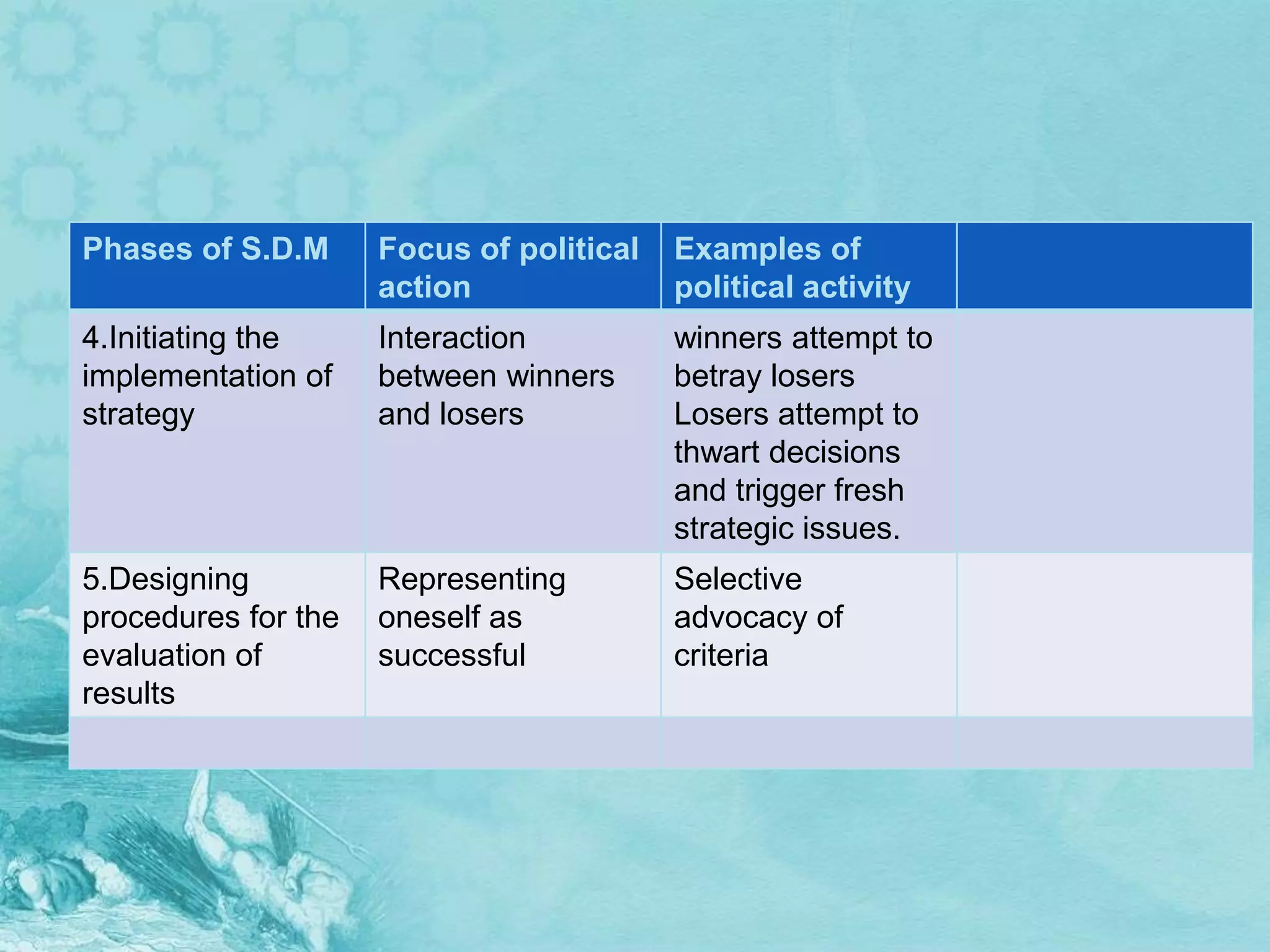
The document discusses strategic decision making and the role of politics within organizations. It outlines 5 Ps of strategic decisions including plans, ploys, patterns, position, and perspective. It also describes different types of strategic decision makers and contexts for decision making. Finally, it analyzes the political activities that occur within each phase of the strategic decision making process, such as controlling agendas, forming coalitions, and selectively advocating for criteria.