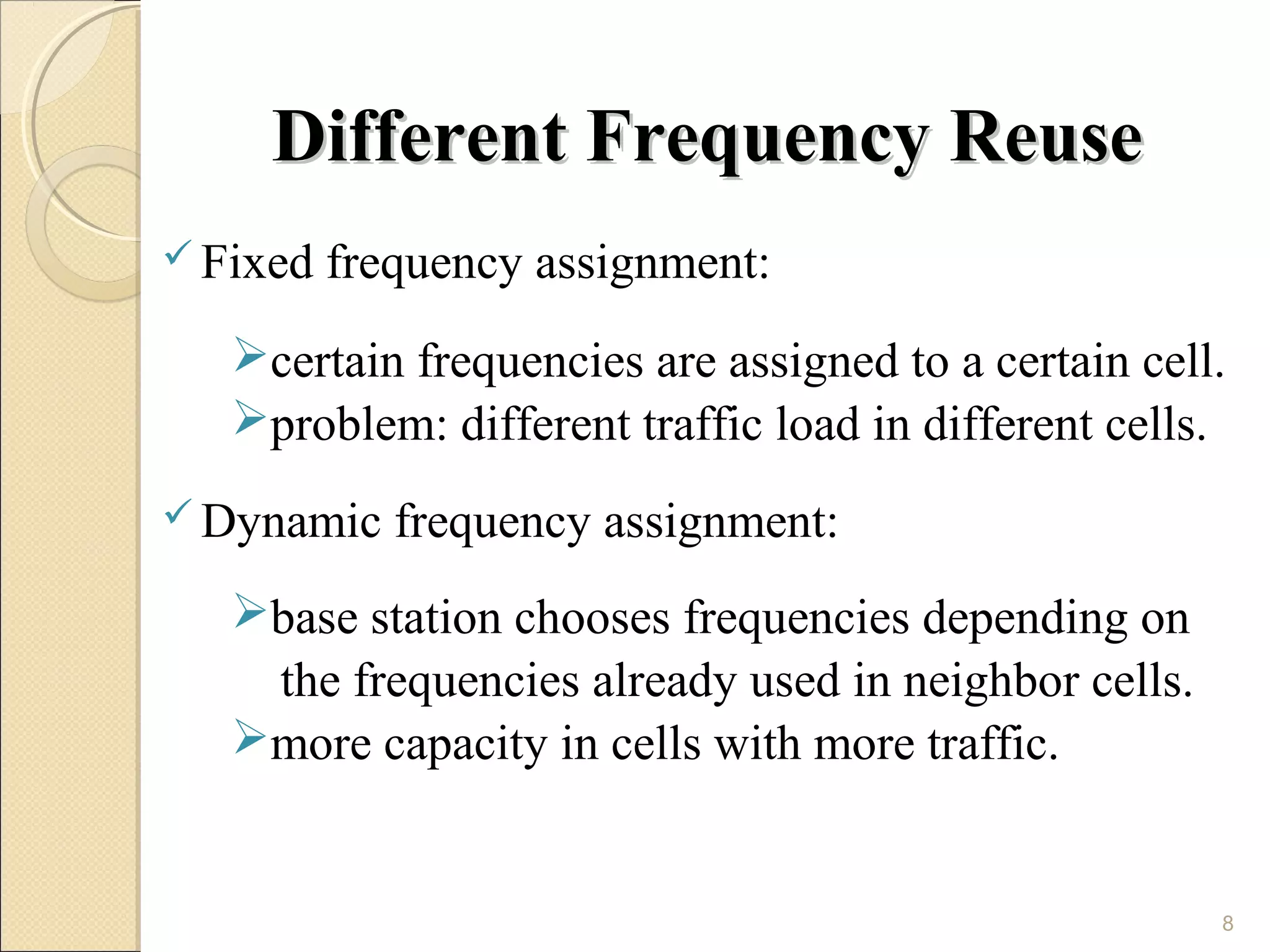
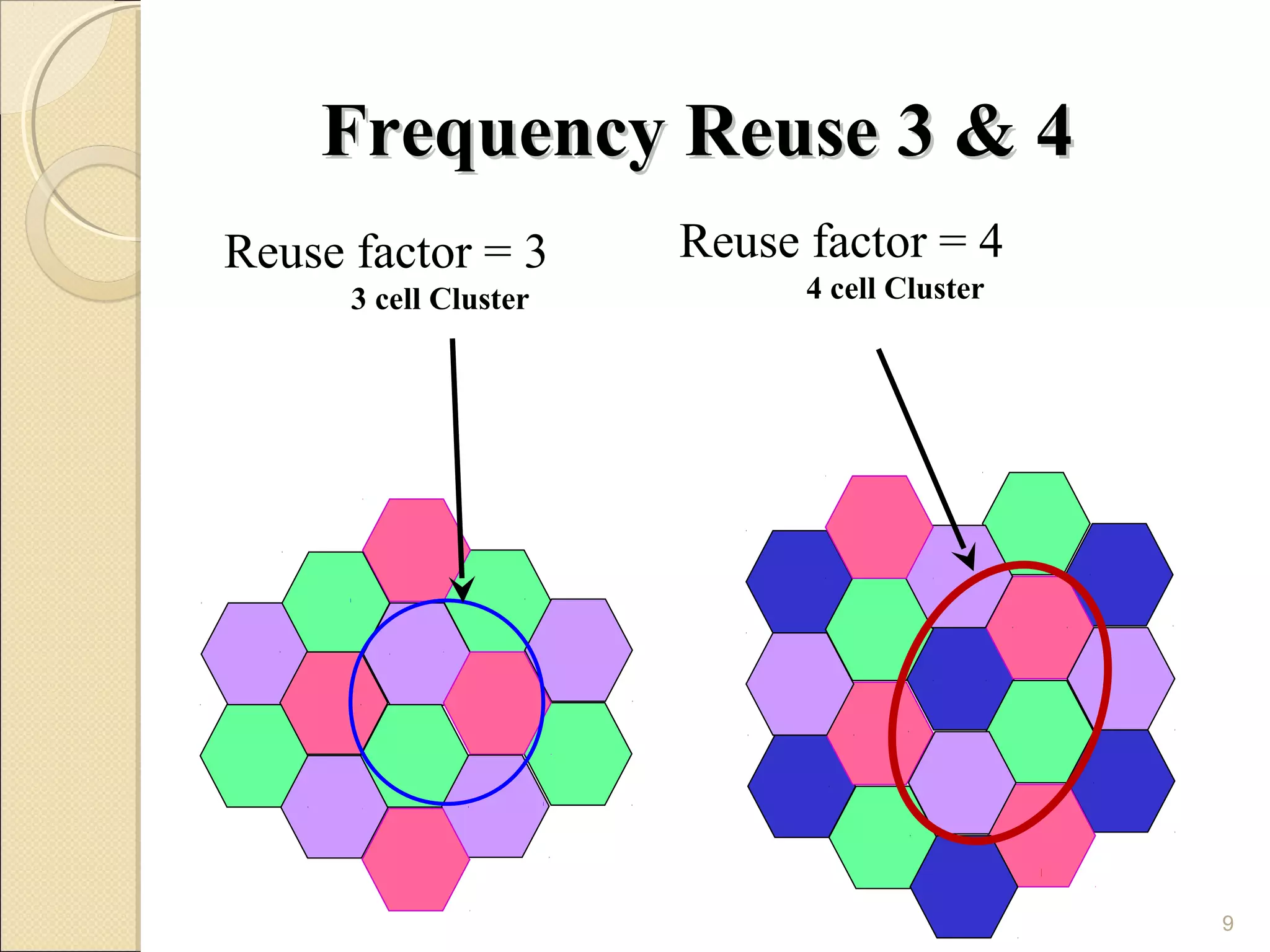
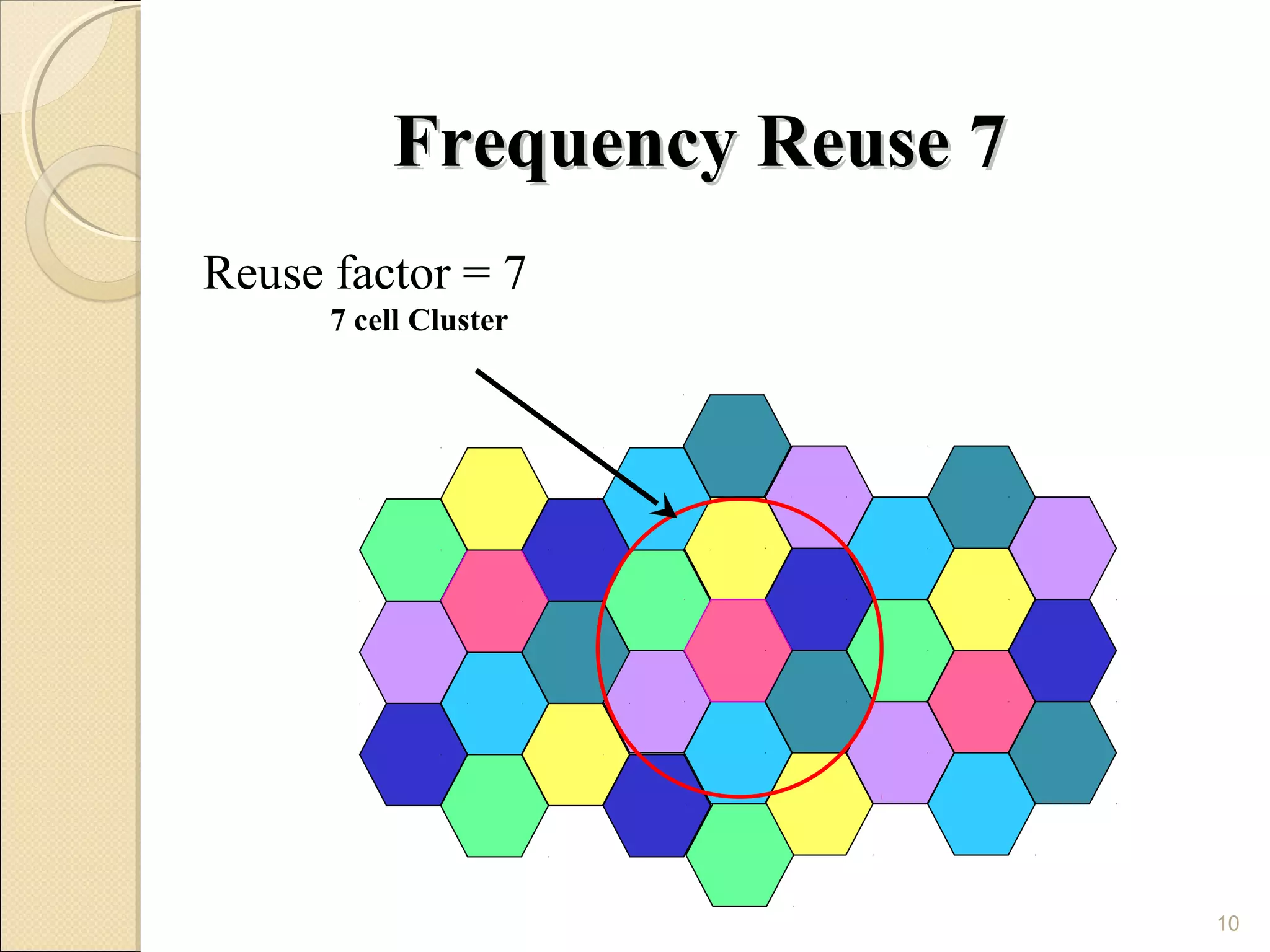
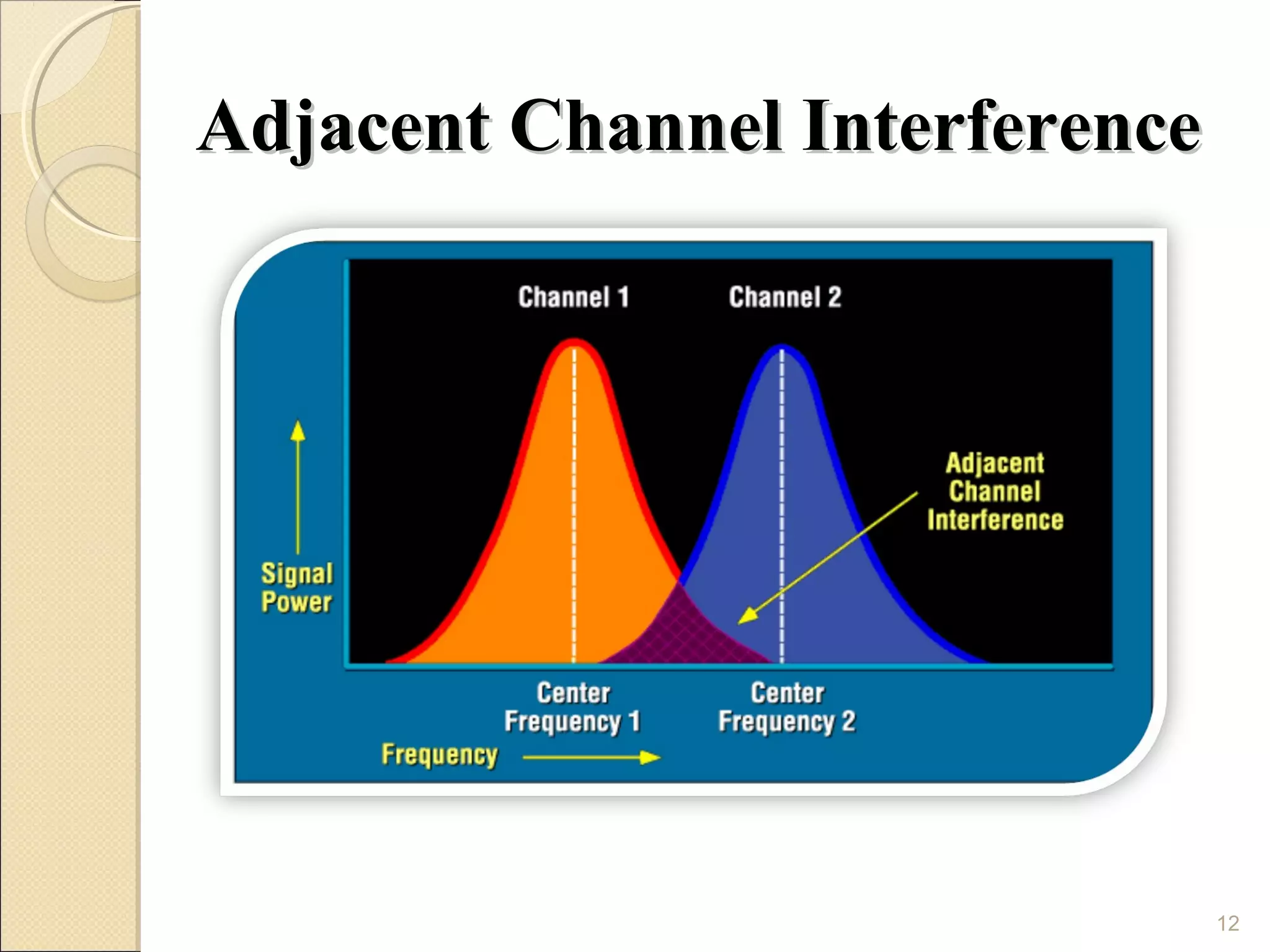
