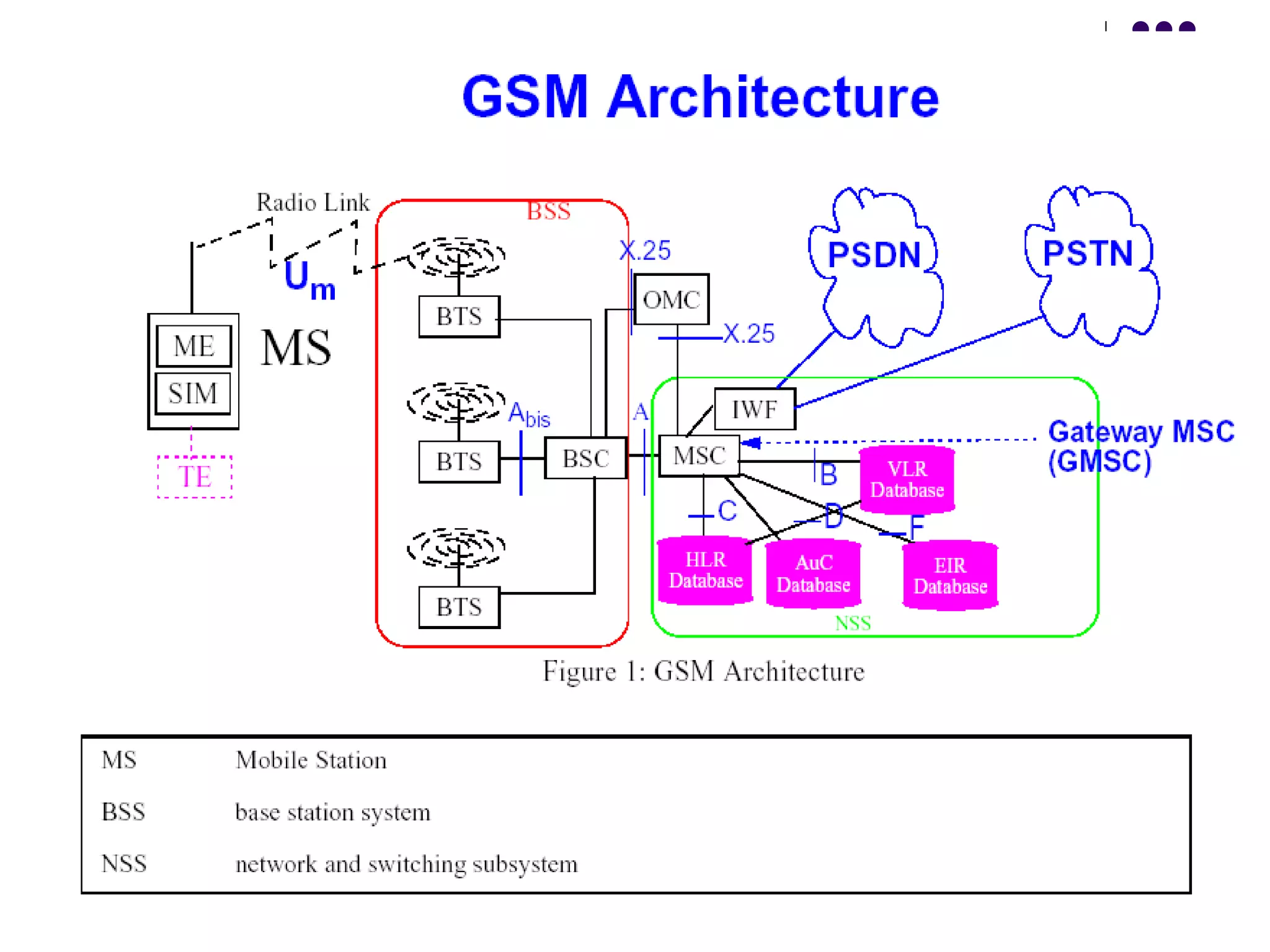
