1) Heat exchangers are devices that transfer thermal energy between two or more fluids without mixing the fluids. They are commonly used in industries like petroleum refining, power plants, and HVAC systems.
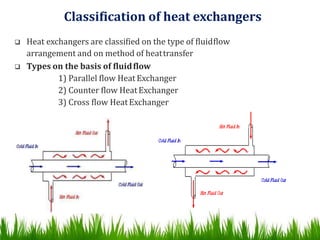
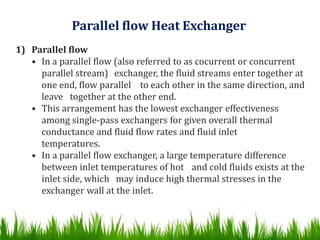
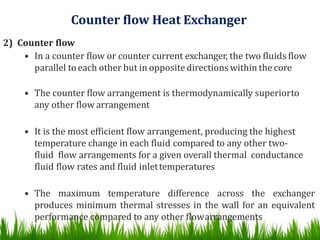
2) Heat exchangers can be classified based on fluid flow patterns (parallel, countercurrent, crossflow) and heat transfer methods. Countercurrent flow is the most efficient as it produces the highest temperature changes in each fluid.
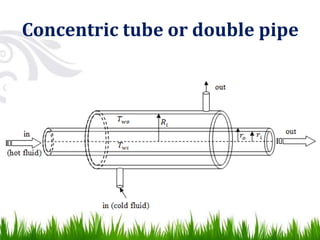
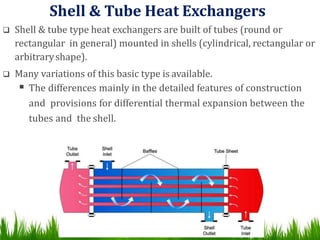
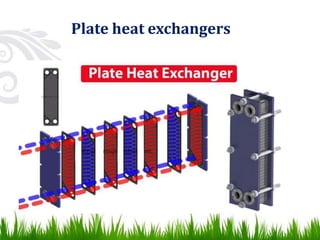
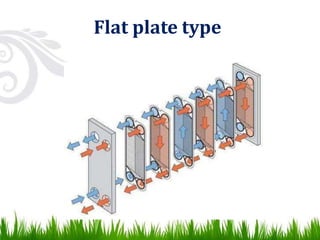
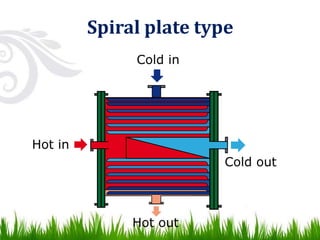
3) Common types of heat exchangers include tubular (shell and tube, concentric tube), plate (flat plate, spiral plate), and extended surface heat exchangers. Tubular heat exchangers involve one fluid flowing inside tubes while another flows