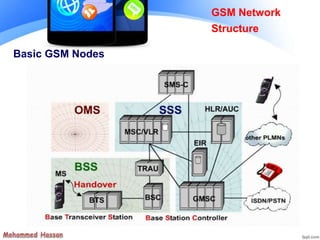
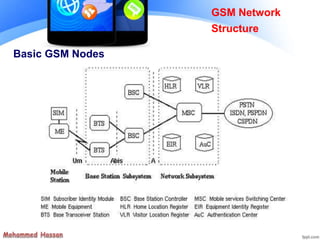
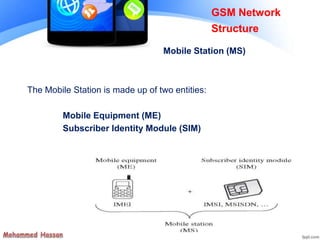
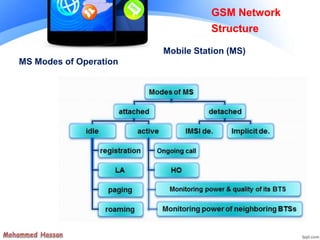
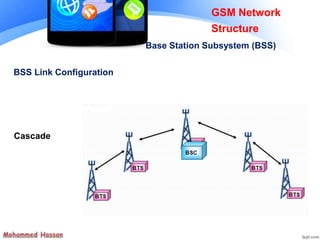
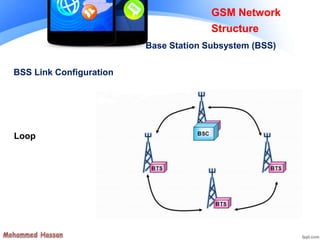
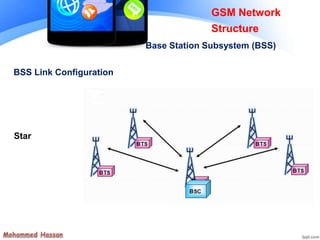
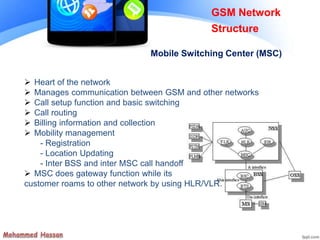
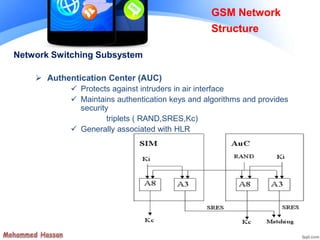
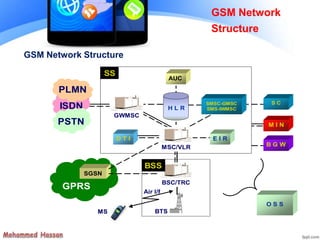
The document provides an overview of the Global System for Mobile (GSM) network structure. It describes the basic nodes that compose the GSM network including the mobile station, base station subsystem consisting of base transceiver stations and base station controllers, and the network switching subsystem containing elements like the mobile switching center, home location register, and visitor location register. It also outlines the services offered in GSM like teleservices, bearer services, and supplementary services.