Embed presentation
Downloaded 674 times



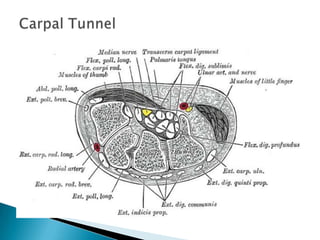
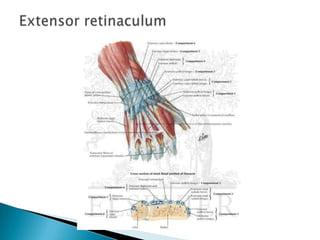
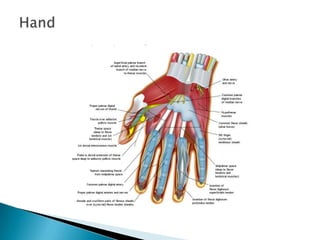
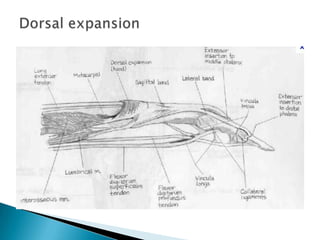





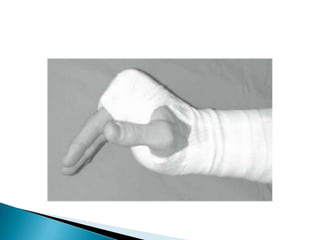

This document provides an overview of upper limb anatomy and assessment of common hand injuries seen in the emergency department. It discusses the history, examination, and management of various types of injuries including lacerations, tendon injuries, fractures, nerve injuries, and fingertip amputations. Treatment options such as irrigation, splinting, and immobilization are covered. Anatomical structures like the flexor and extensor compartments are also reviewed.














