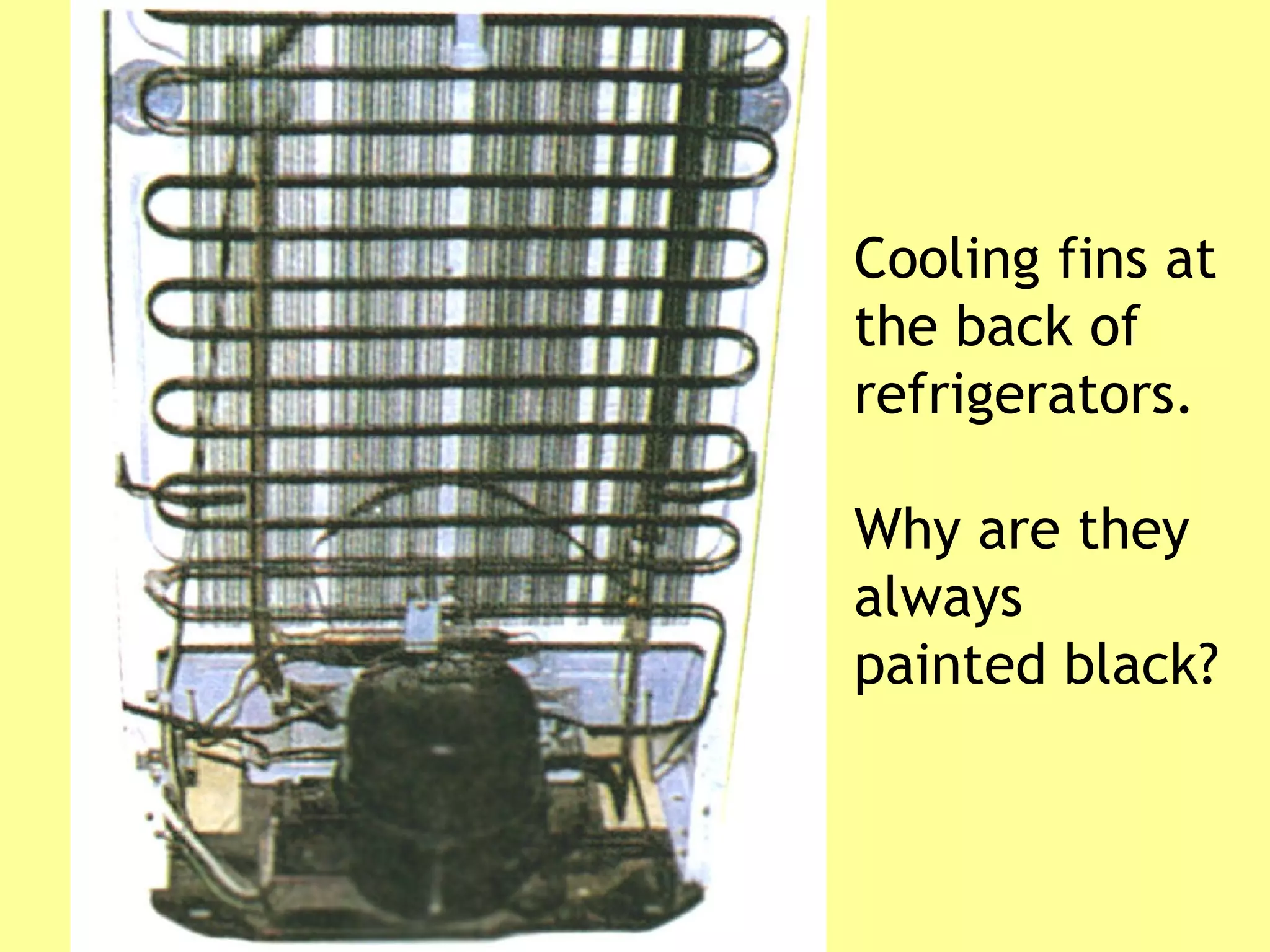
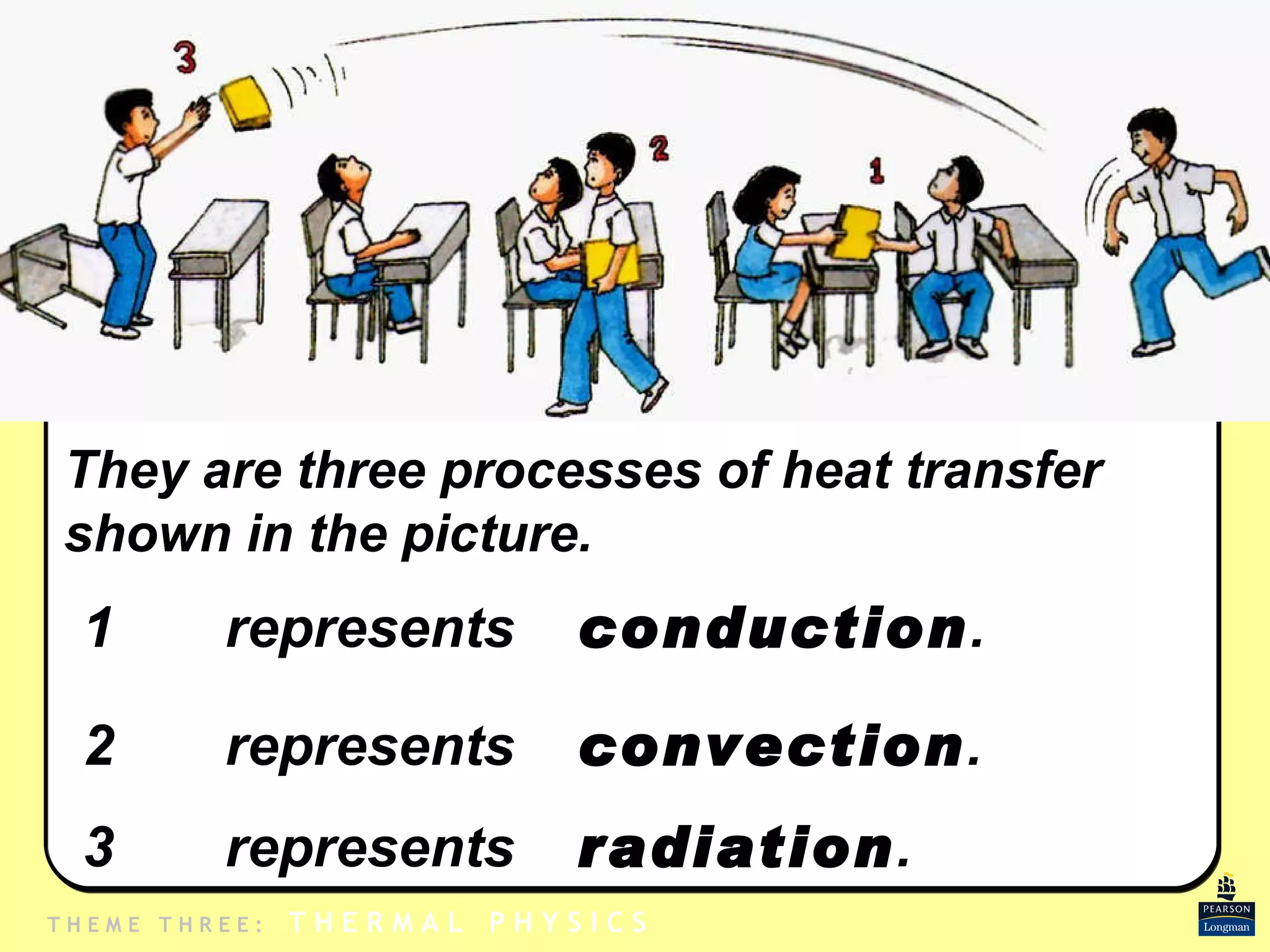
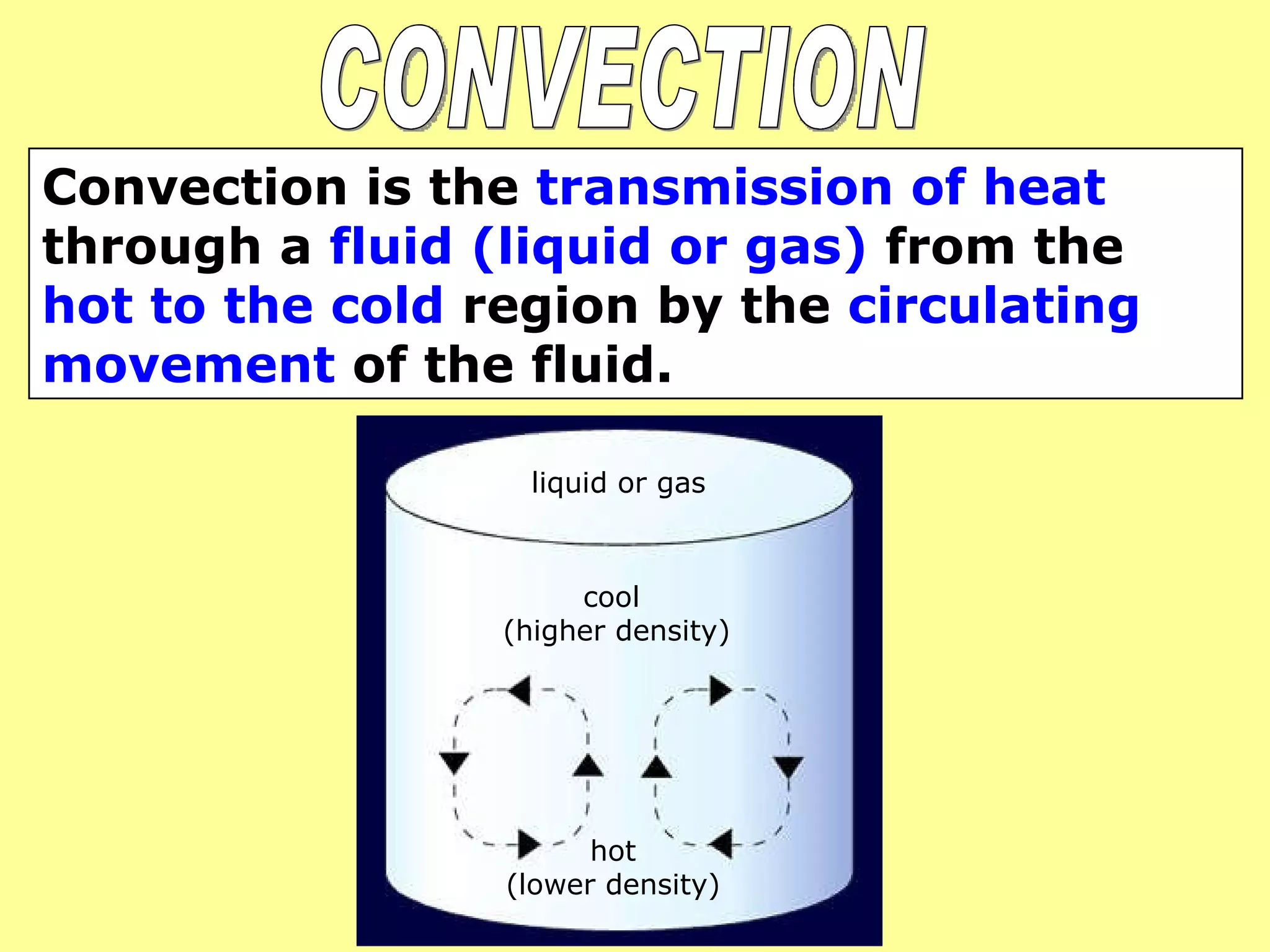
