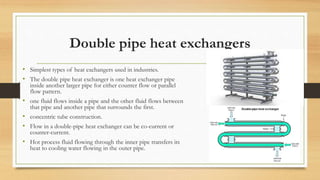
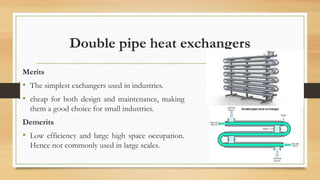
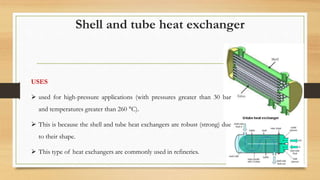
Heat exchangers are devices used to transfer heat between fluids. They transfer heat from outgoing vapors and liquids to incoming fluids to reduce fuel consumption. Common applications include heating, cooling, power generation, and industrial processes. The main types are double pipe, shell and tube, plate, plate and shell, and spiral heat exchangers. Double pipe exchangers have one pipe inside another but low efficiency. Shell and tube exchangers use bundles of tubes in a shell and are robust for high pressures. Plate exchangers use parallel plates for compactness while spiral exchangers use coiled tubes. Selection depends on parameters like pressure, temperature, and space.