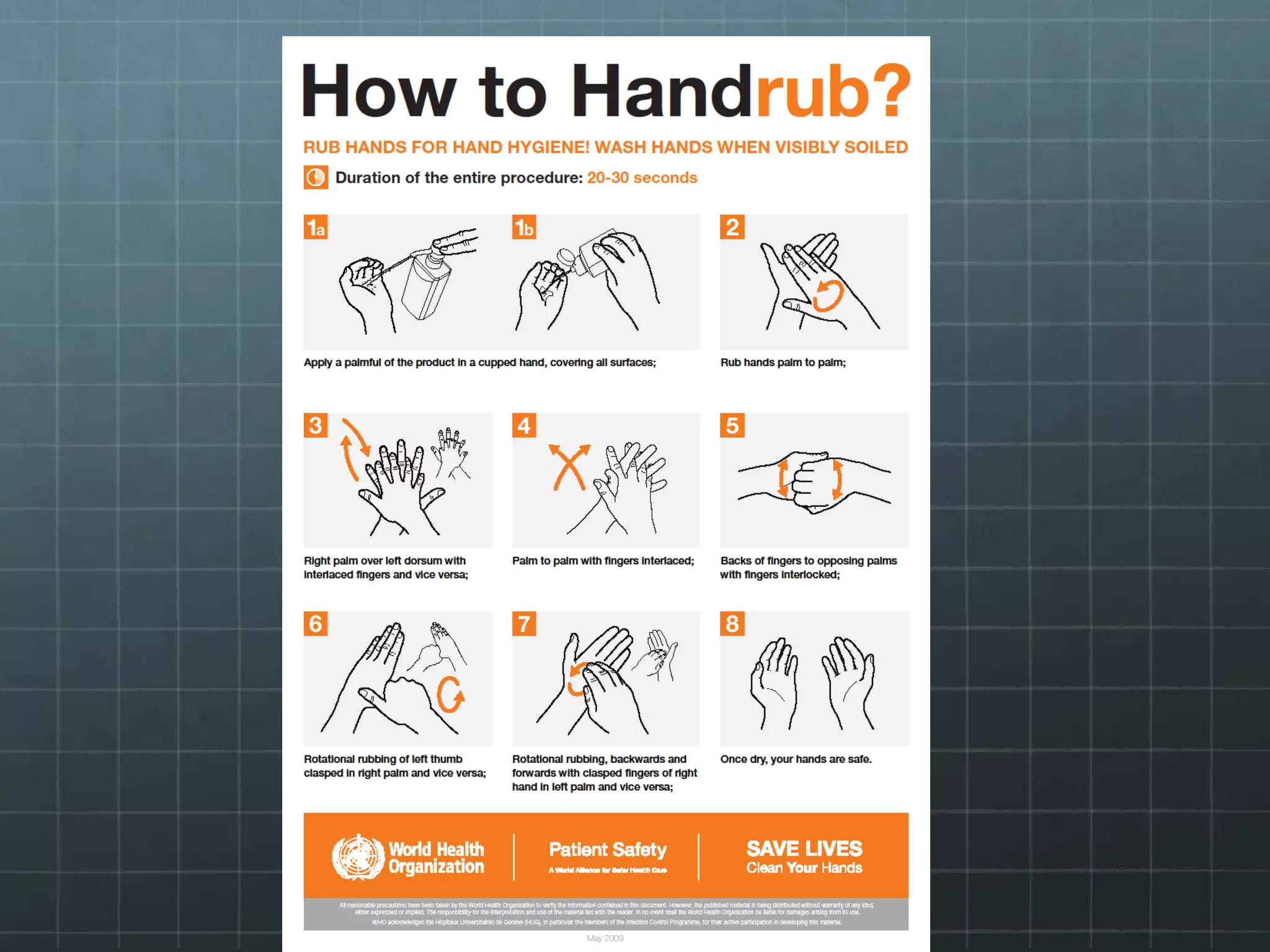
Hand hygiene and isolation precautions are important for preventing the spread of infections in hospitals. An estimated 1.7 million hospital-acquired infections occur annually in the US, resulting in 99,000 deaths and $6 billion in costs. Proper hand hygiene using soap, alcohol-based sanitizers, or chlorhexidine can reduce transmission. Standard precautions assume all patients may harbor infectious organisms and require gloves, gowns, masks, and eye protection. Isolation precautions with additional protective equipment and cleaning protocols are implemented for patients confirmed to have diseases like MRSA, C. difficile, or influenza. Proper use and removal of protective equipment helps limit disease transmission in healthcare settings.