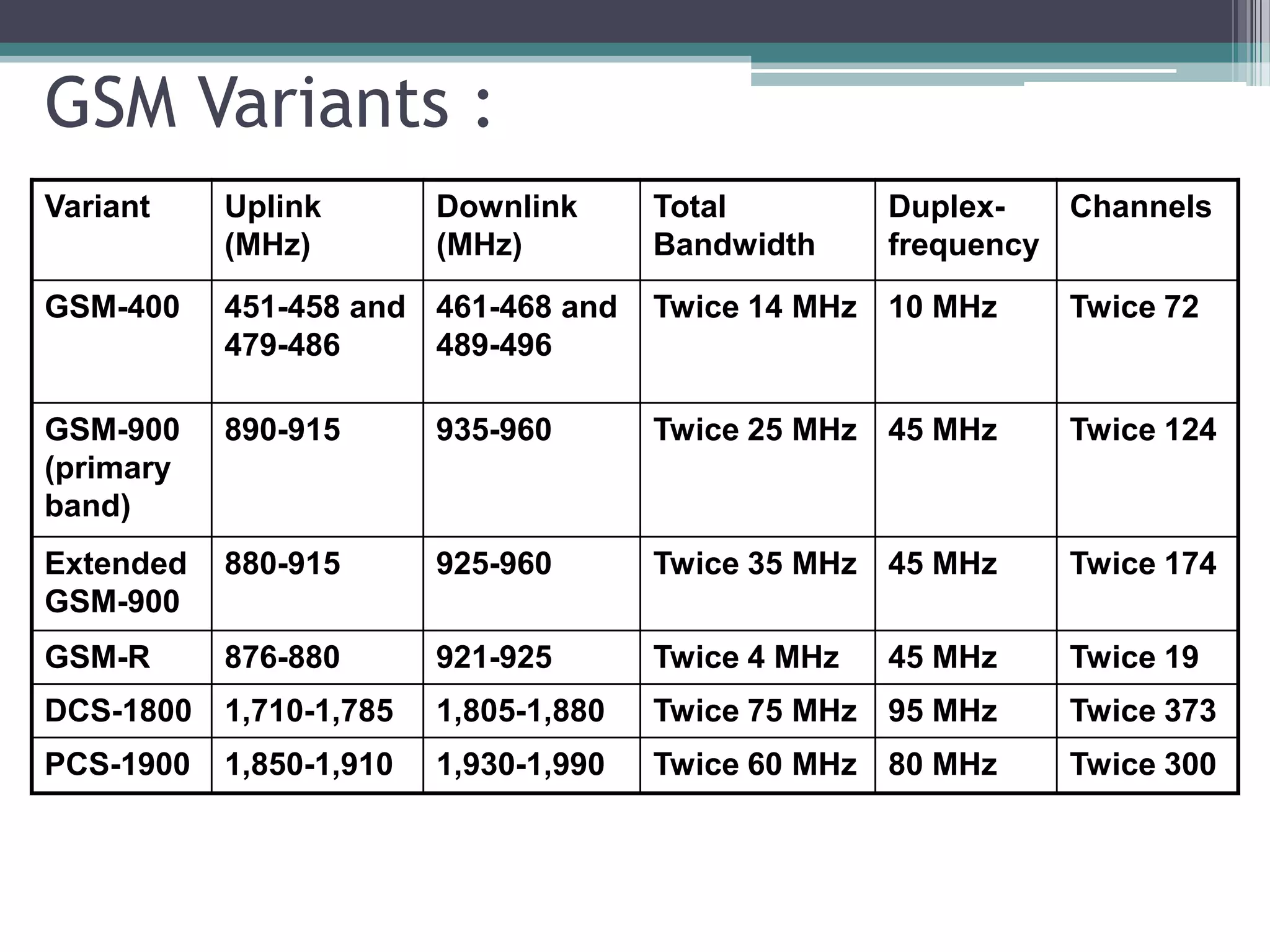
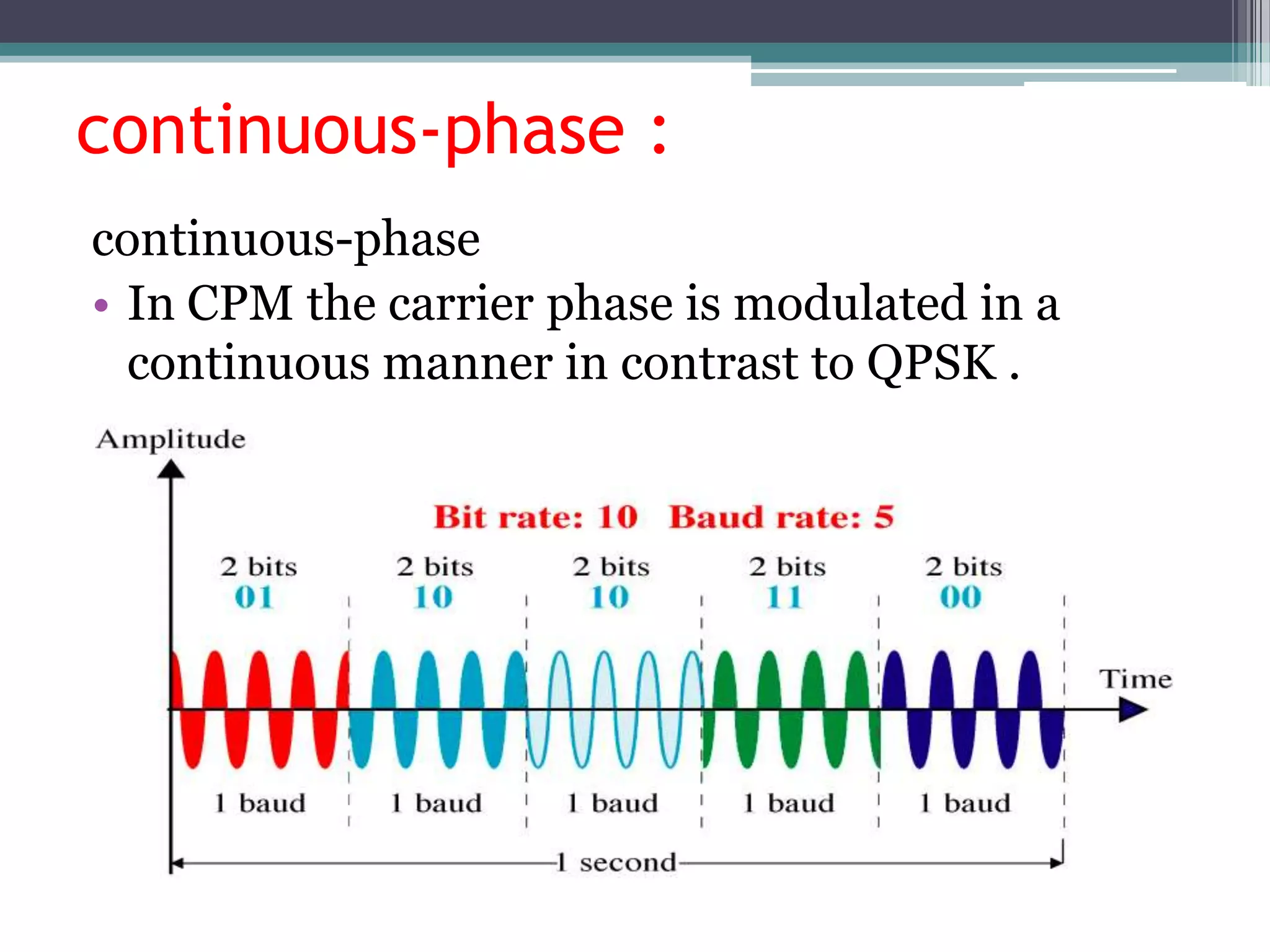
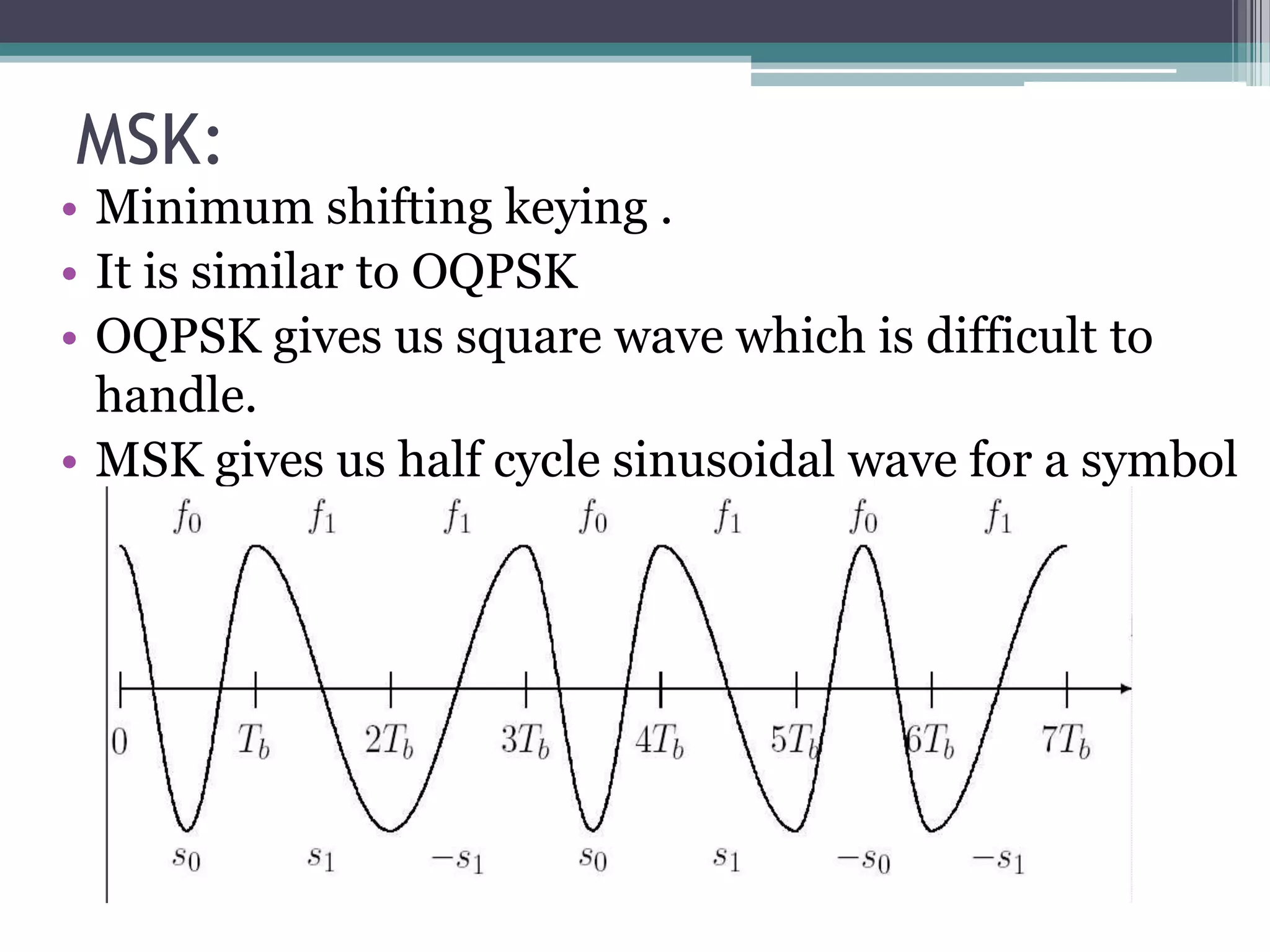
