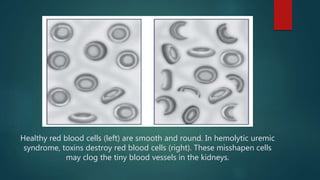
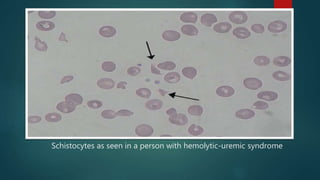
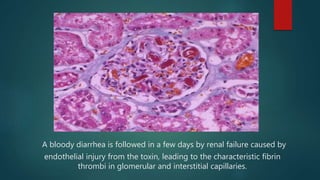
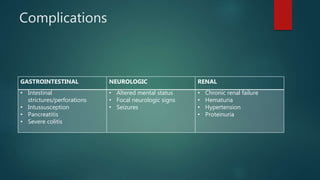
Hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS) is a disease characterized by microangiopathic hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, and acute kidney injury. It is most commonly caused by infections from Shiga toxin-producing bacteria like E. coli O157:H7. The Shiga toxin damages endothelial cells and causes blood clots to form in the kidneys. Treatment involves fluid replacement, dialysis, and plasma exchange to support kidney function and replace lost blood cells. While the prognosis is generally good for typical HUS caused by infection, atypical non-infection related HUS has a worse prognosis.



![Types of hus
Classified into 2 main categories, depending on whether it is associated with Shiga-like
toxin or not.
1. TYPICAL HUS:
Typical HUS follows a diarrheal infection often caused by E. coli OH157:H7. Infection
related Shiga toxin producing E.coli/Shigella Pneumococcal infection HIV Typical
Other viral or bacterial infections. Only the diarrheal form of HUS is considered to be
typical HUS and is usually a disease of infants and children younger than 3 years of
age
2. ATYPICAL HUS
caused by exposure to certain medications (eg ciclosporin, tacrolimus), genetic
mutations in the complement pathway[4] and systemic conditions, including lupus,
cancer and pregnancy.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/naviihus-161024201317/85/HUS-4-320.jpg)