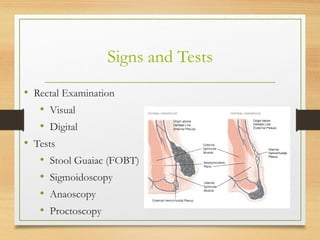
Hemorrhoids, also known as piles, are enlarged or swollen veins in the lower rectum and anus. They are common in adults, especially between ages 45-65. Hemorrhoids are classified based on their location as internal or external. Symptoms include rectal bleeding, itching, and pain. Treatments range from lifestyle and diet changes to office procedures and surgery. Preventing constipation and straining during bowel movements can help prevent hemorrhoids.