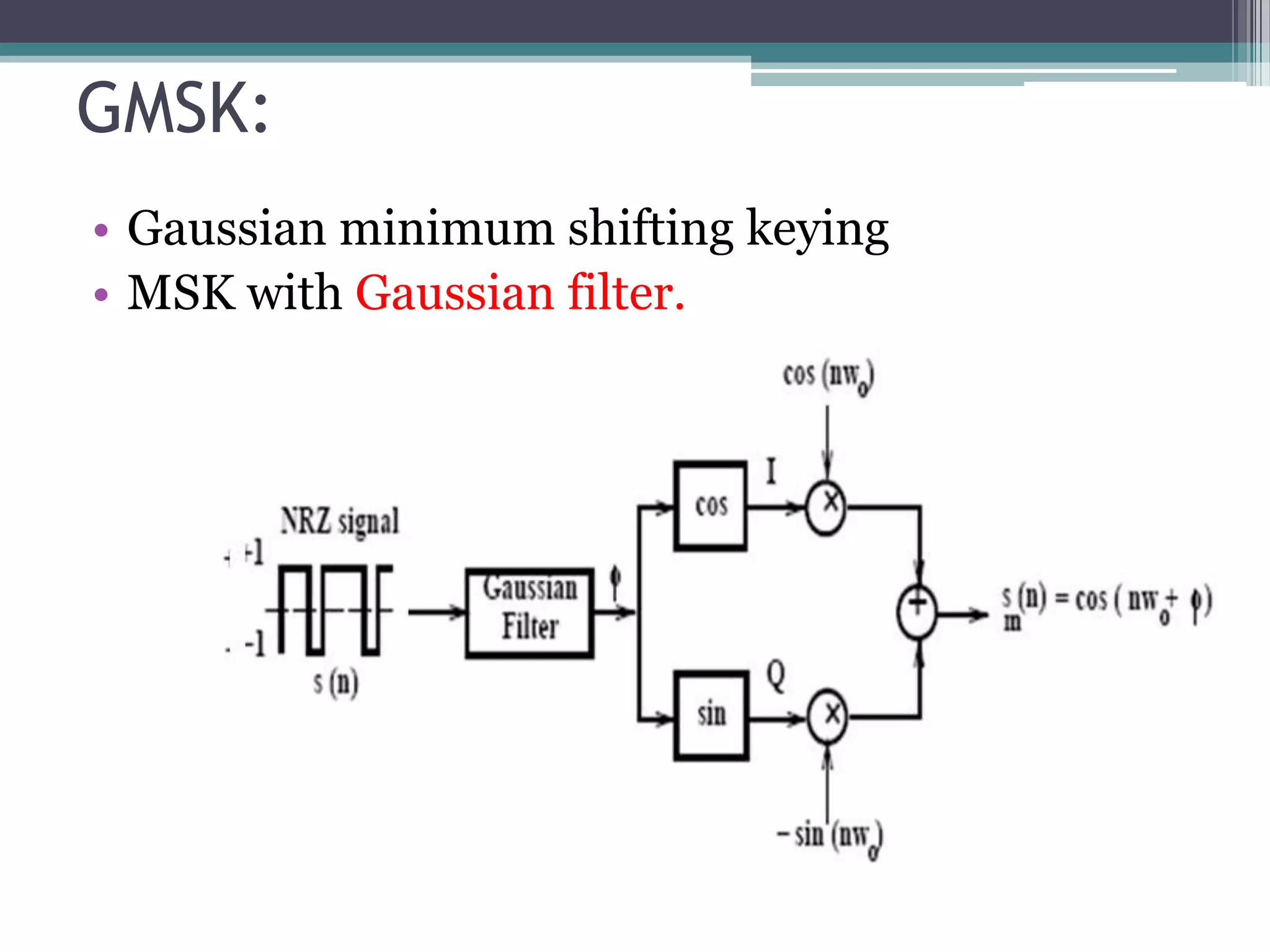
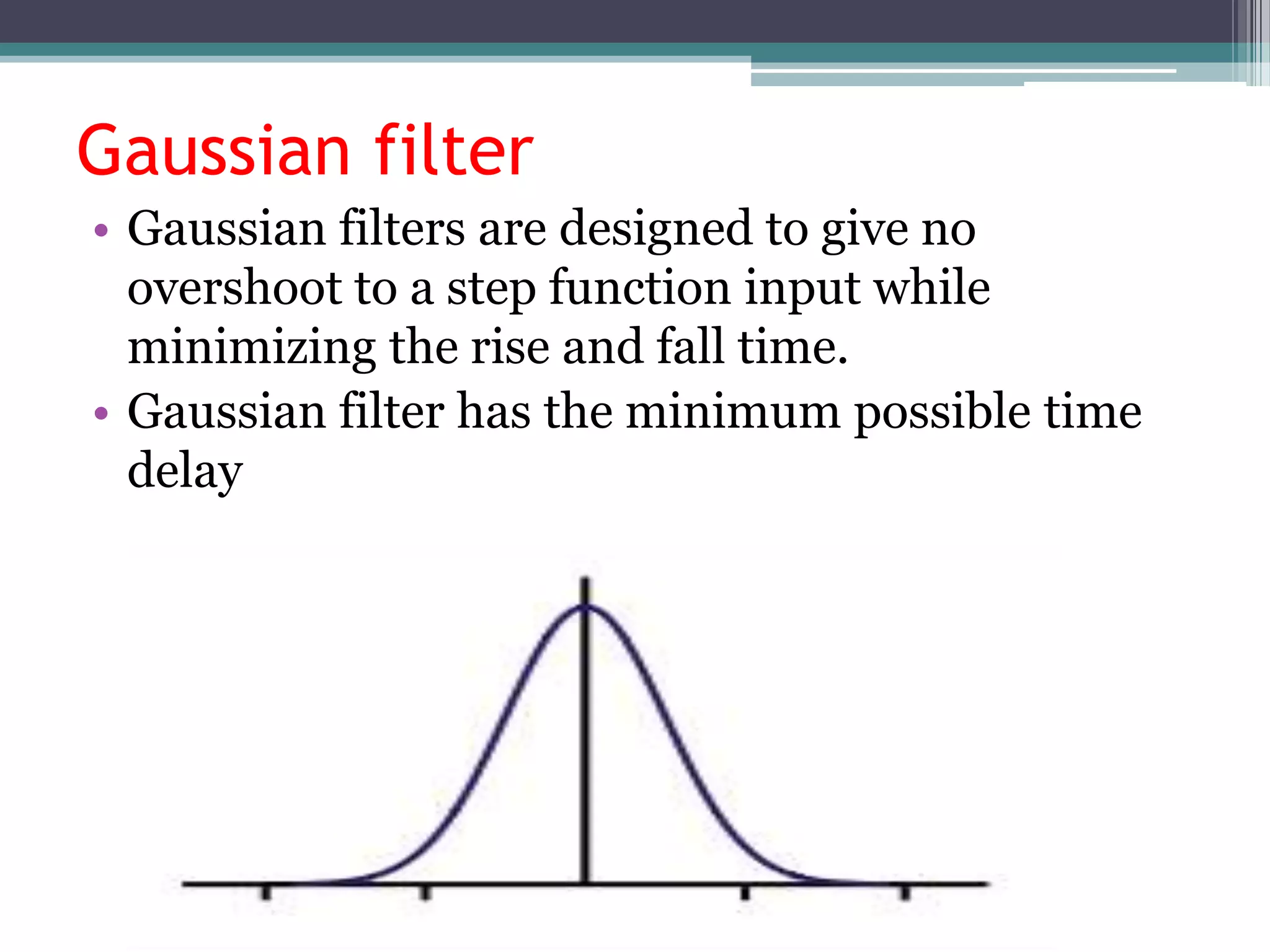
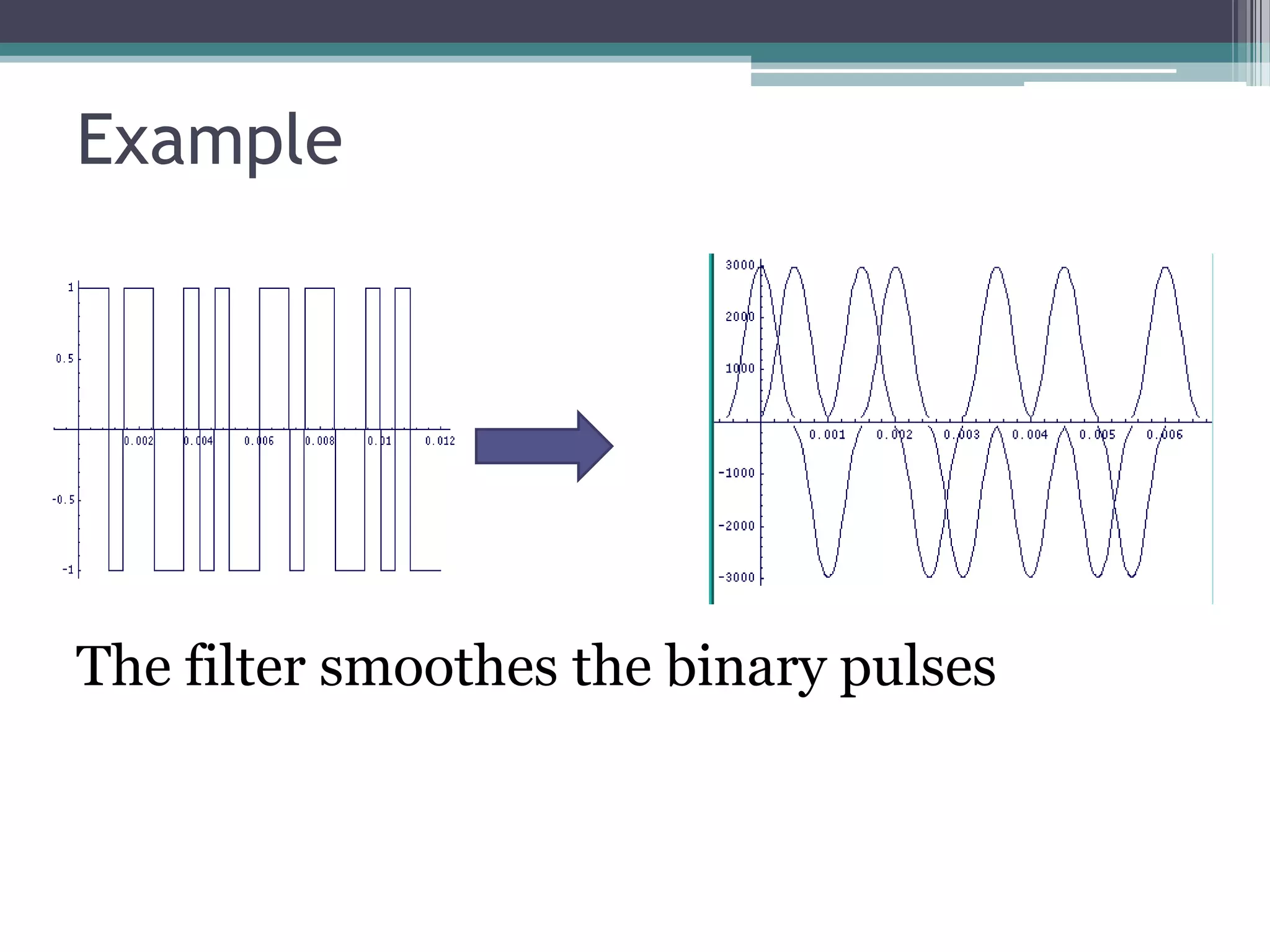
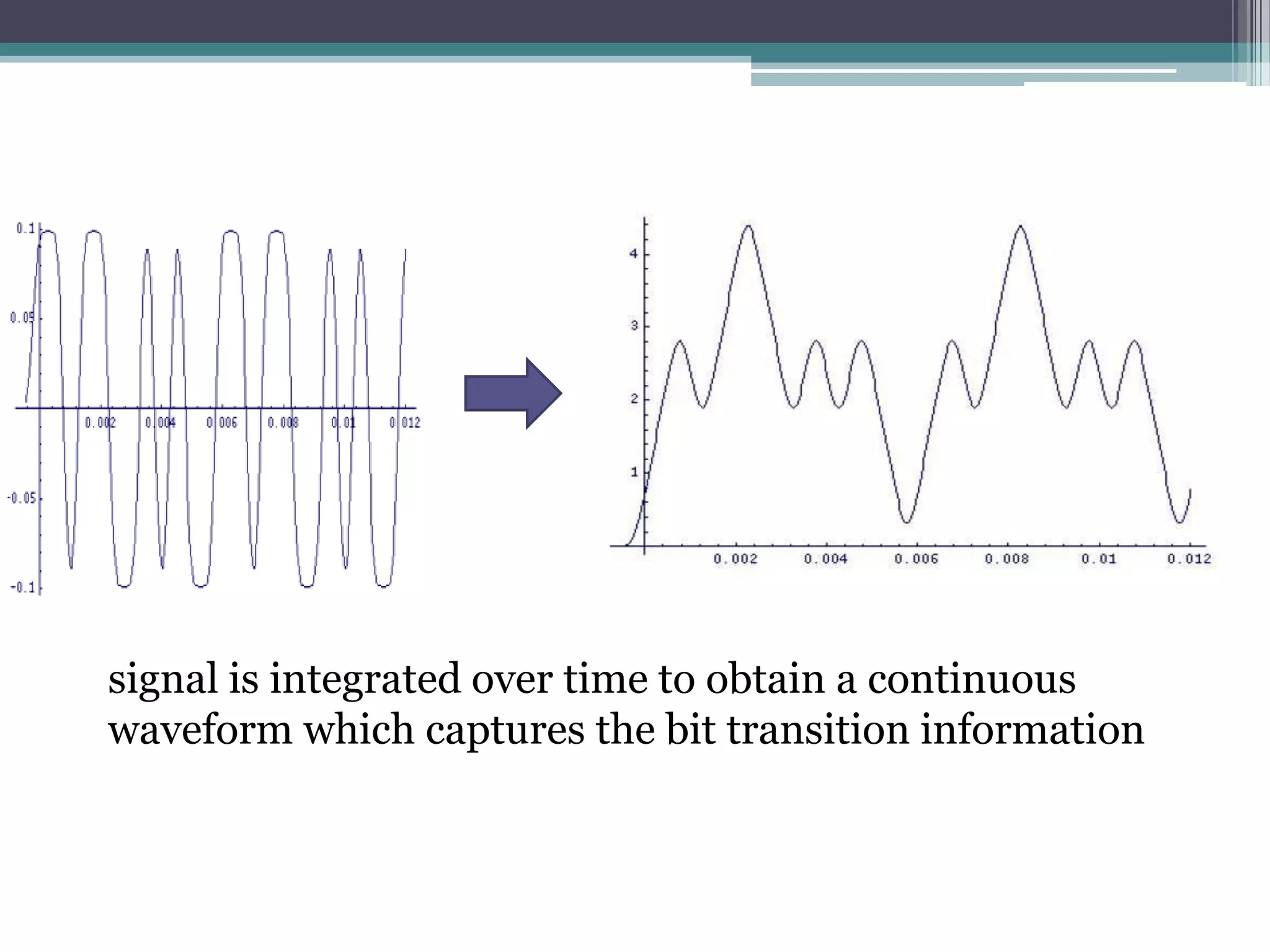
