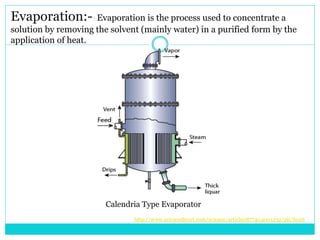
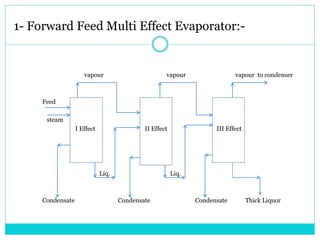
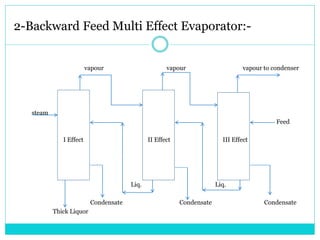
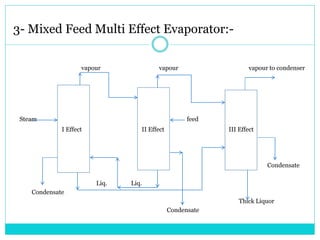
The document summarizes multi effect evaporation, which is a popular method for concentrating aqueous solutions. It does this using multiple evaporation effects where steam heats successive vessels to boil the solution and remove water as vapor, which is then condensed. There are three types - forward, backward, and mixed feed - depending on the direction of the feed and condensate. The multi effect evaporator efficiently uses heat from steam to evaporate water. It has applications in product concentration, solvent recovery, and crystallization, and advantages of being advanced, easy to operate and maintain, and cost effective.