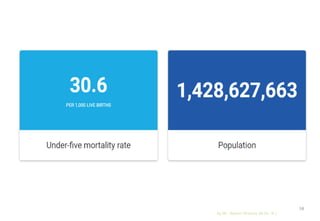
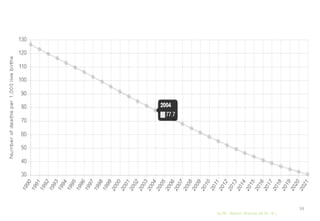
The document discusses child health nursing, highlighting its evolution from a disease-focused approach to a comprehensive model that includes family involvement and preventive care. It outlines the roles and responsibilities of pediatric nurses, including caregiving, health education, and advocacy for children's welfare. The content also addresses emerging challenges in pediatric nursing and the significance of vital statistics in assessing community health.