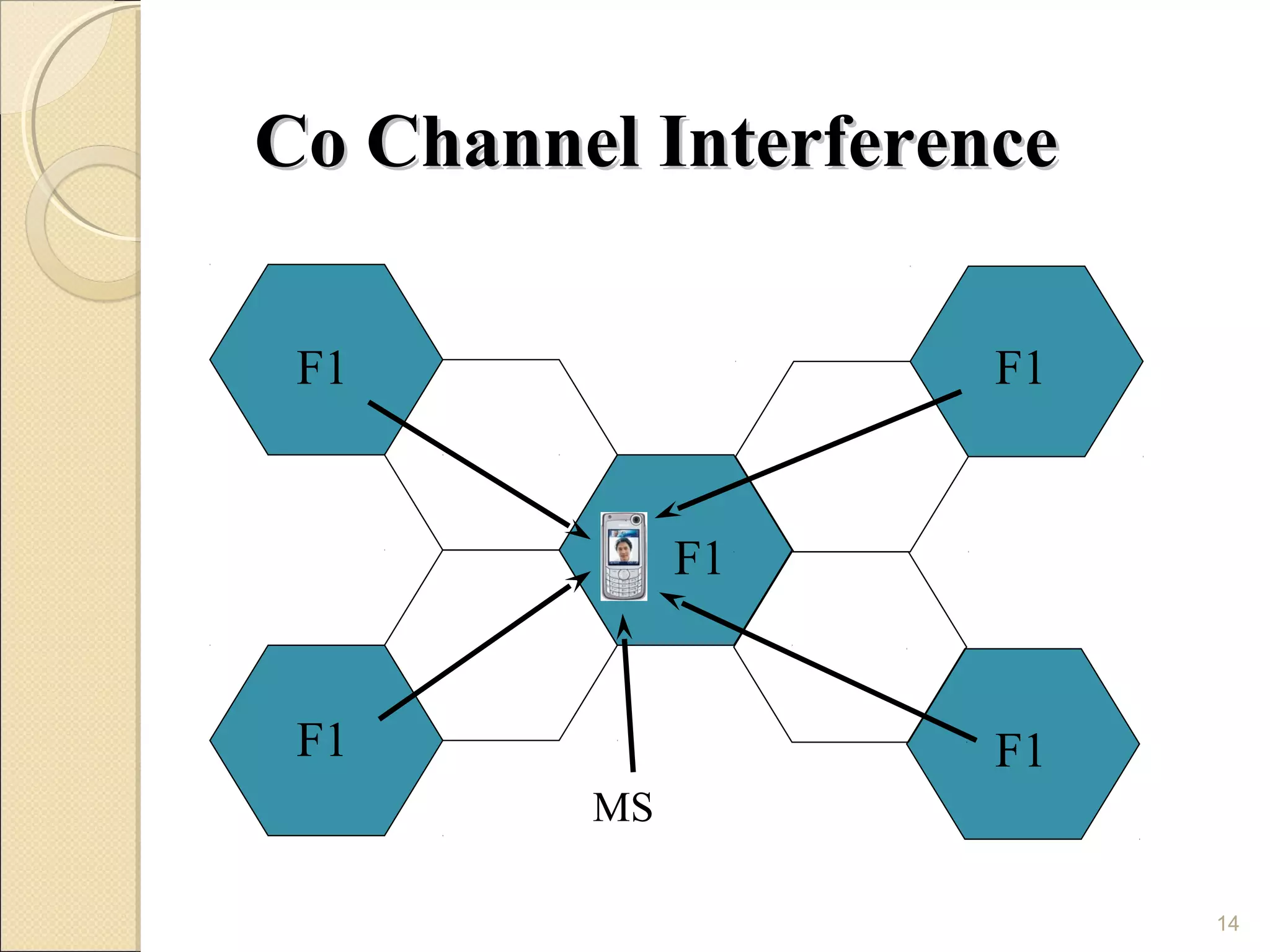
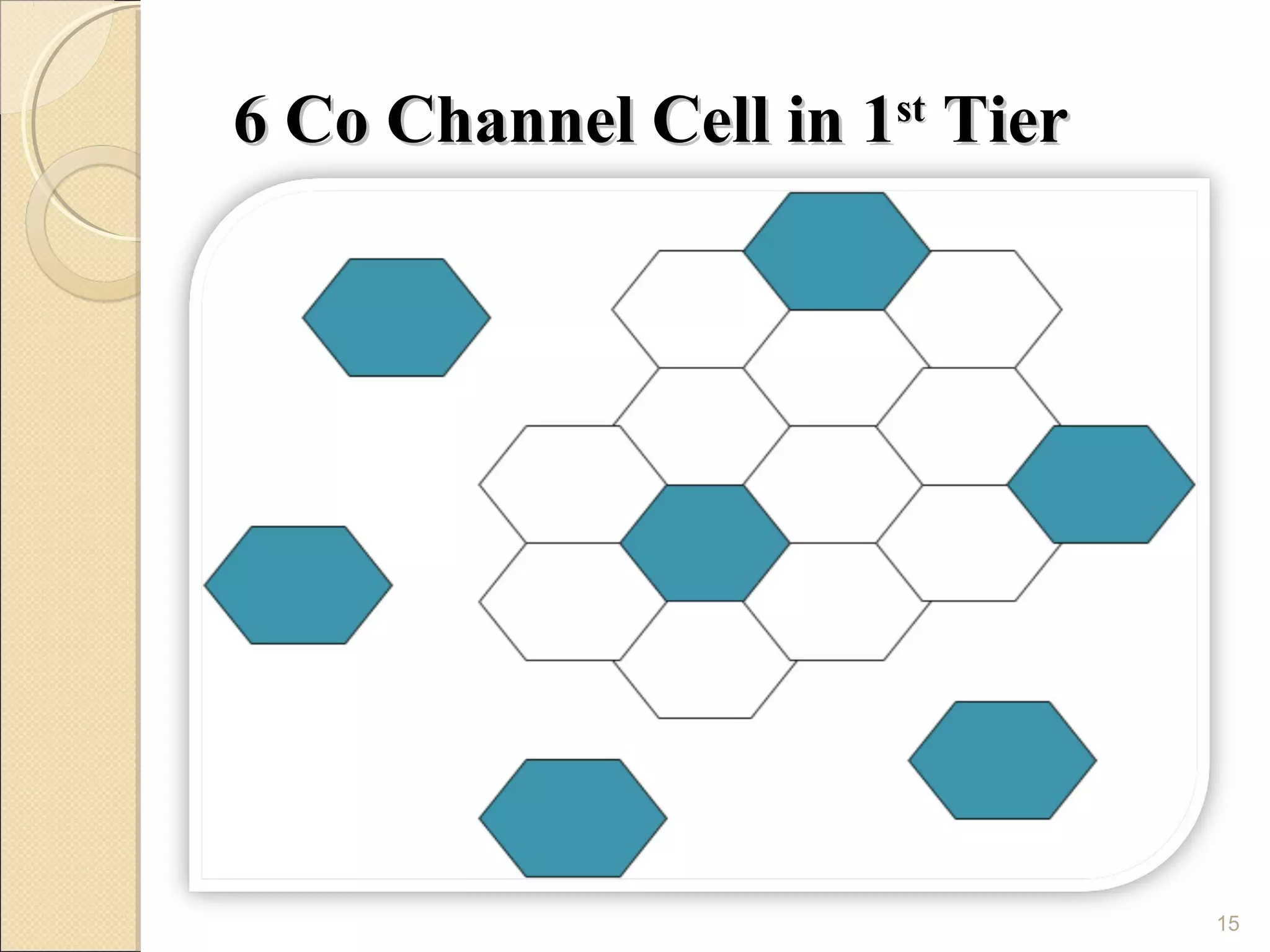
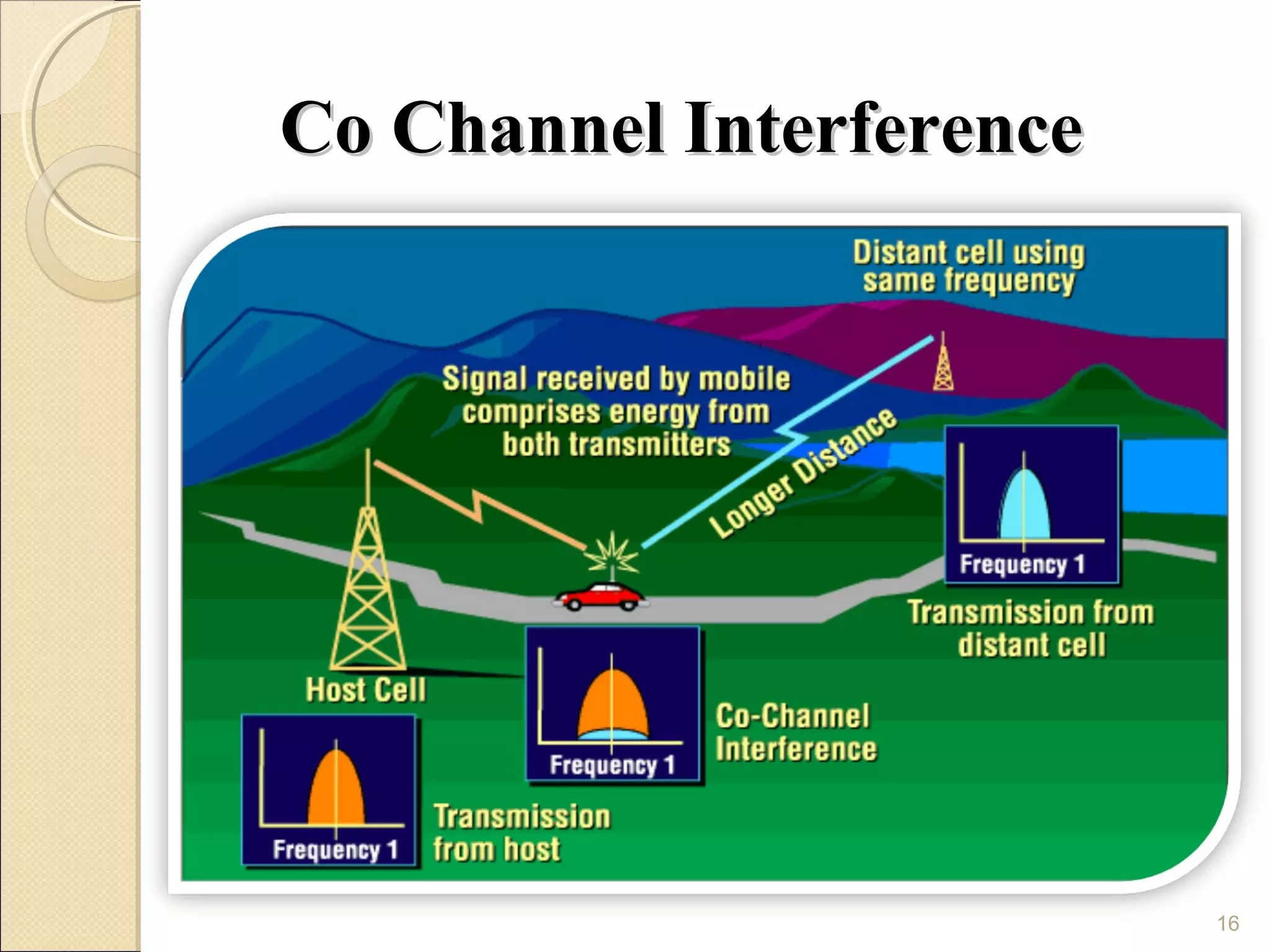
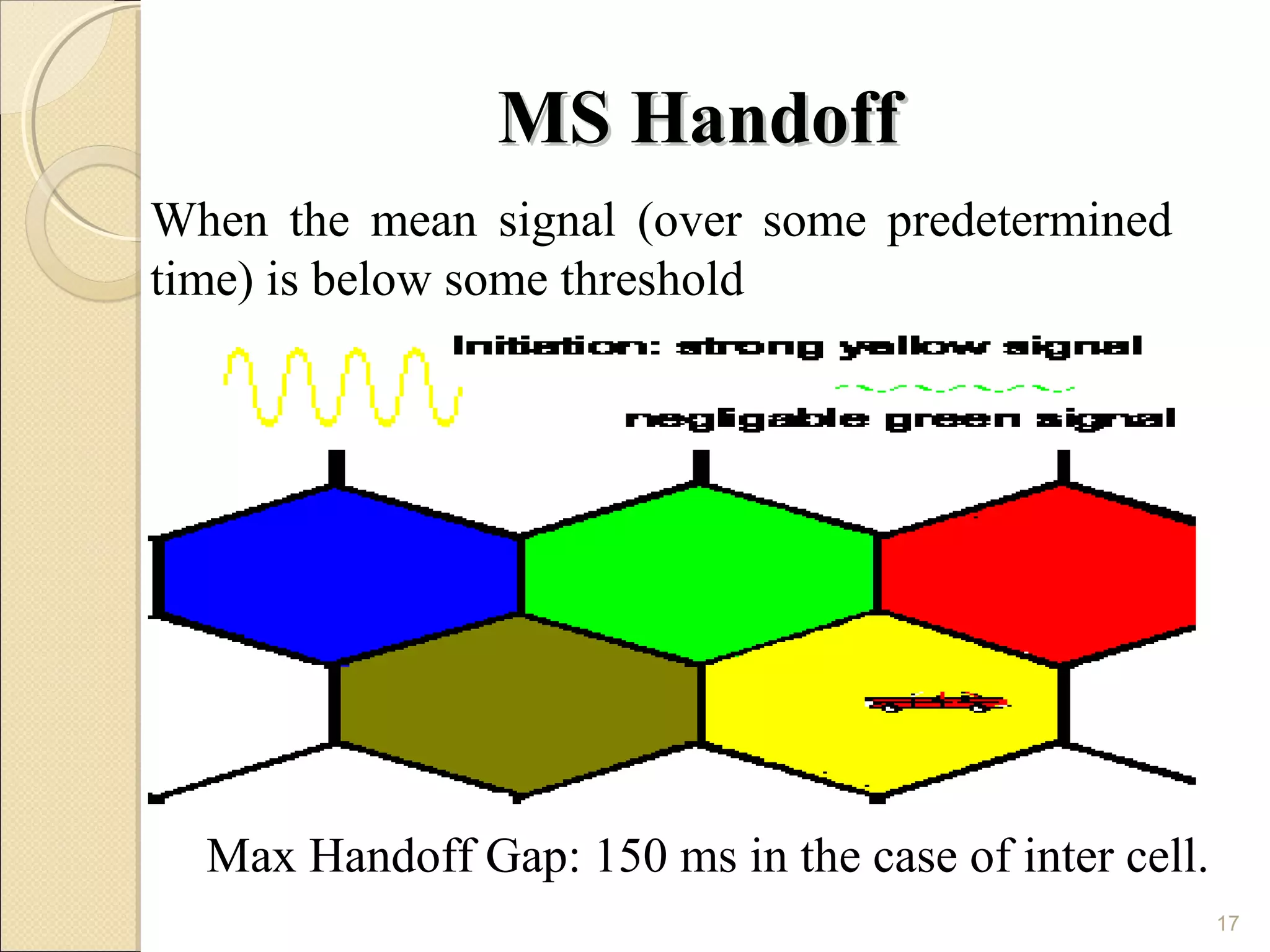