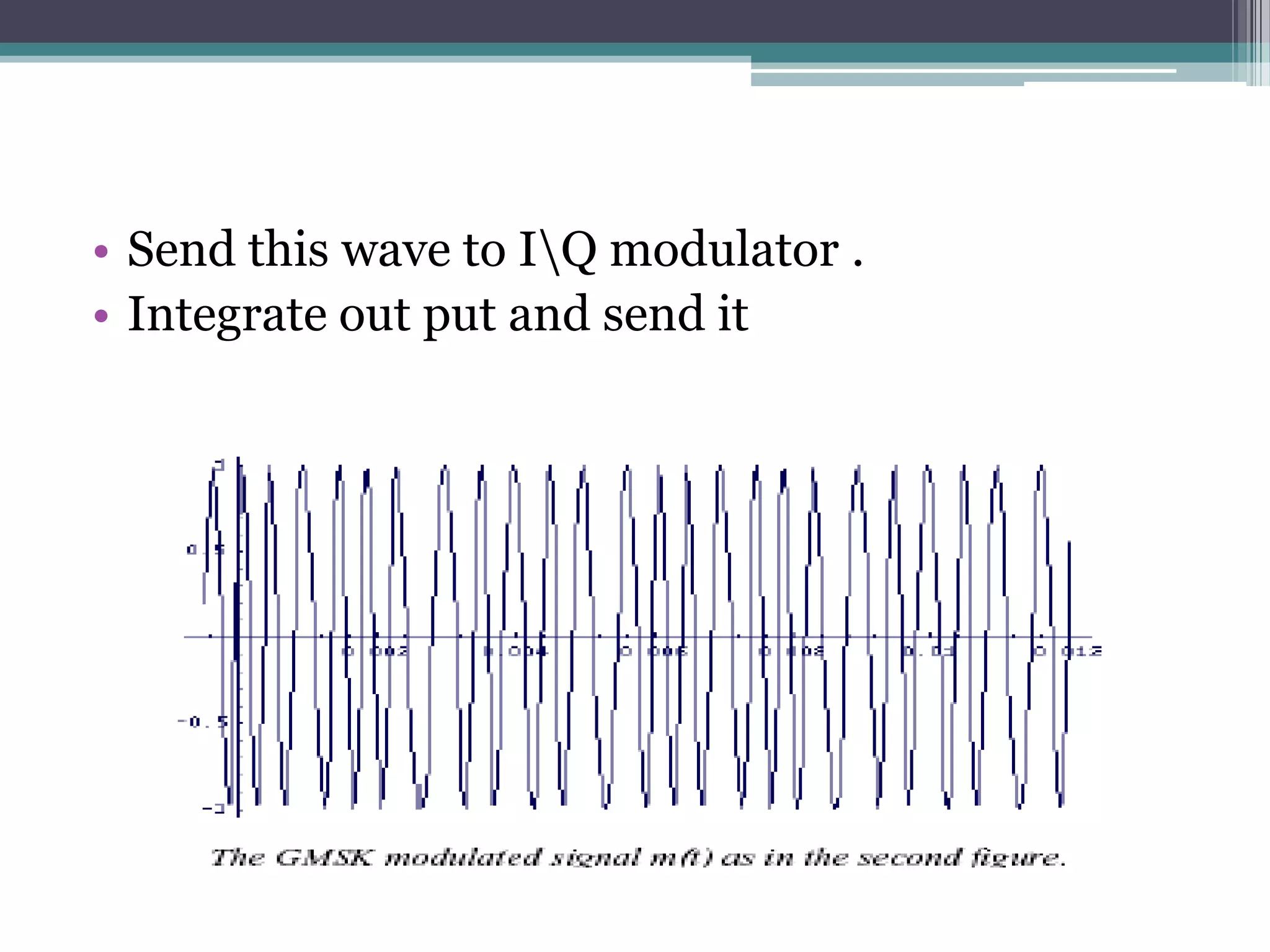
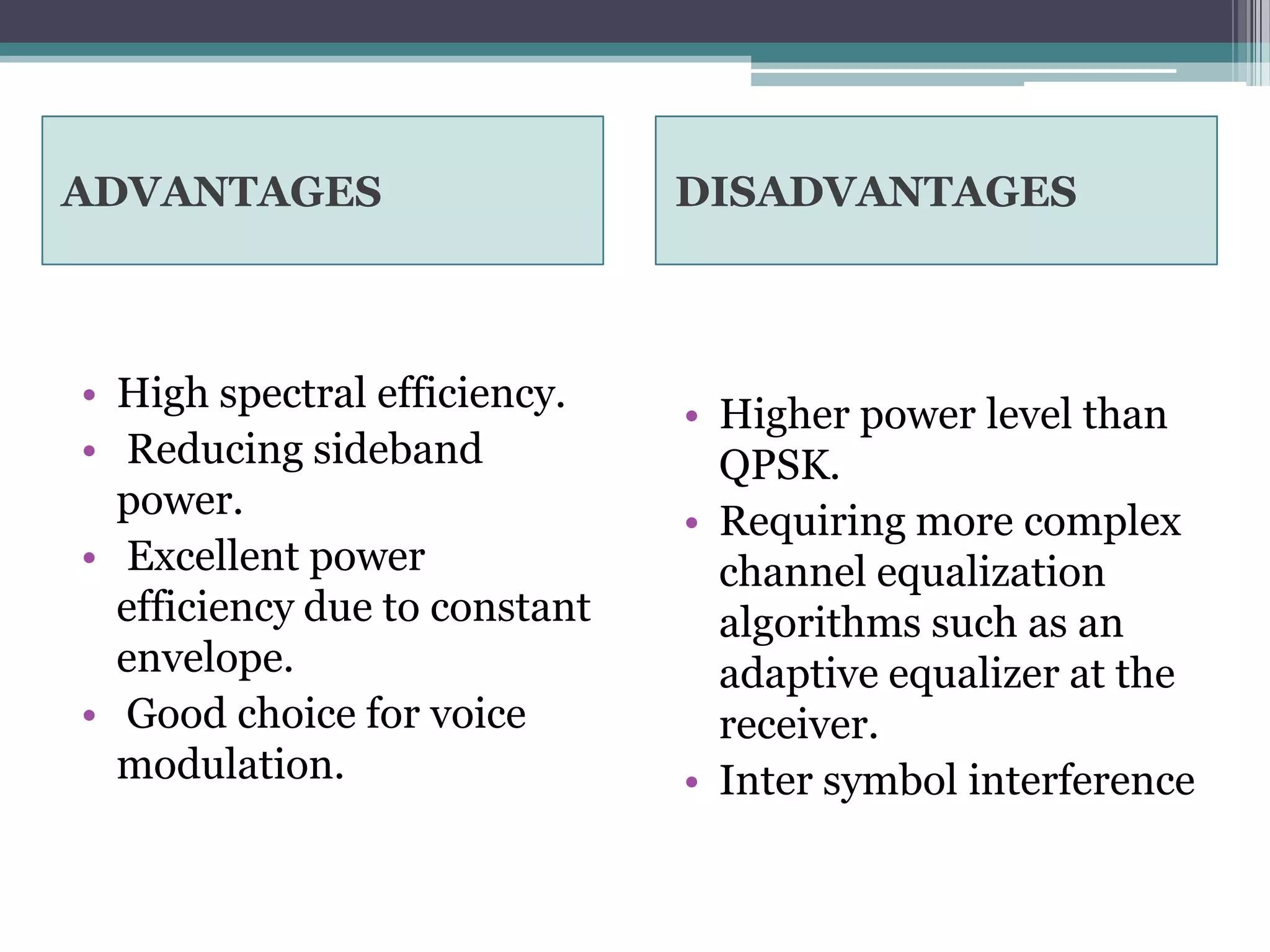
- GSM is a standard for 2G digital cellular networks that uses narrowband TDMA. It describes protocols for features like GPRS, EDGE, authentication, encryption, and more.
