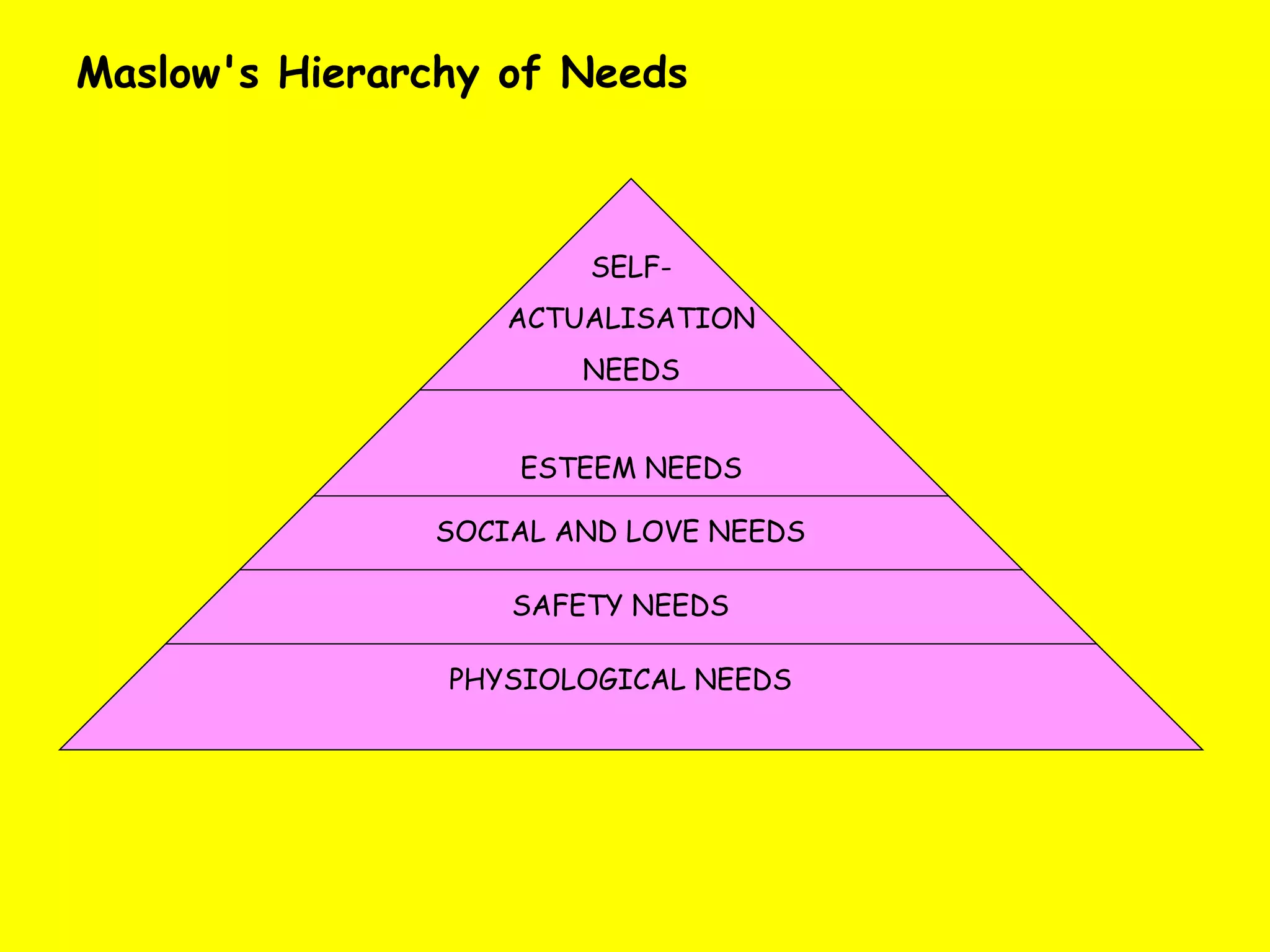
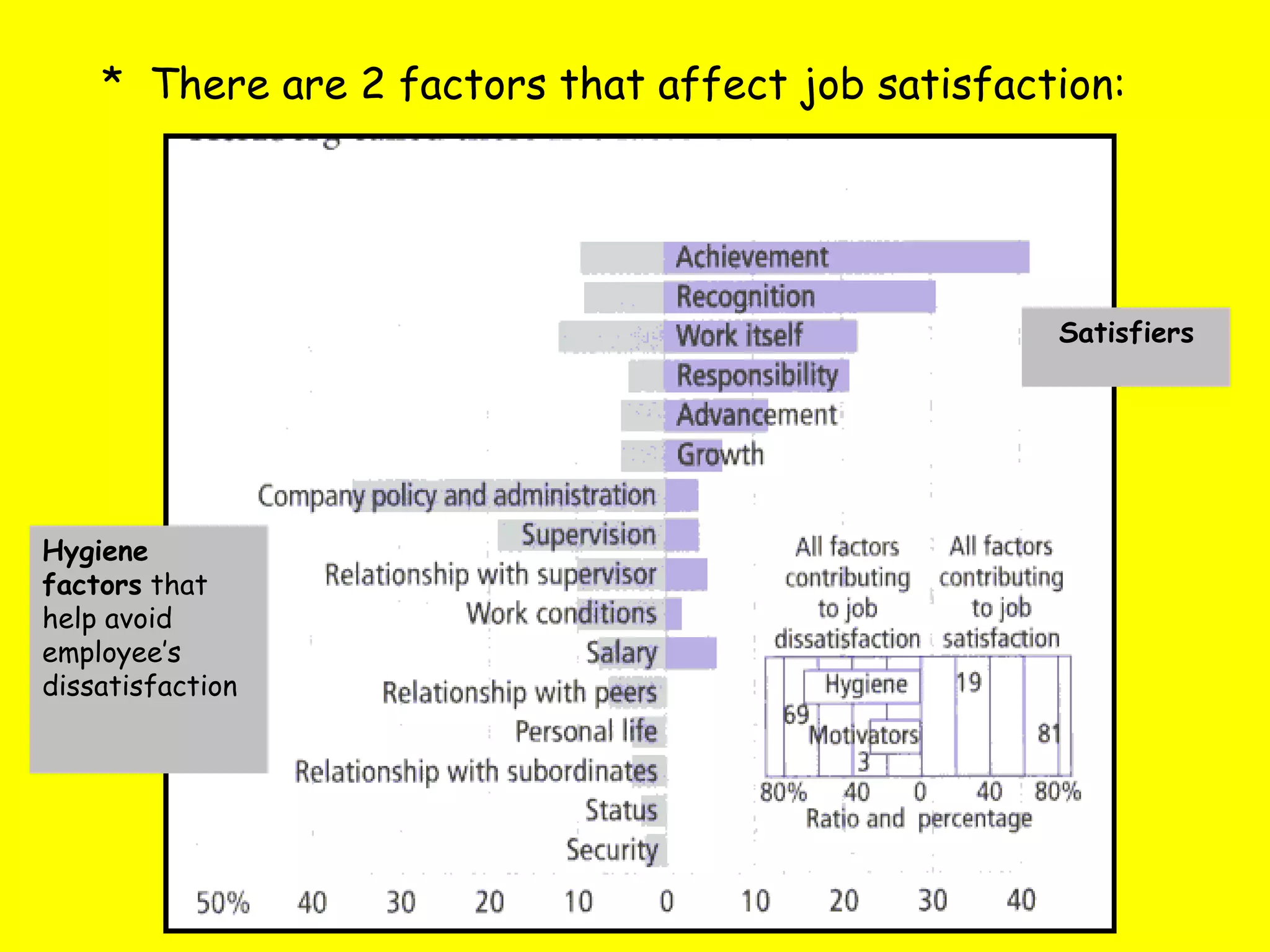
The document discusses various theories of motivation in the workplace, including Maslow's hierarchy of needs and Herzberg's two-factor theory. It also examines different methods that managers can use to motivate employees, such as financial rewards, empowerment, job design approaches like enrichment and rotation, and quality circles. Challenges in implementing some of these motivational techniques are also addressed.