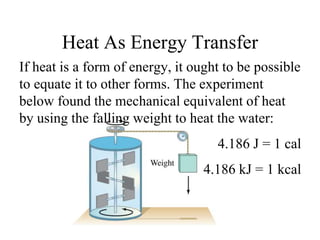
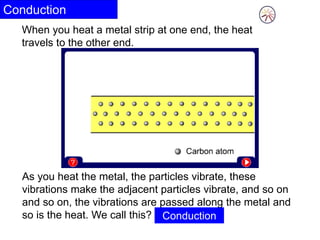
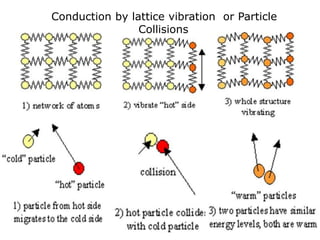
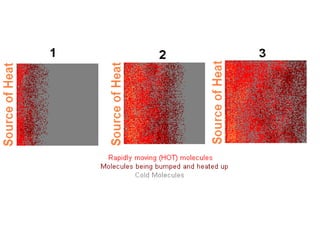
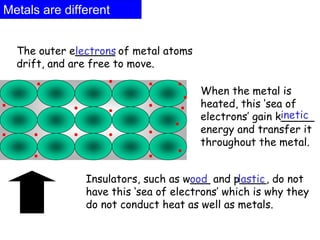
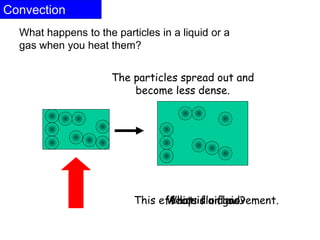
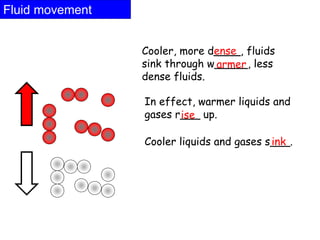
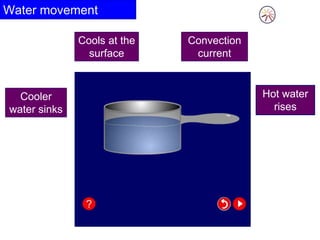
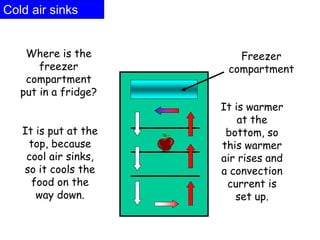
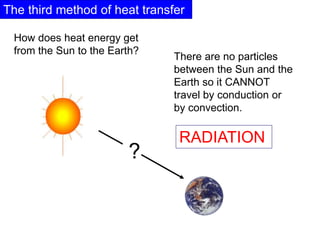
Heat always moves from warmer to cooler objects through three methods of heat transfer: conduction, convection, and radiation. Conduction involves the transfer of thermal energy through direct contact of particles. Convection involves the transfer of heat by the circulation of fluids like gases and liquids. Radiation involves the transfer of heat through electromagnetic waves and does not require a medium. Understanding these three methods of heat transfer is important in applications like manufacturing and building design.