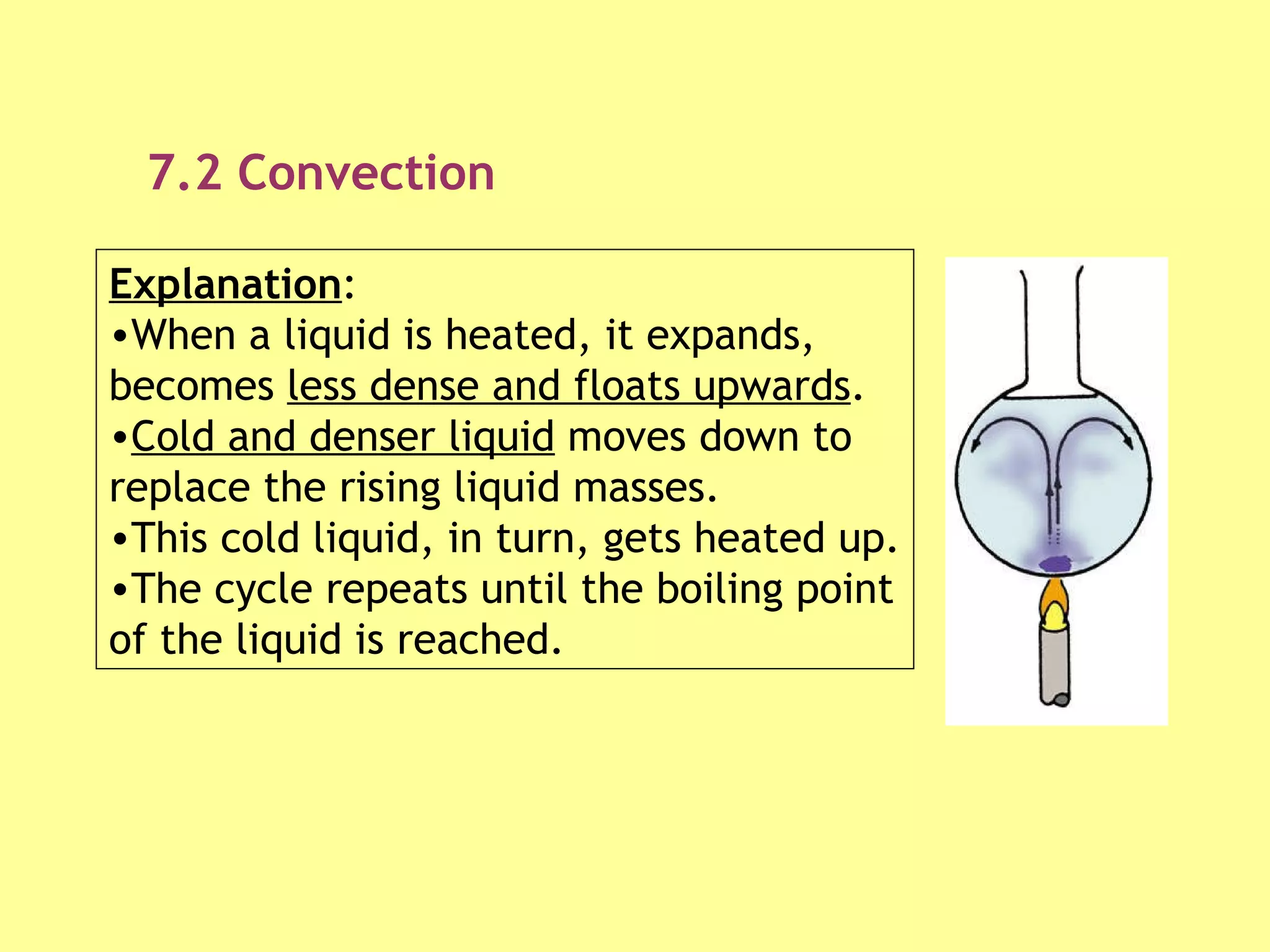
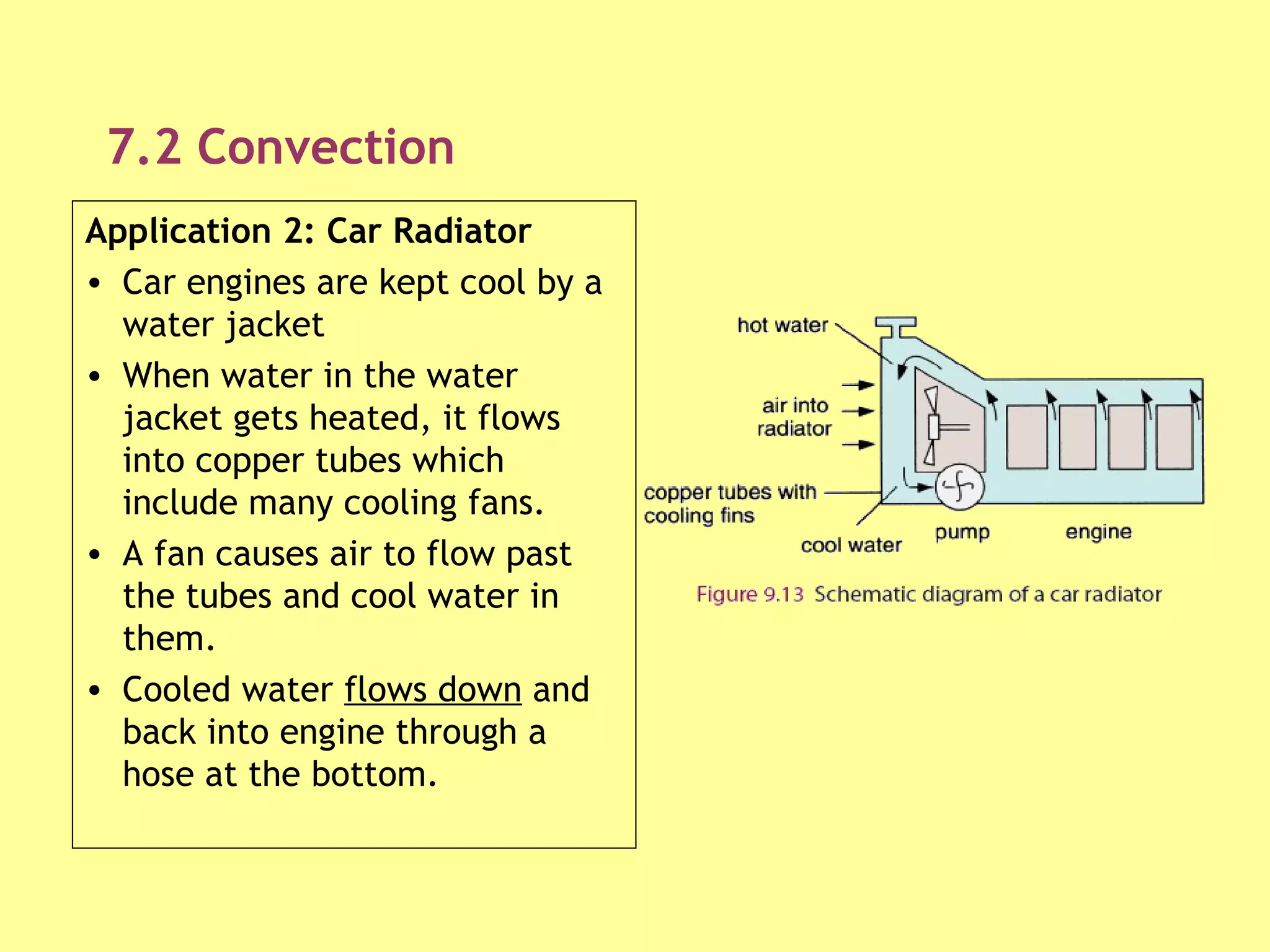
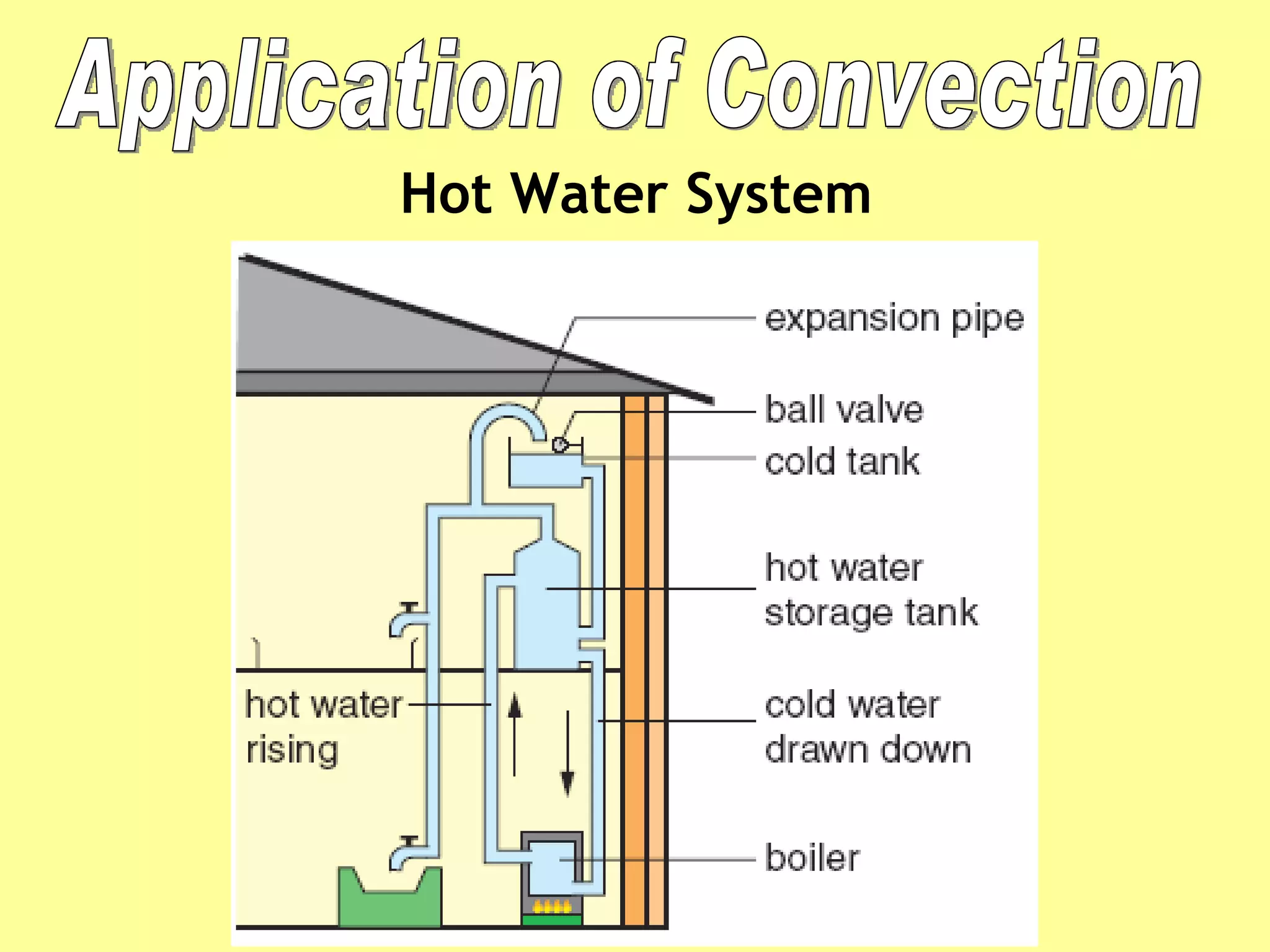
1. Heat is transmitted