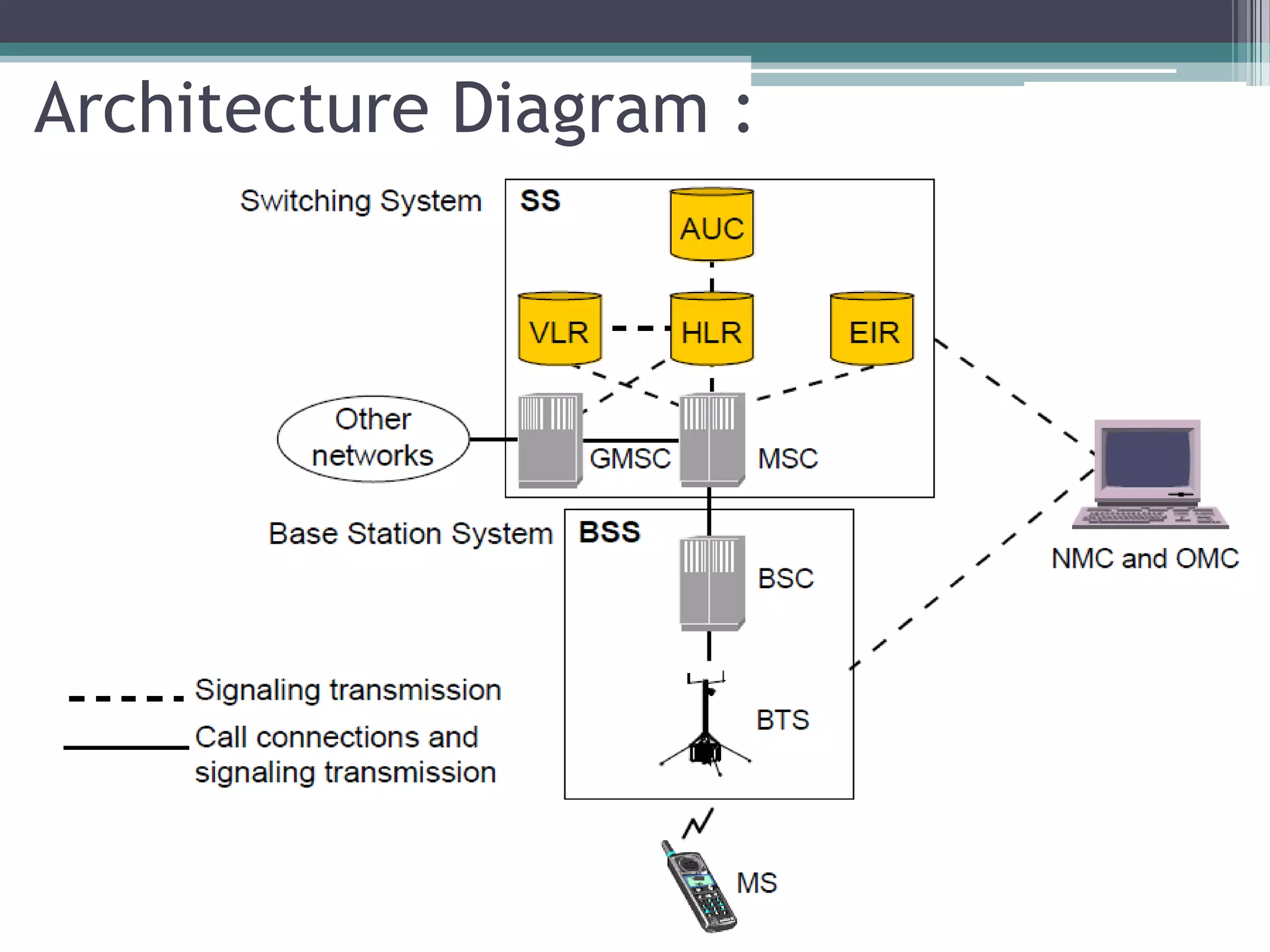
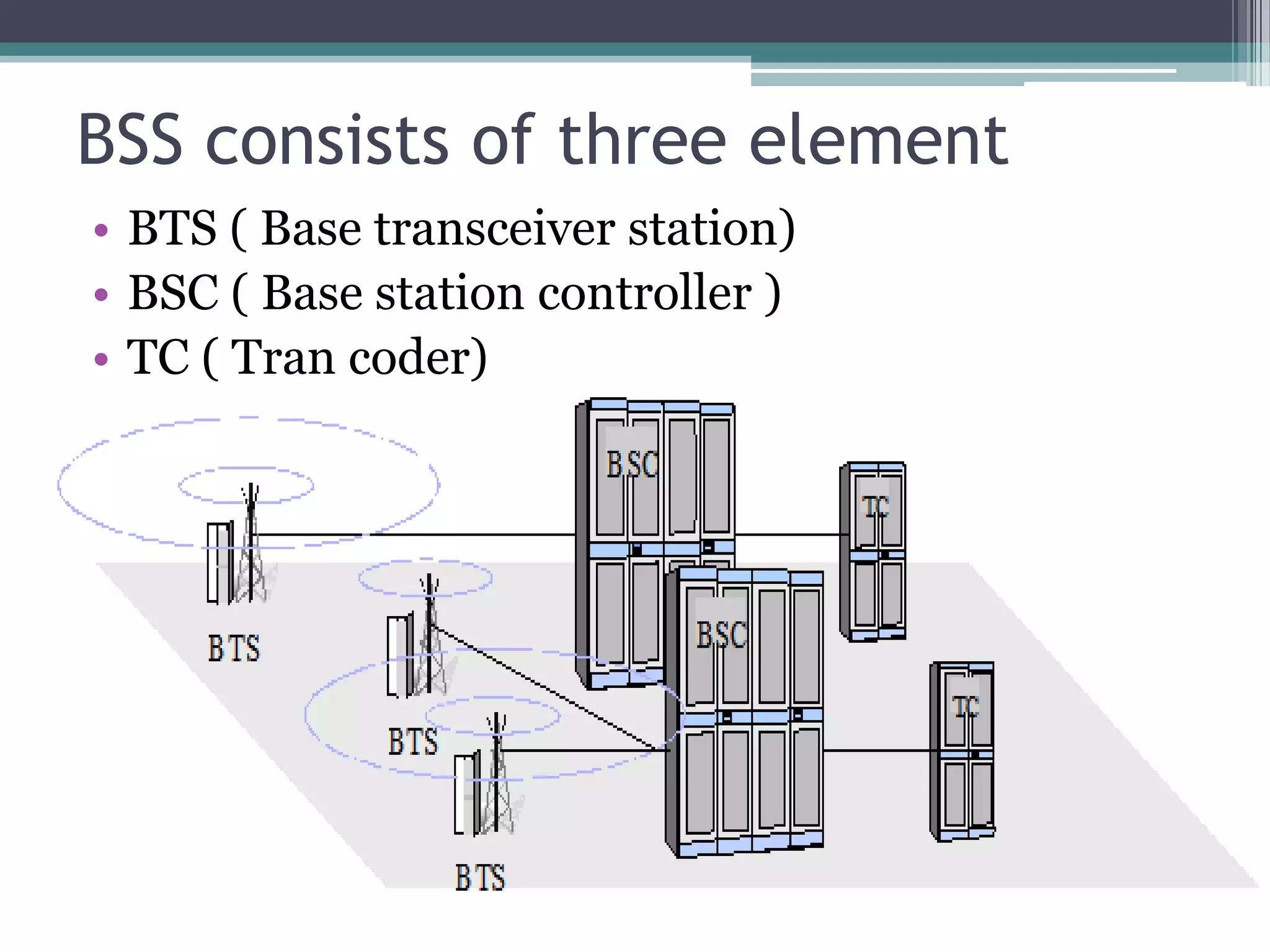
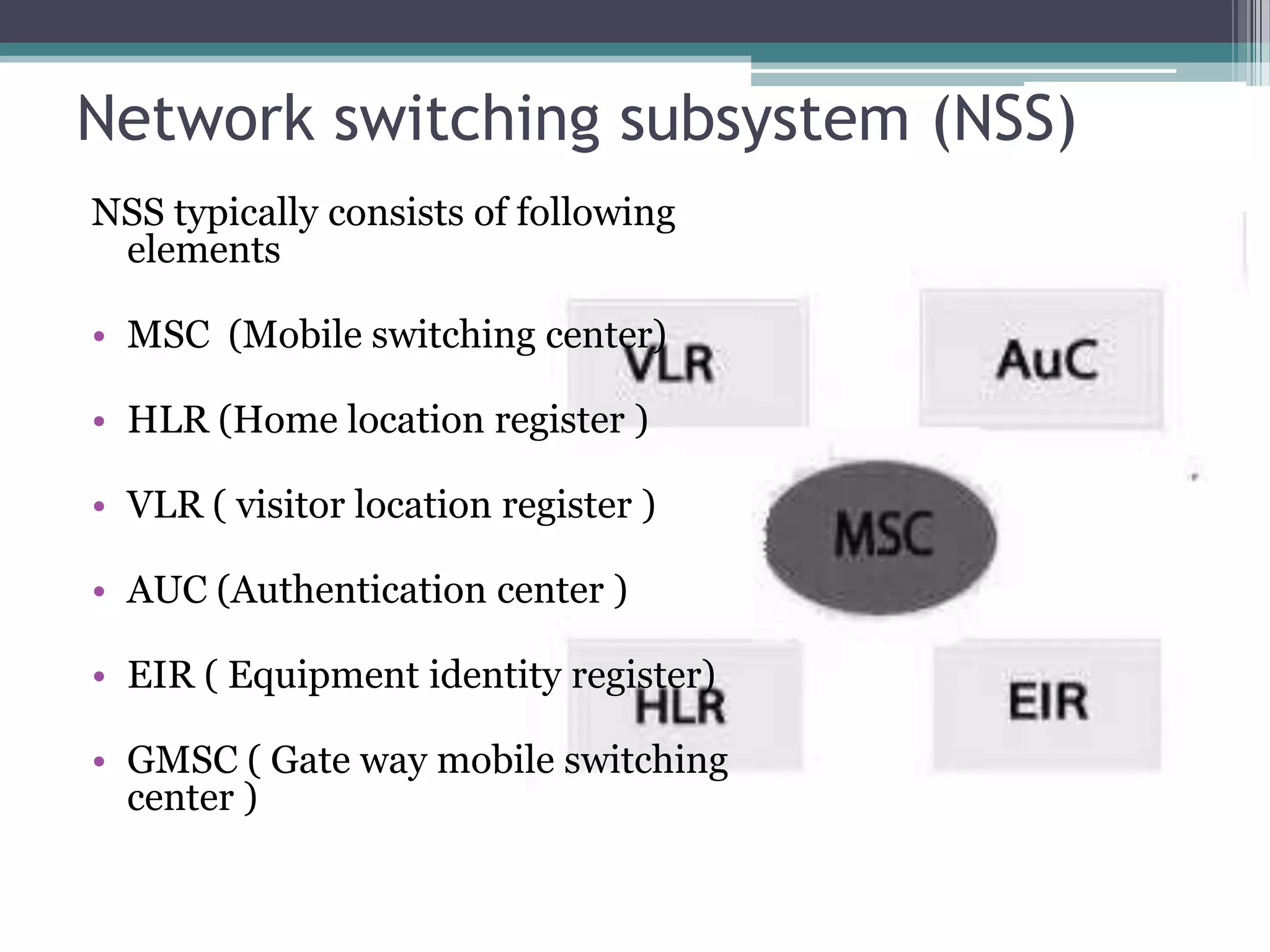
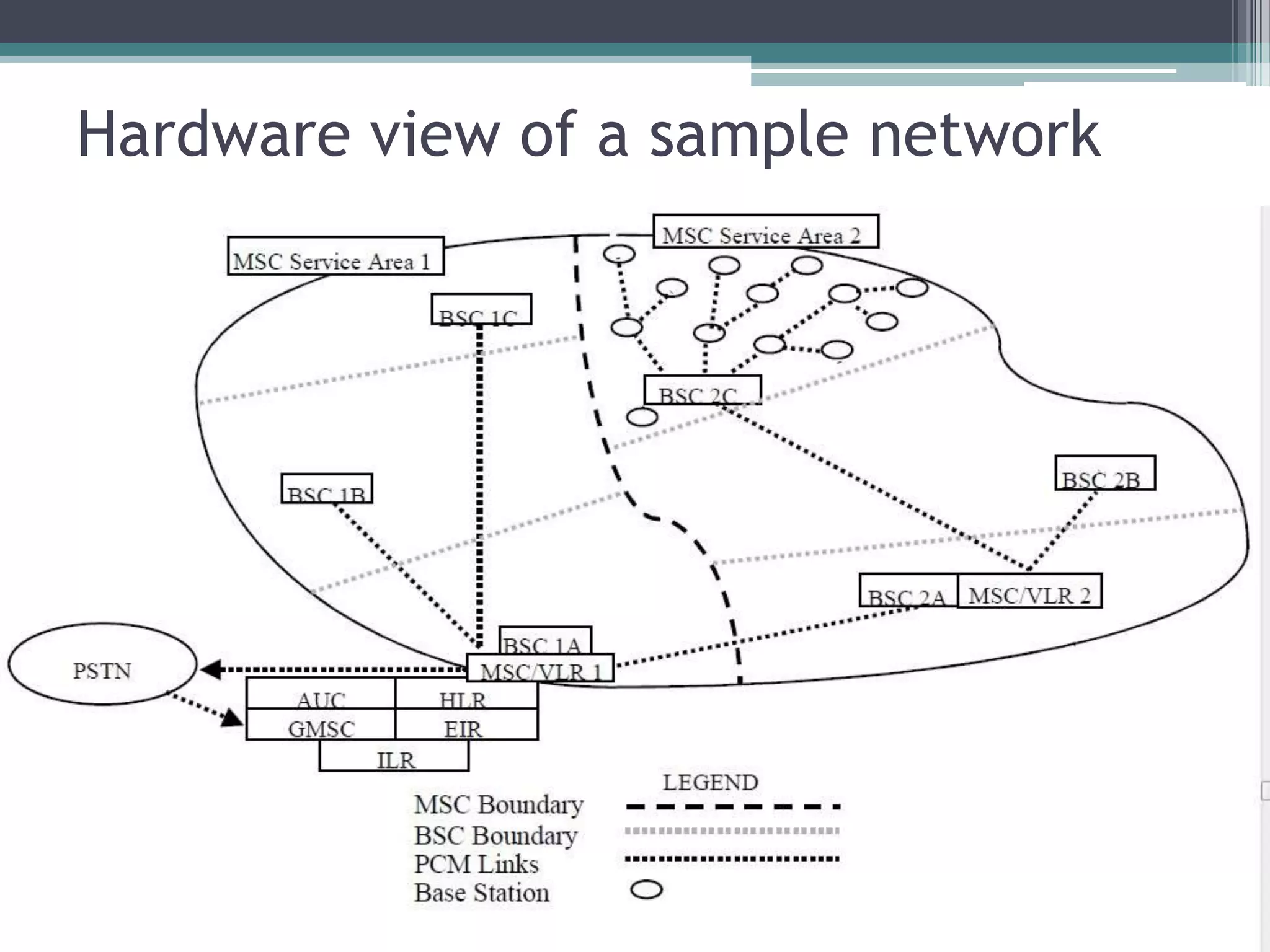
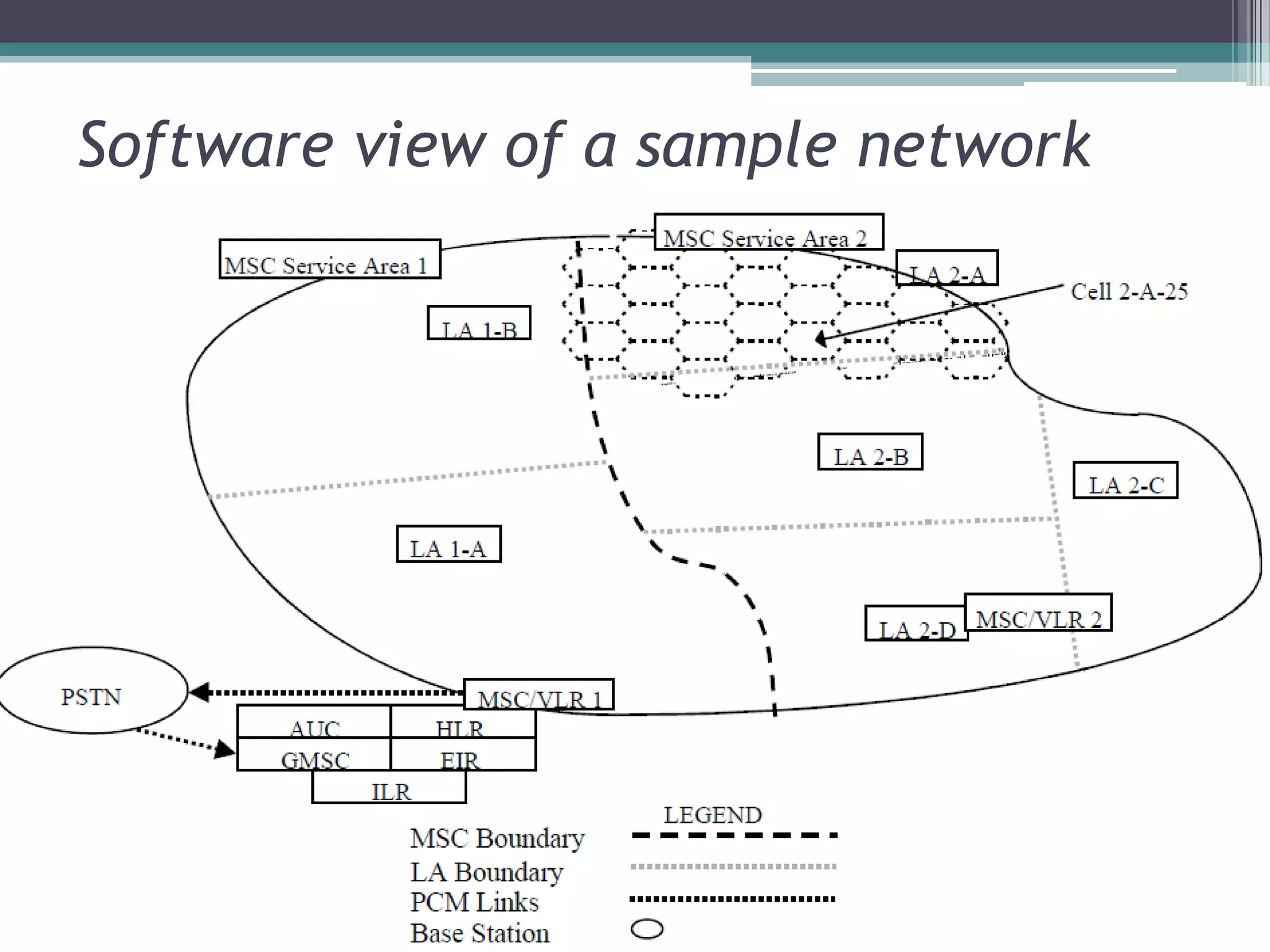
