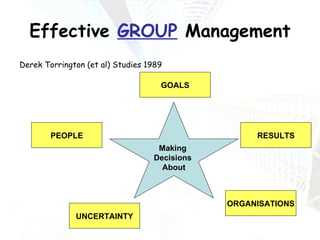
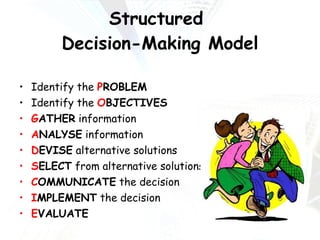
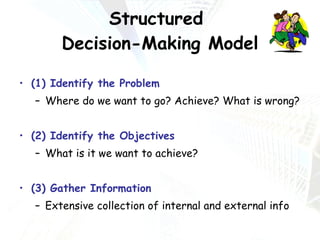
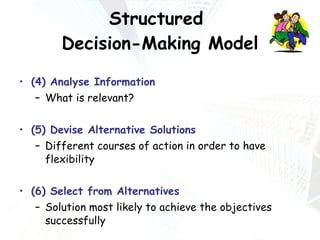
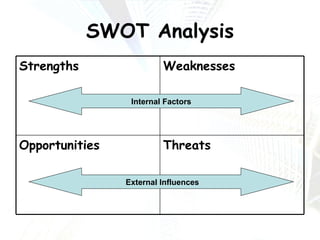
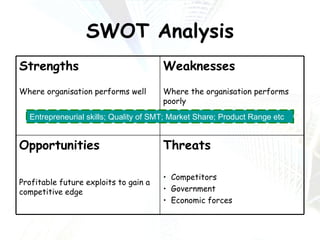
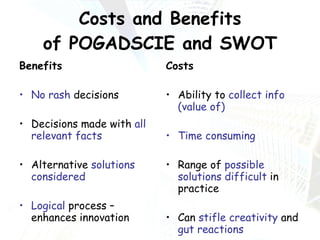
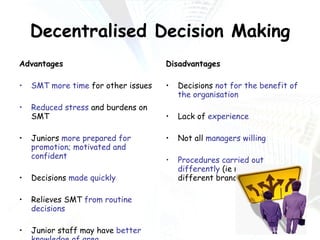
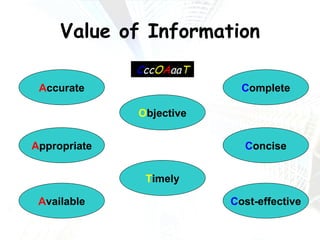
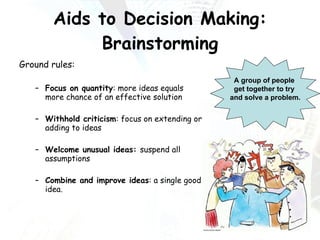
Managers at all levels of an organization are constantly making decisions ranging from routine day-to-day operational decisions to long-term strategic decisions that shape the future of the company. Effective decision making involves following a structured process such as identifying problems and objectives, gathering and analyzing information, developing alternative solutions, selecting the best option, implementing it, and evaluating the results. Managers must consider internal factors like resources as well as external factors in the political, economic, social, and technological environment when making decisions to help the organization achieve its goals and objectives.