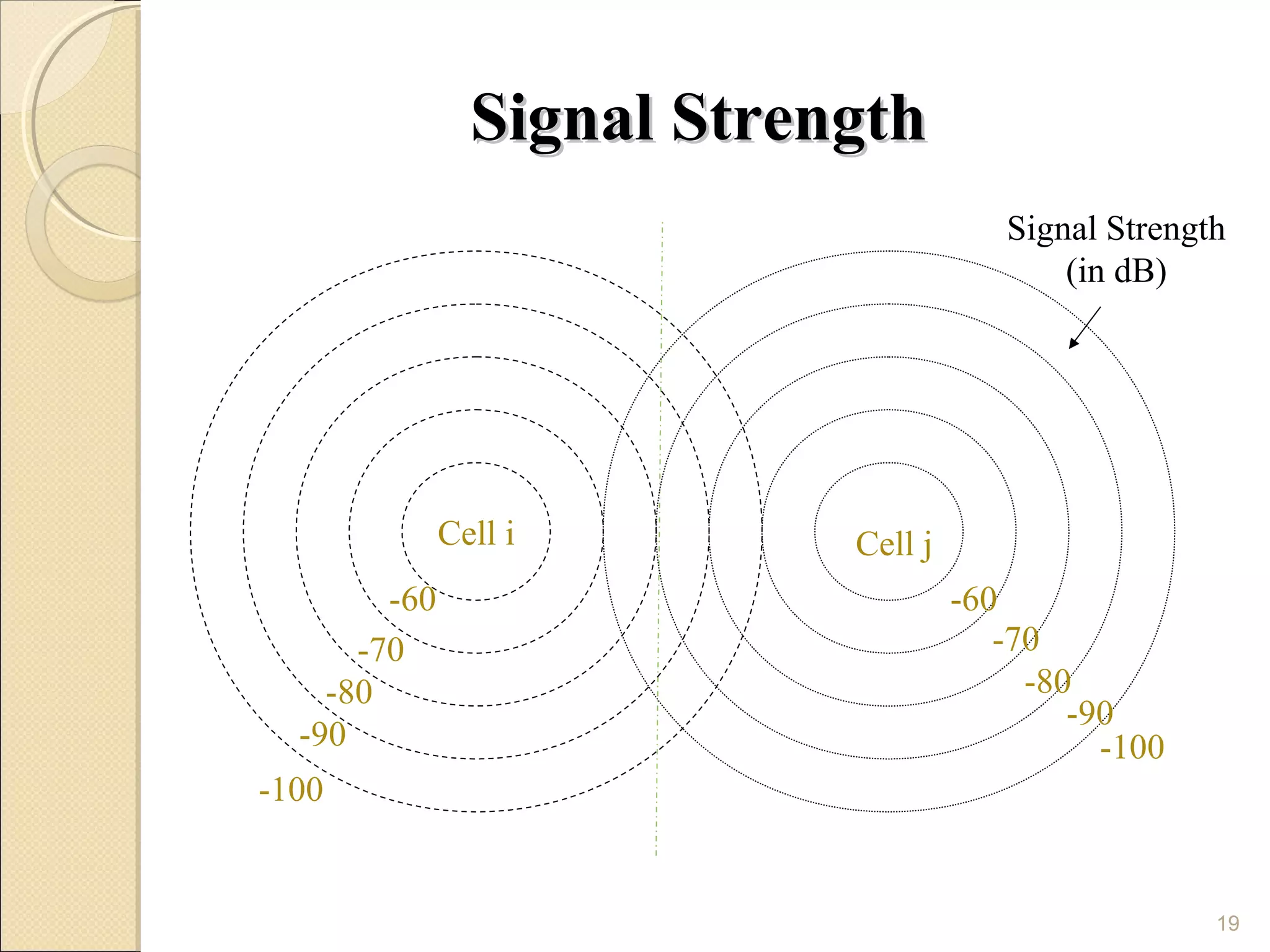
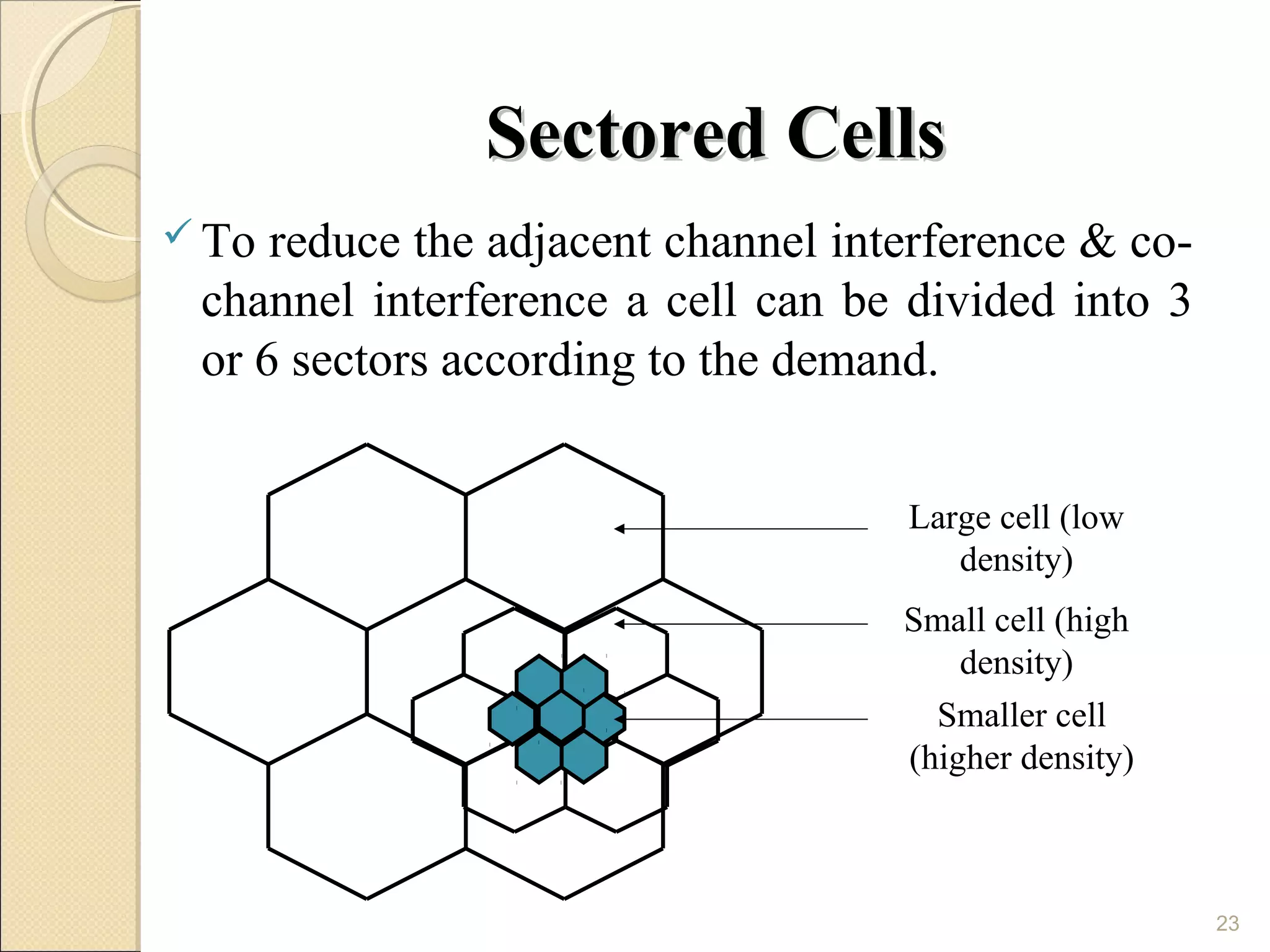
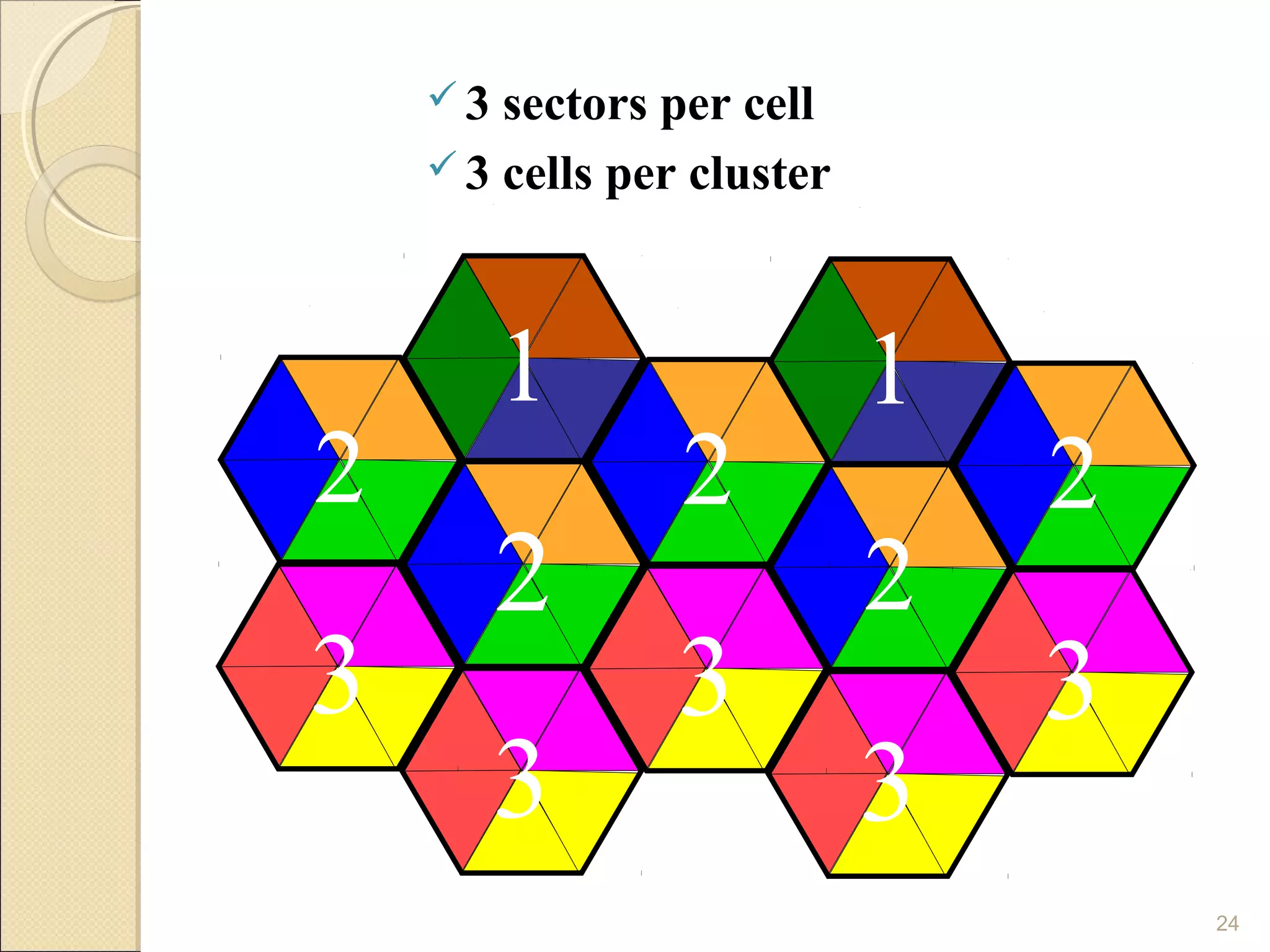
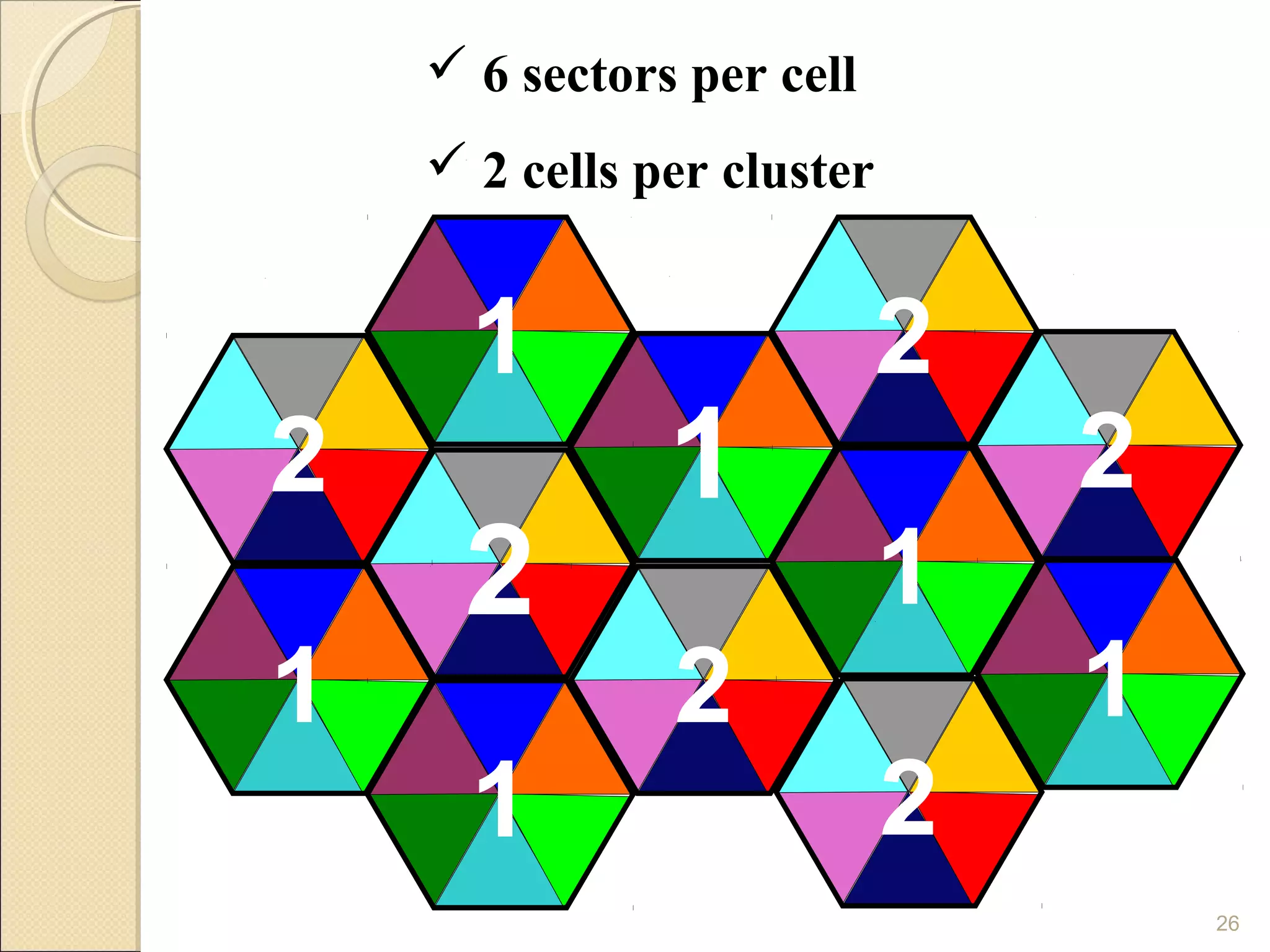
