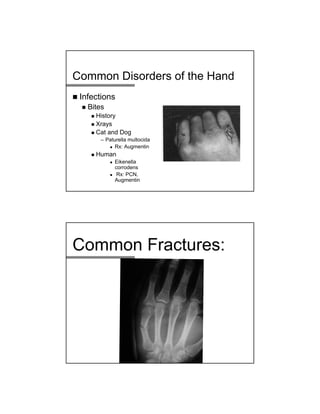
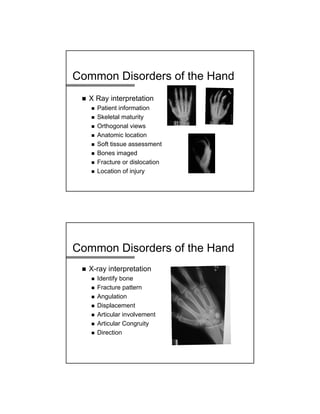
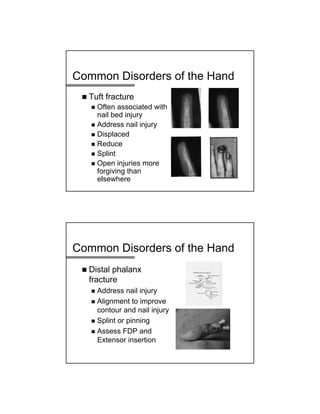
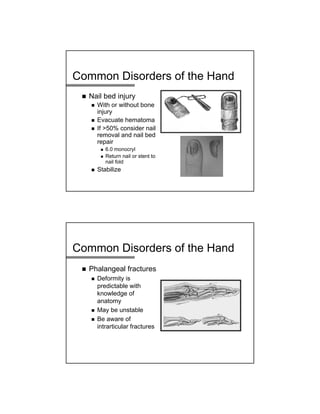
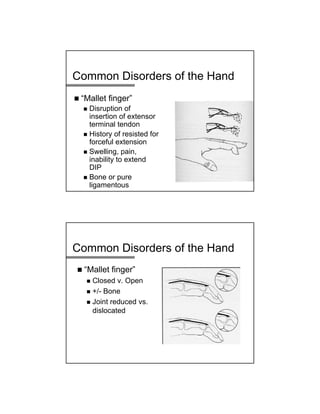
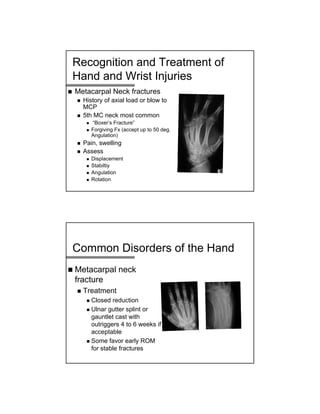
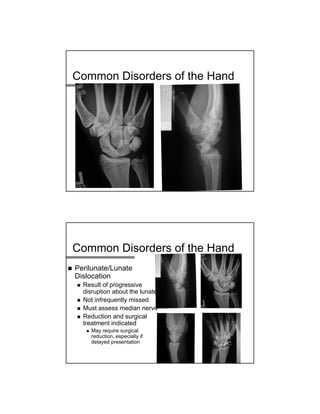
The document provides a comprehensive overview of common hand and wrist injuries, including types of injuries such as fractures, lacerations, infections, and tendonopathies. It details the evaluation and physical examination processes, focusing on specific injuries and their treatment protocols, including anatomy, radiological assessment, and management strategies. Various conditions such as scaphoid fractures, tendon injuries, and ligament disruptions are discussed to guide diagnosis and treatment options.