between objects or regions in three ways: conduction, convection, and radiation.
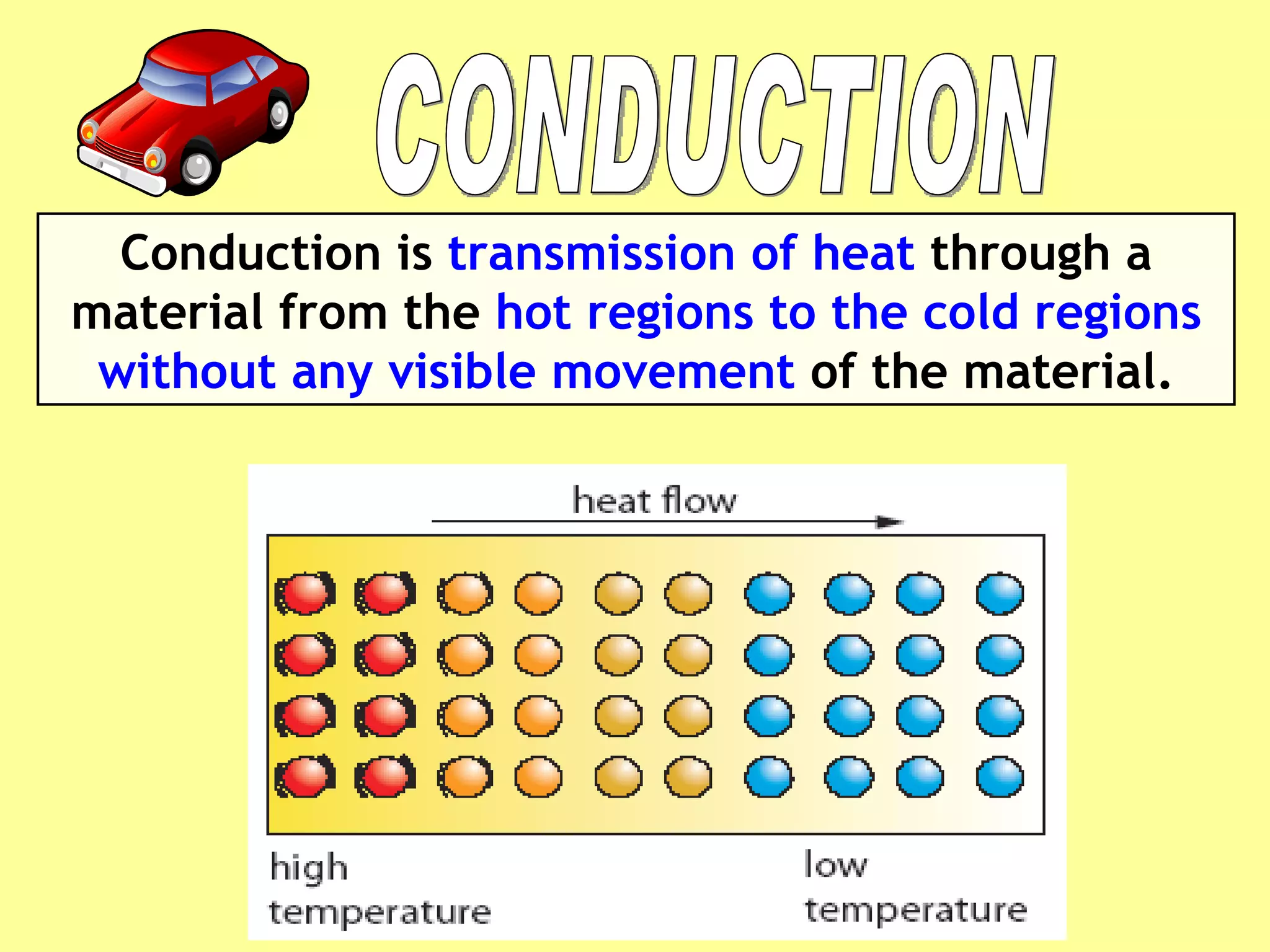