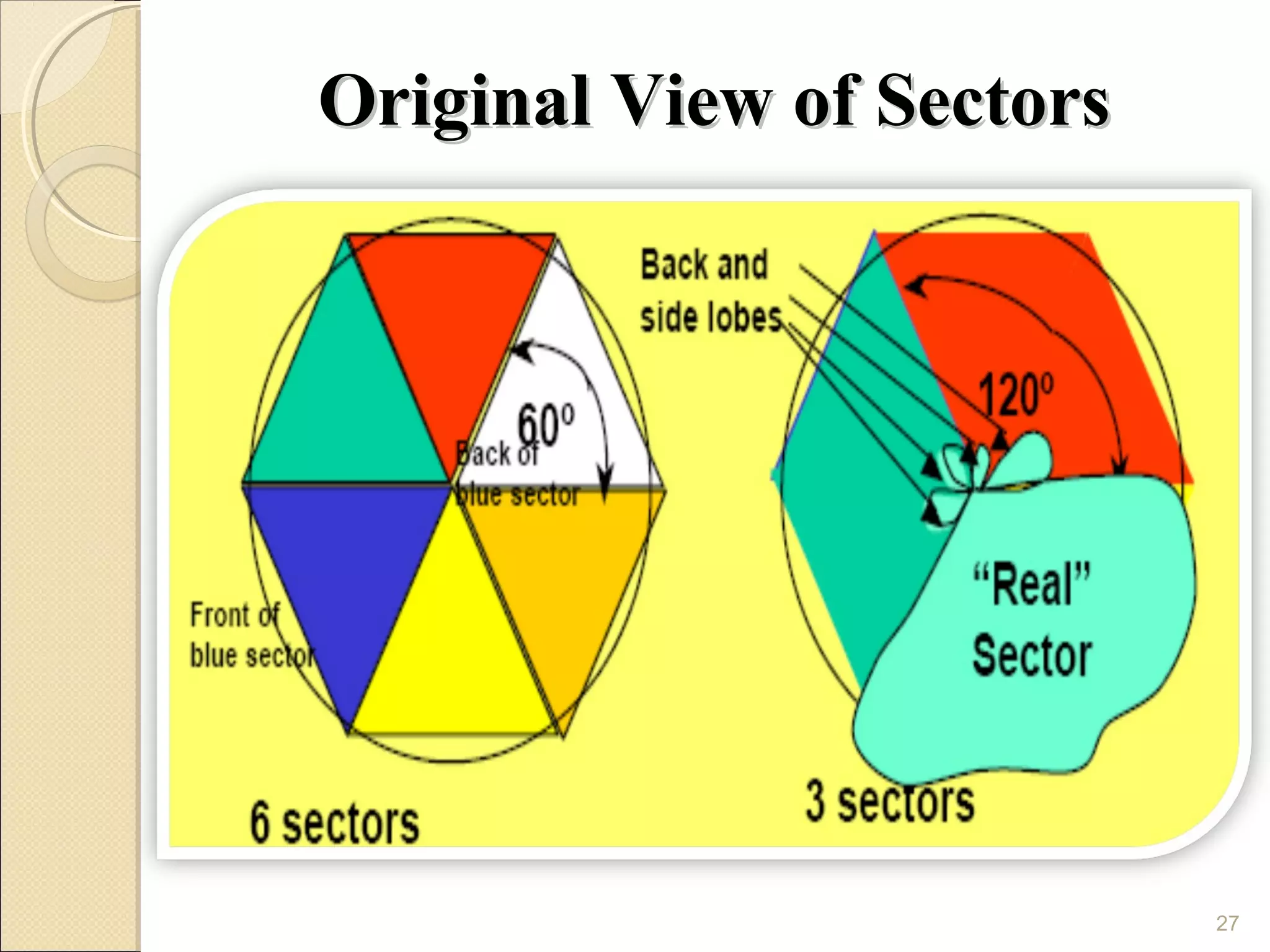
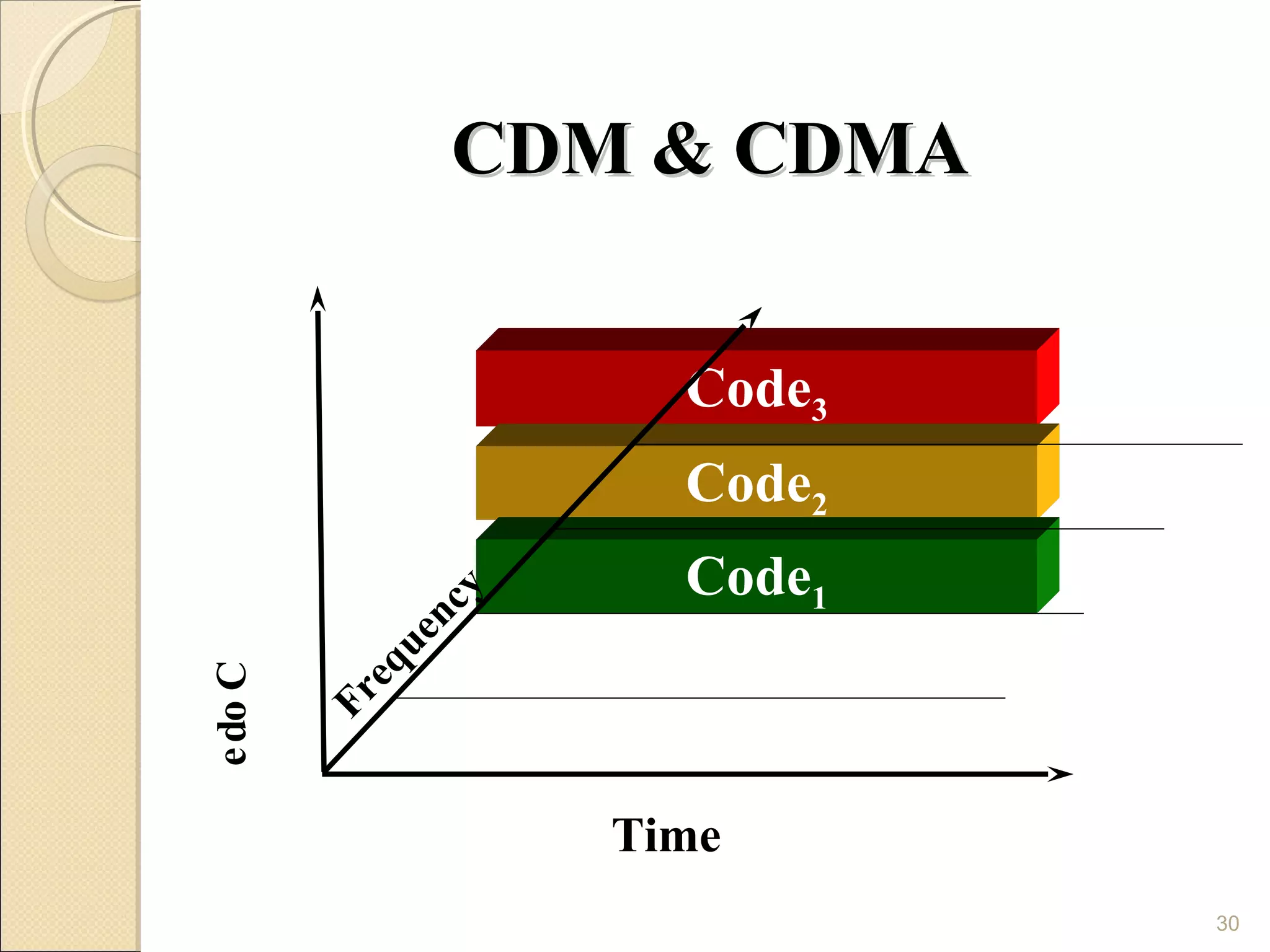
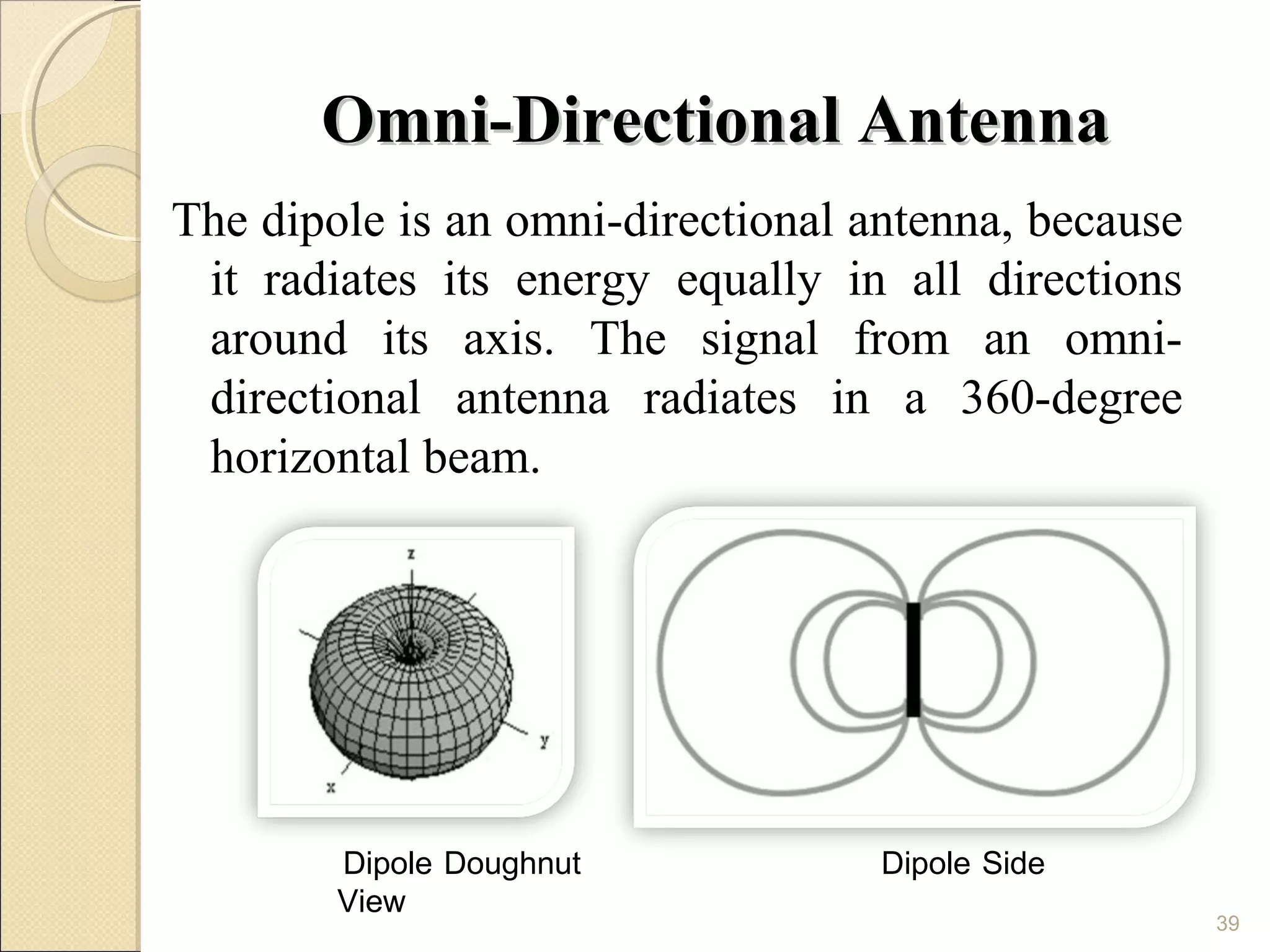