- The GSM architecture consists of mobile equipment (handsets), a base station subsystem for radio network management, a network switching subsystem for call routing, and a network management subsystem.
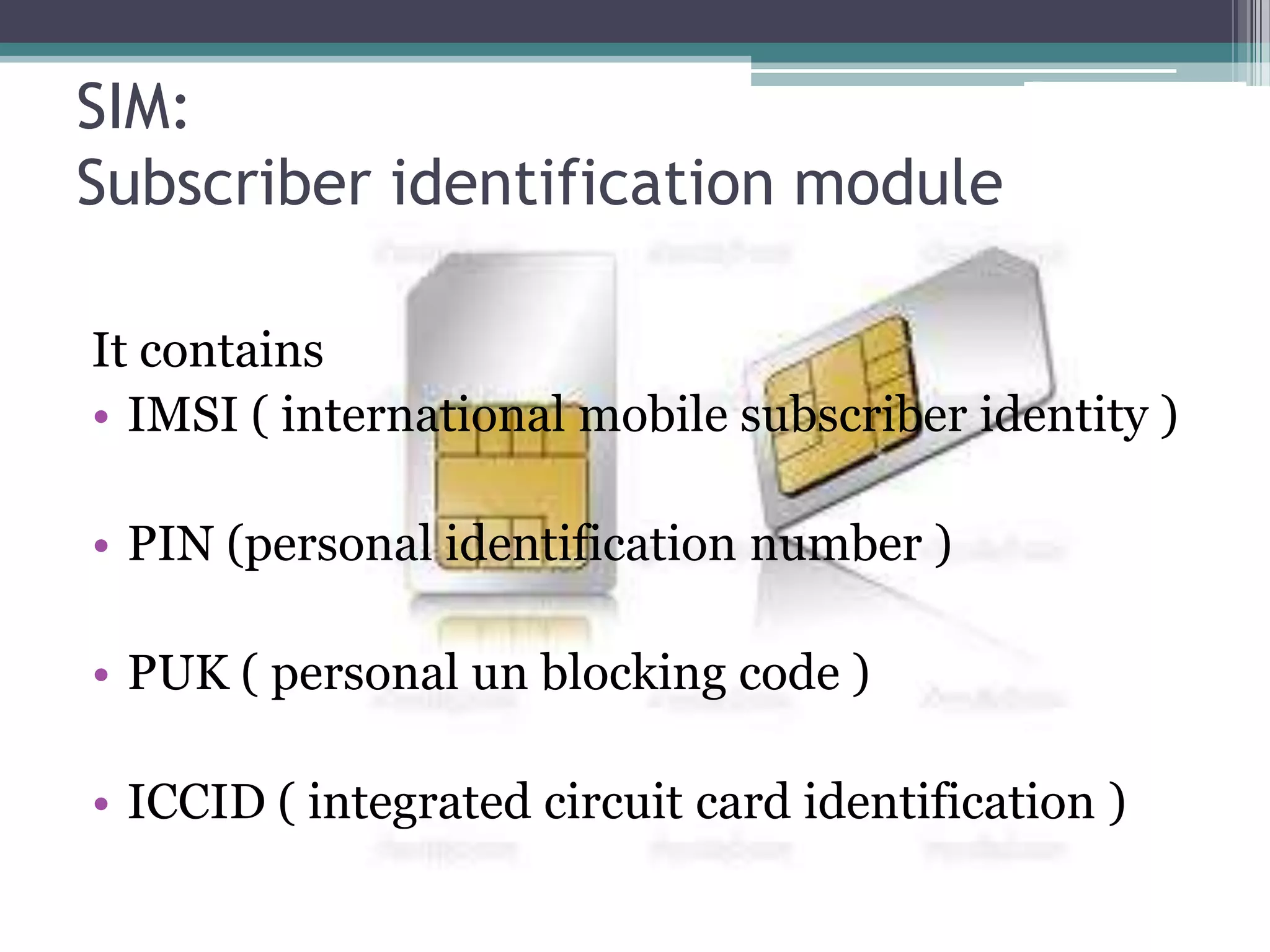
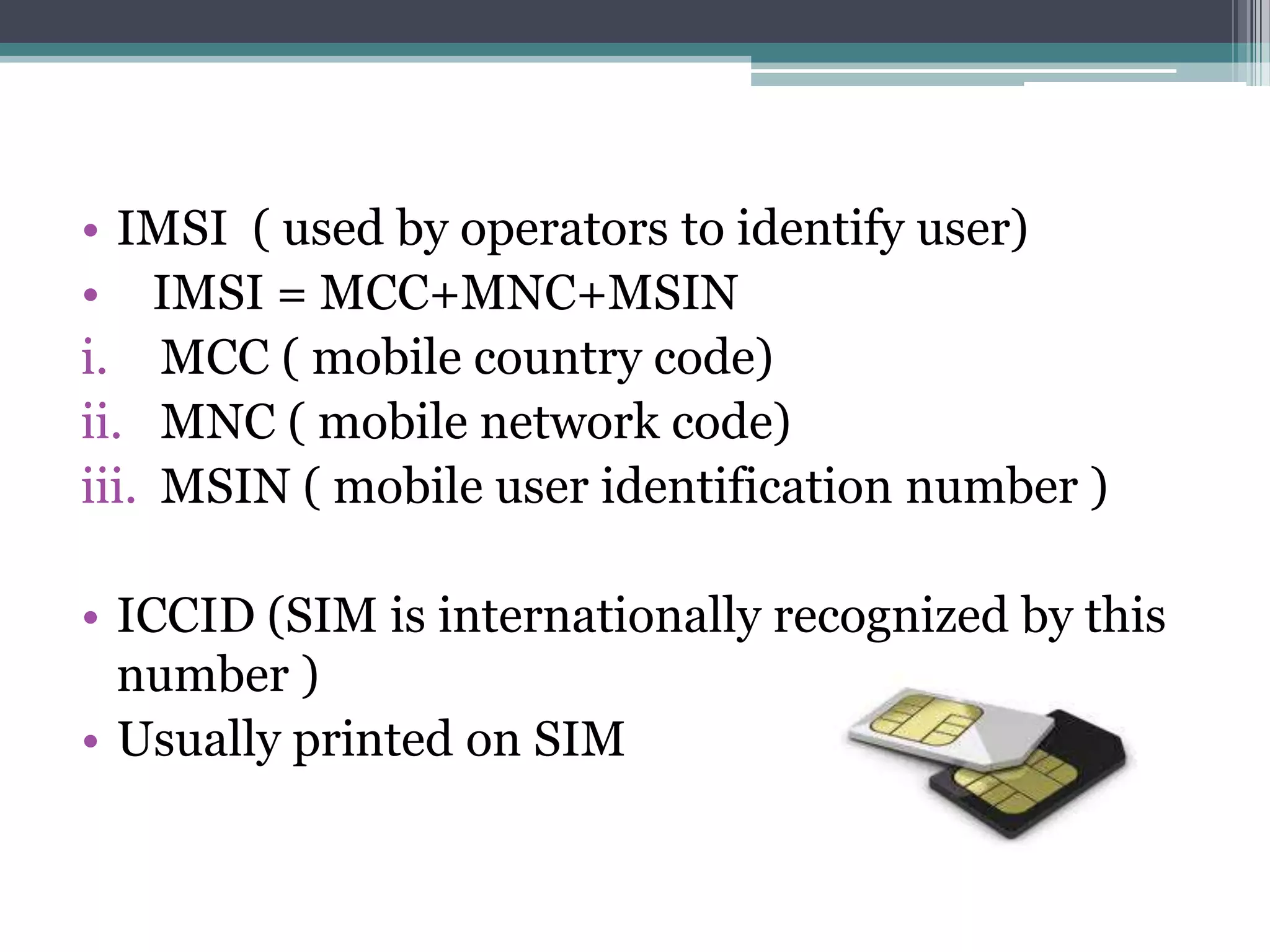
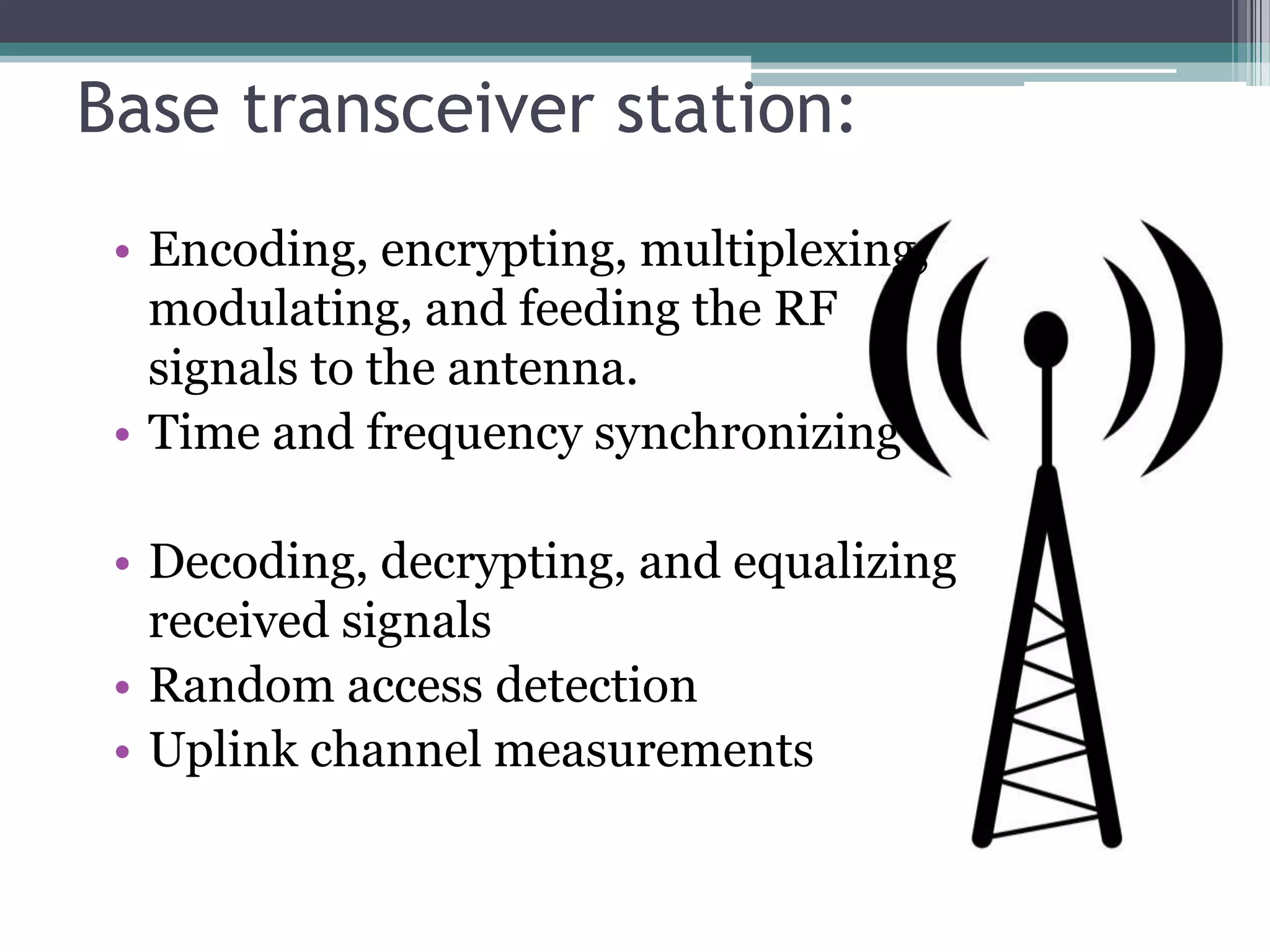
- Key aspects include the SIM card for user identification, base transceiver stations for radio signals, transcoding between speech formats, home and visitor location registers for subscriber data, and authentication/equipment databases.