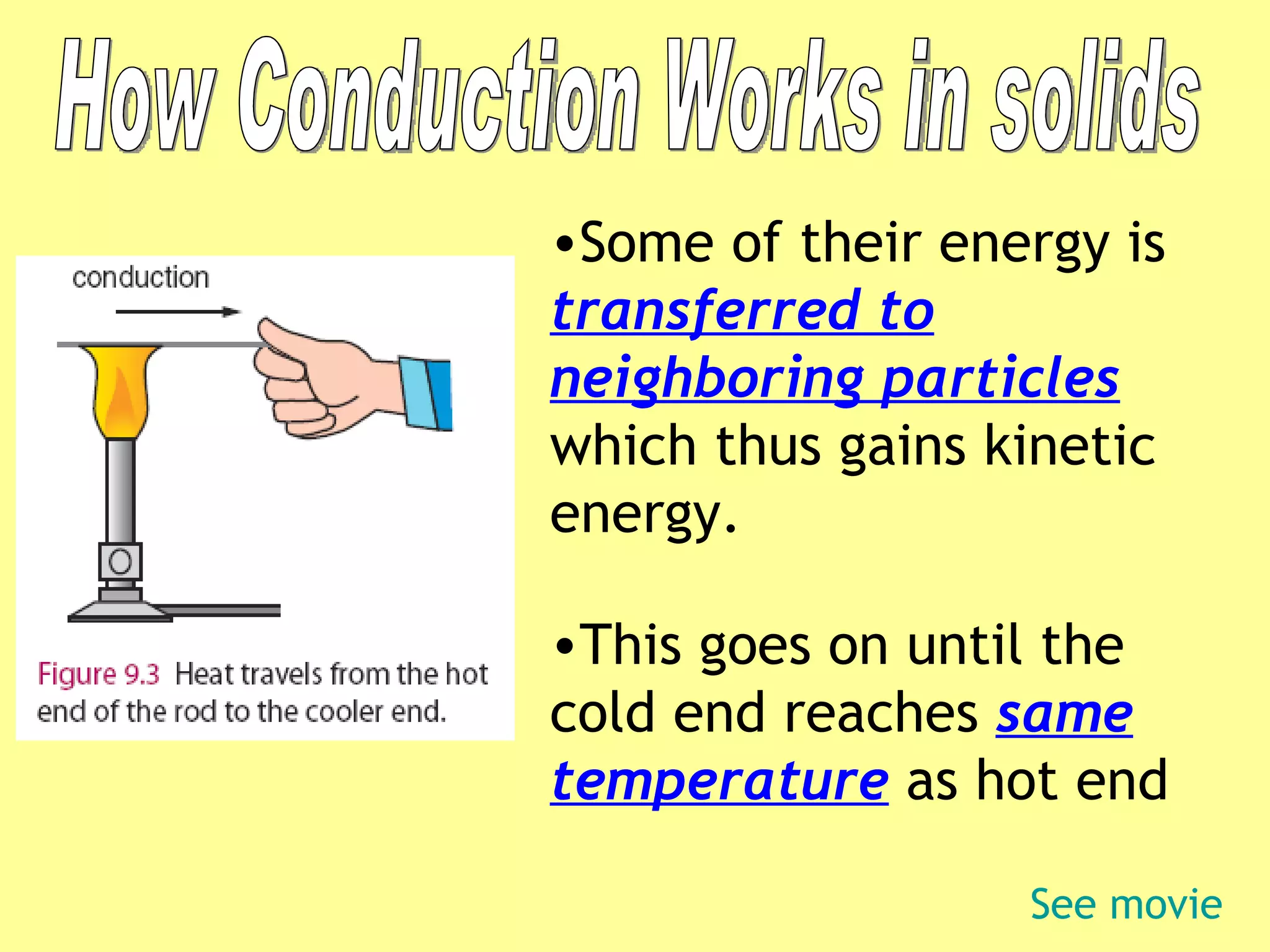
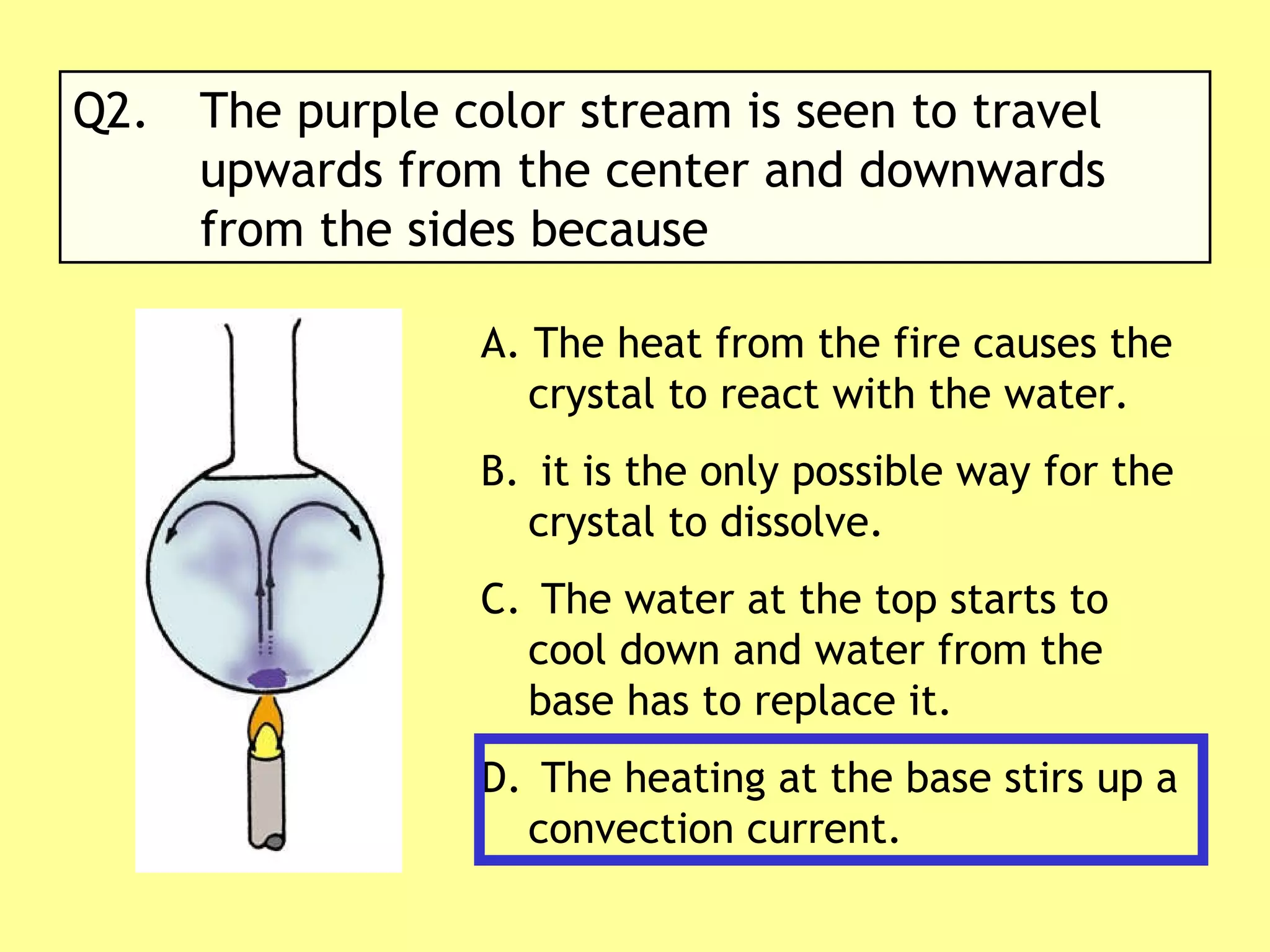
2. Conduction involves direct contact between objects, convection