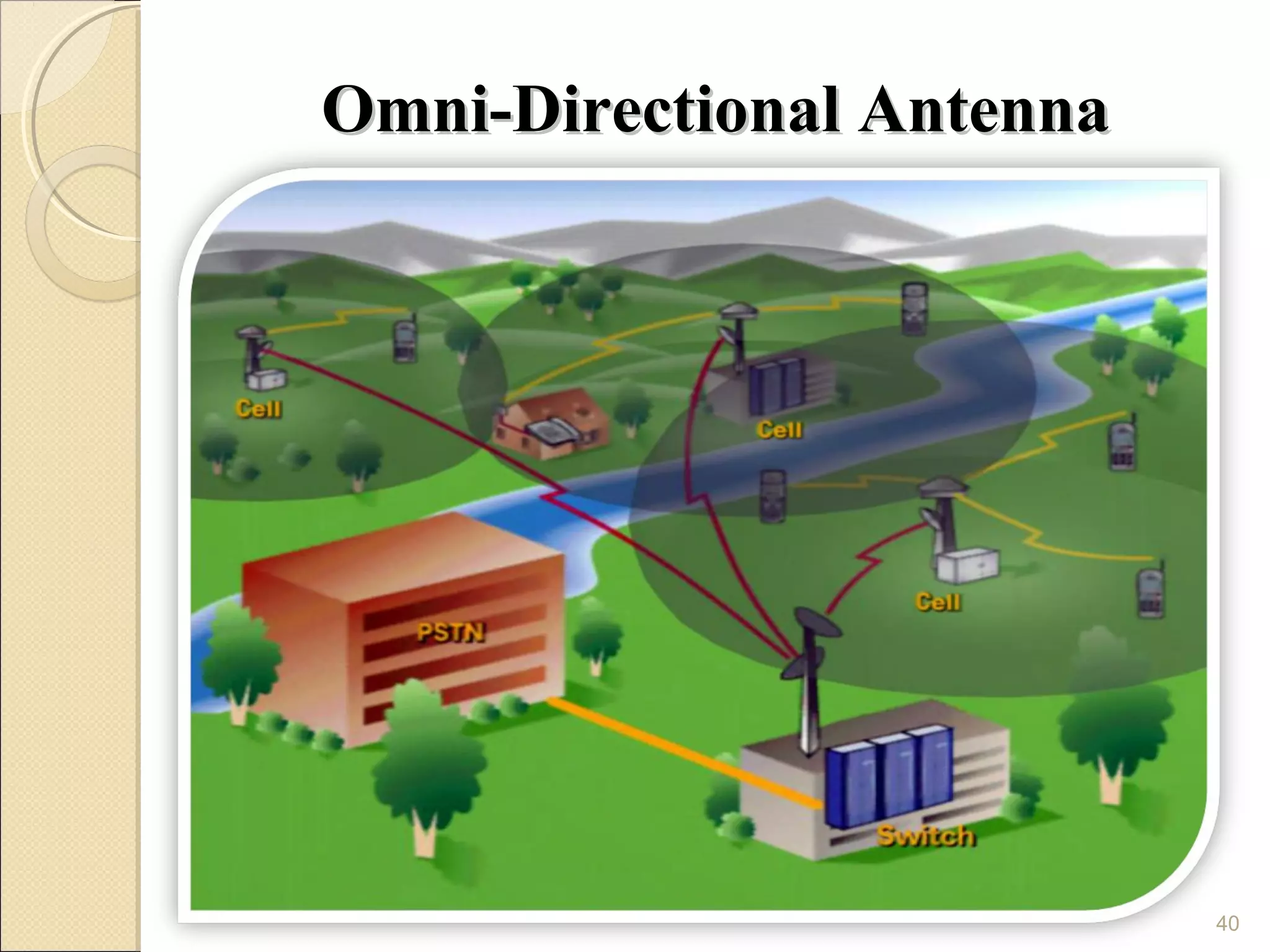
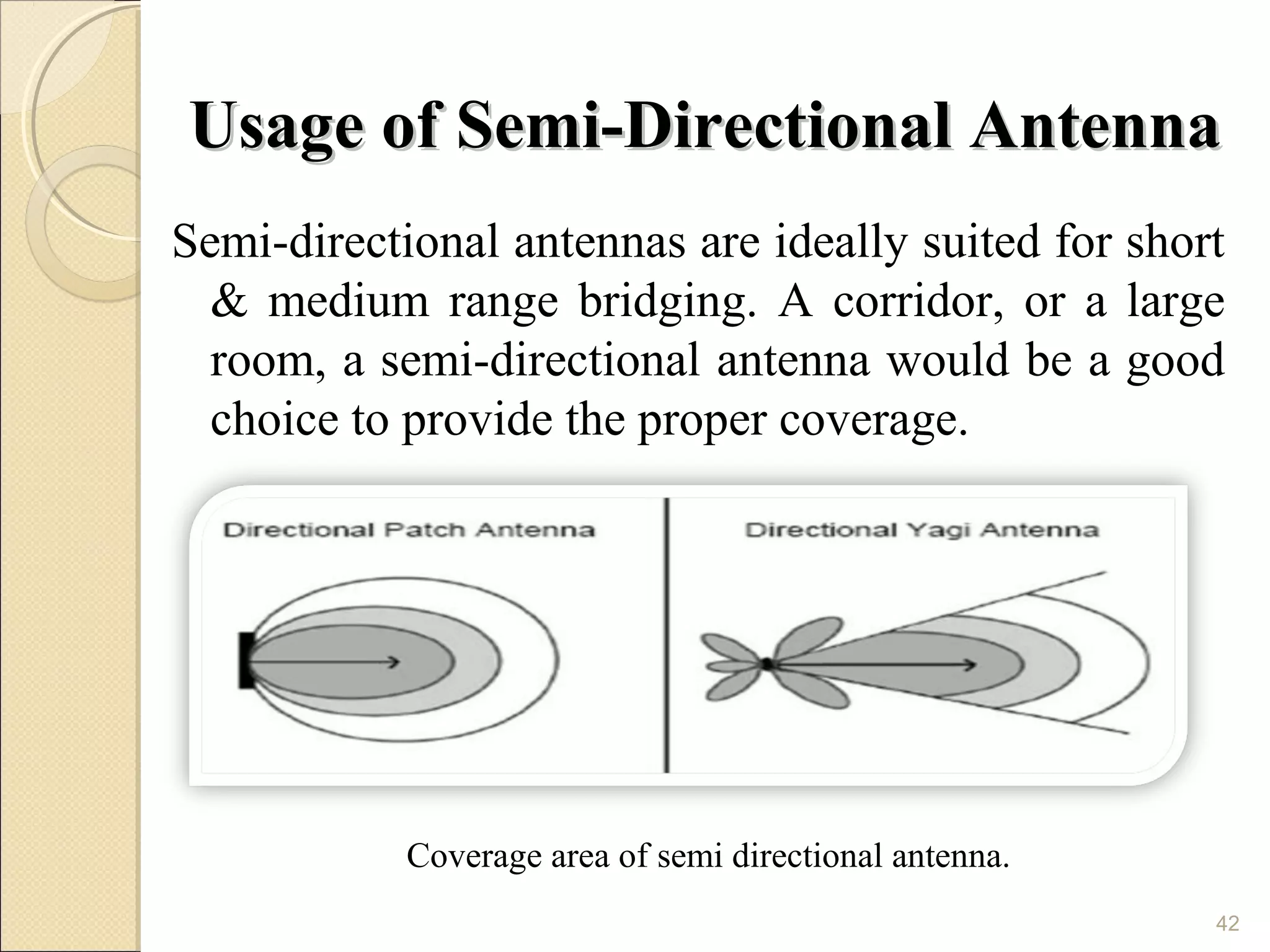
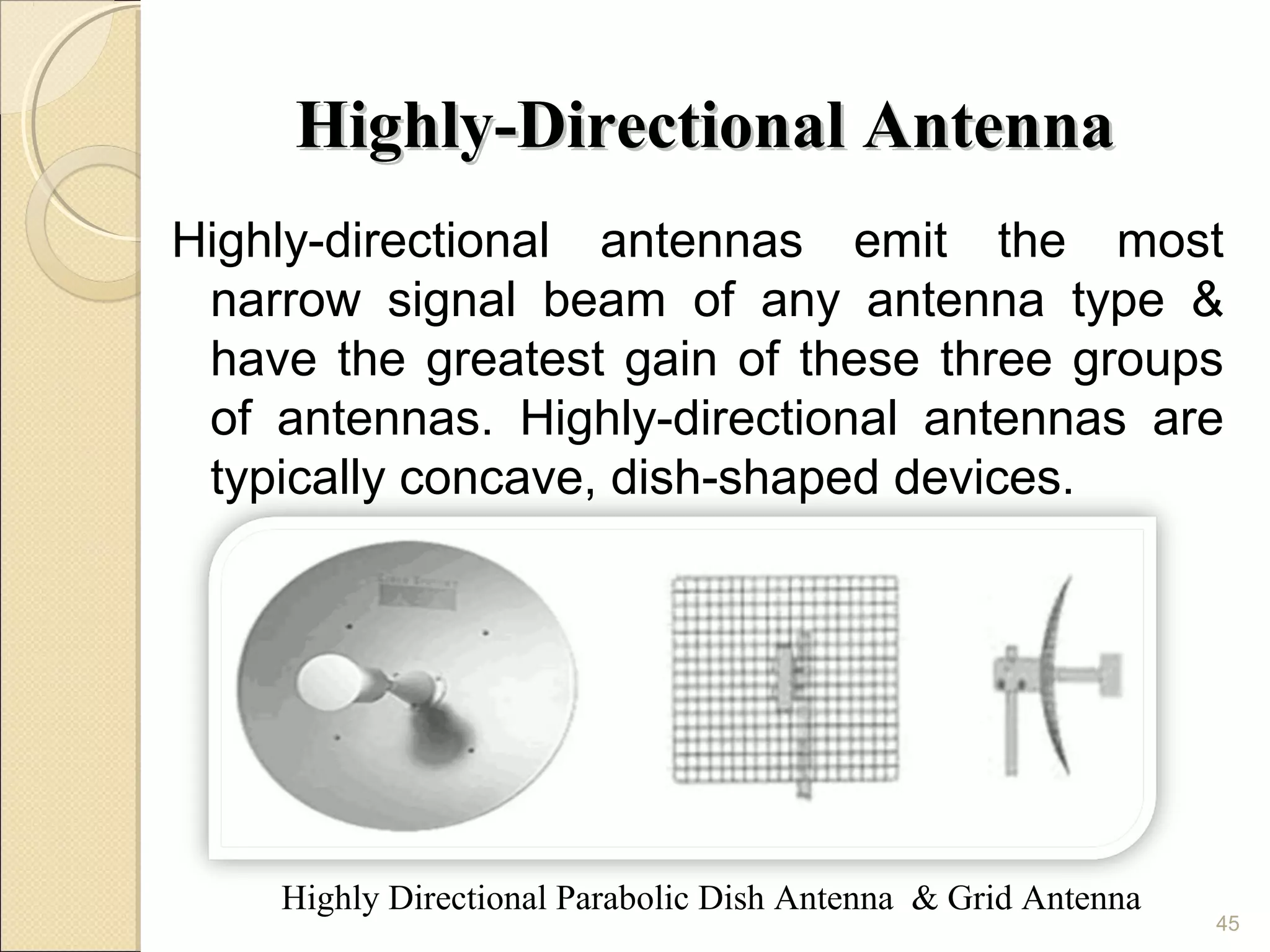
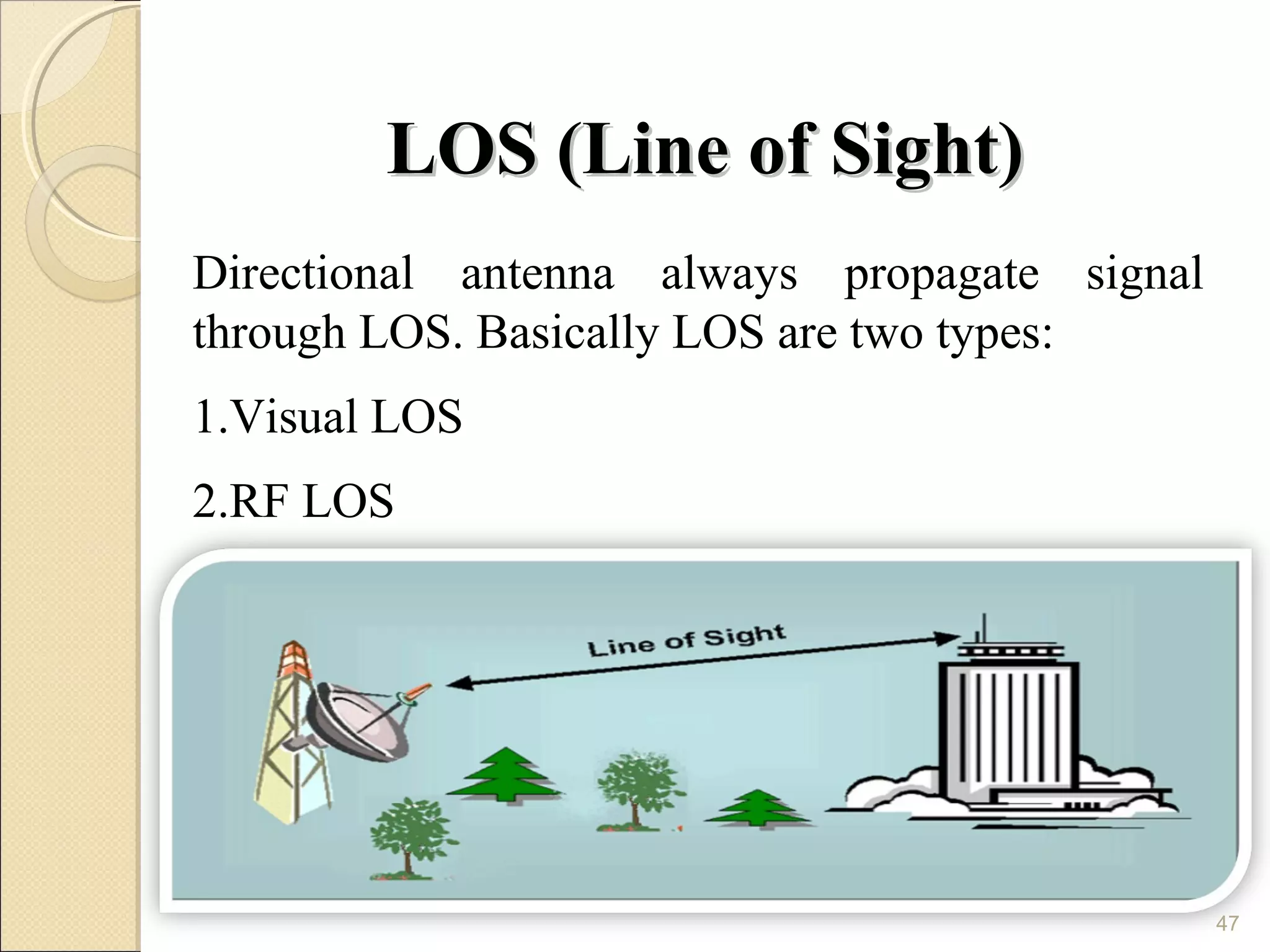