involves the circulation of fluids like air or water, and radiation transfers heat through electromagnetic waves even in a vacuum.
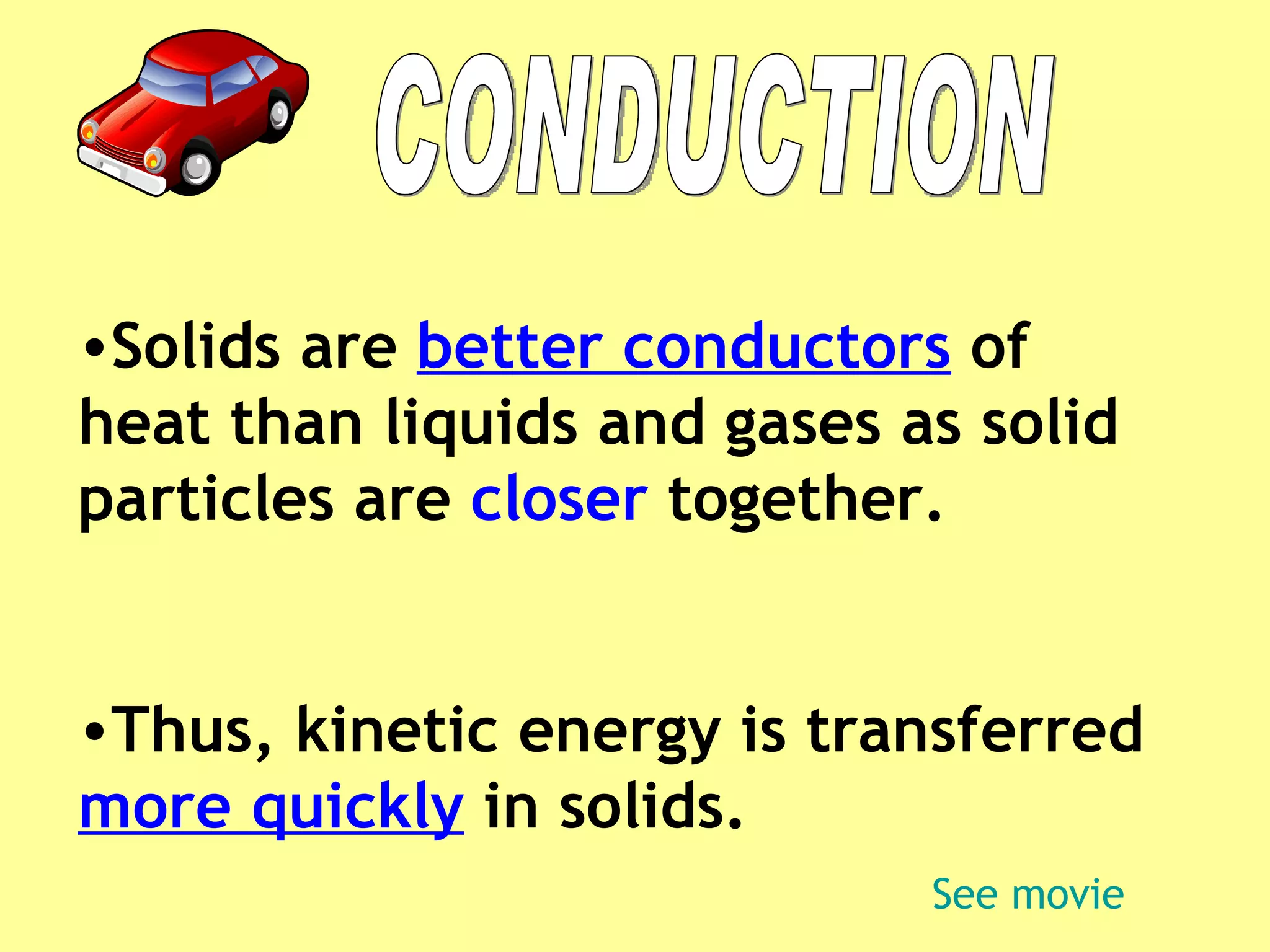
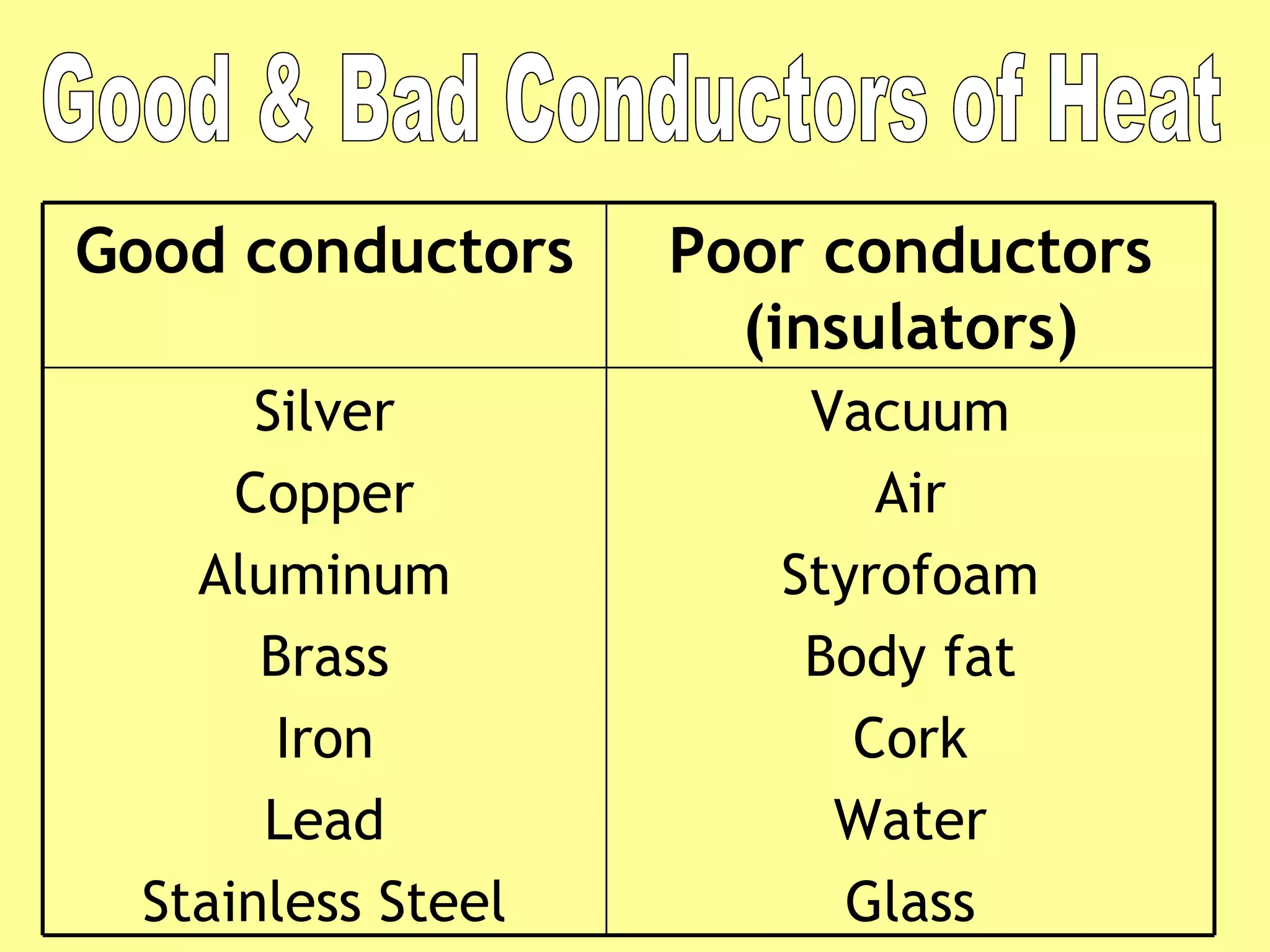
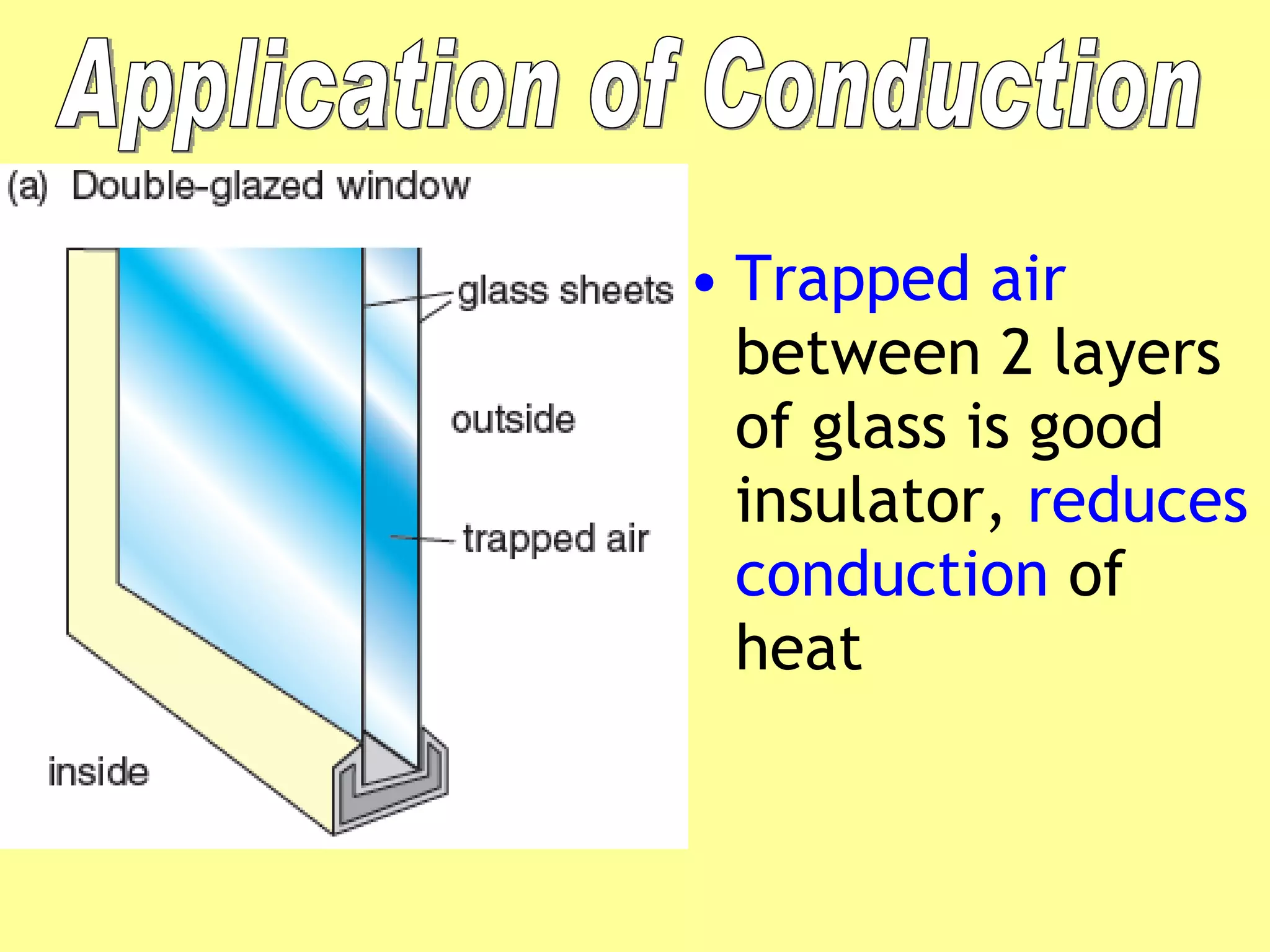
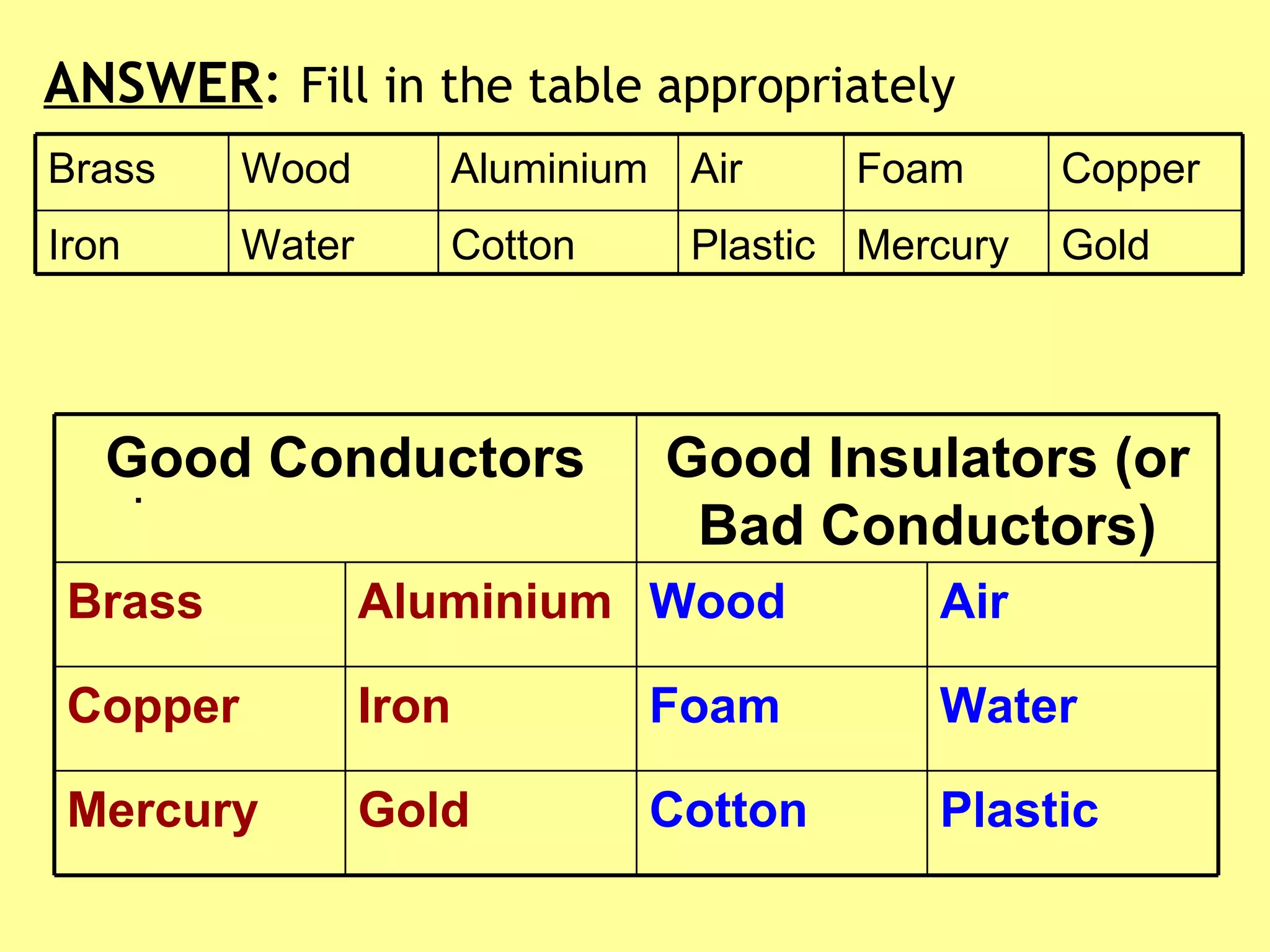
3. Different materials conduct heat at different rates, with metals being good conductors and insulating materials like wood or foam being poor conductors. The rate of heat transfer also depends on other factors like surface area and temperature.