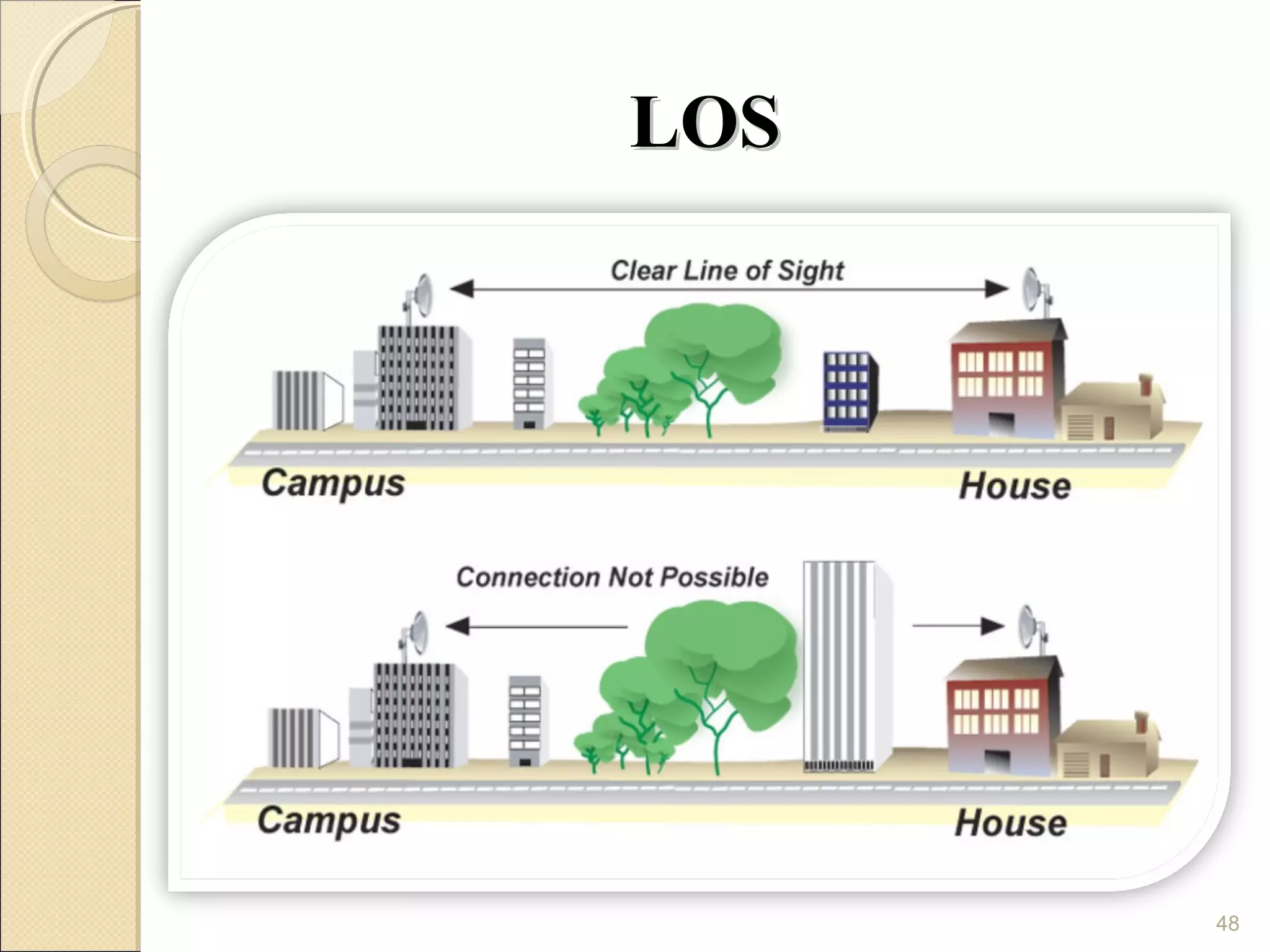
Cellular phones use cellular networks that are divided into hexagonal cells to improve capacity and spectrum efficiency. Each cell uses a different set of frequencies to avoid interference between adjacent cells. As users move between cells, their connection must be handed off seamlessly to the new cell. Network components like base stations and mobile switching centers work together to manage connectivity and roaming across the cellular network.