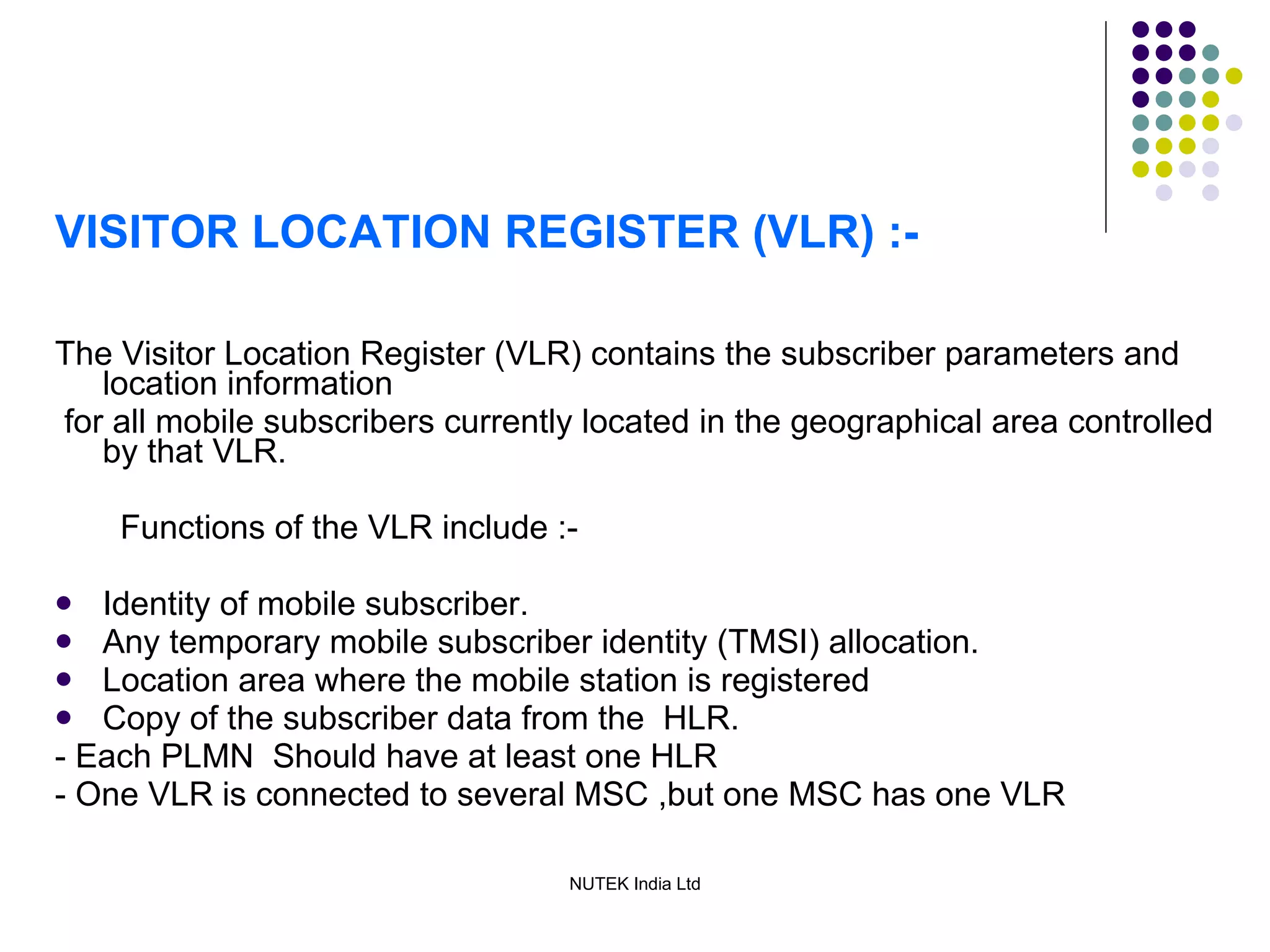
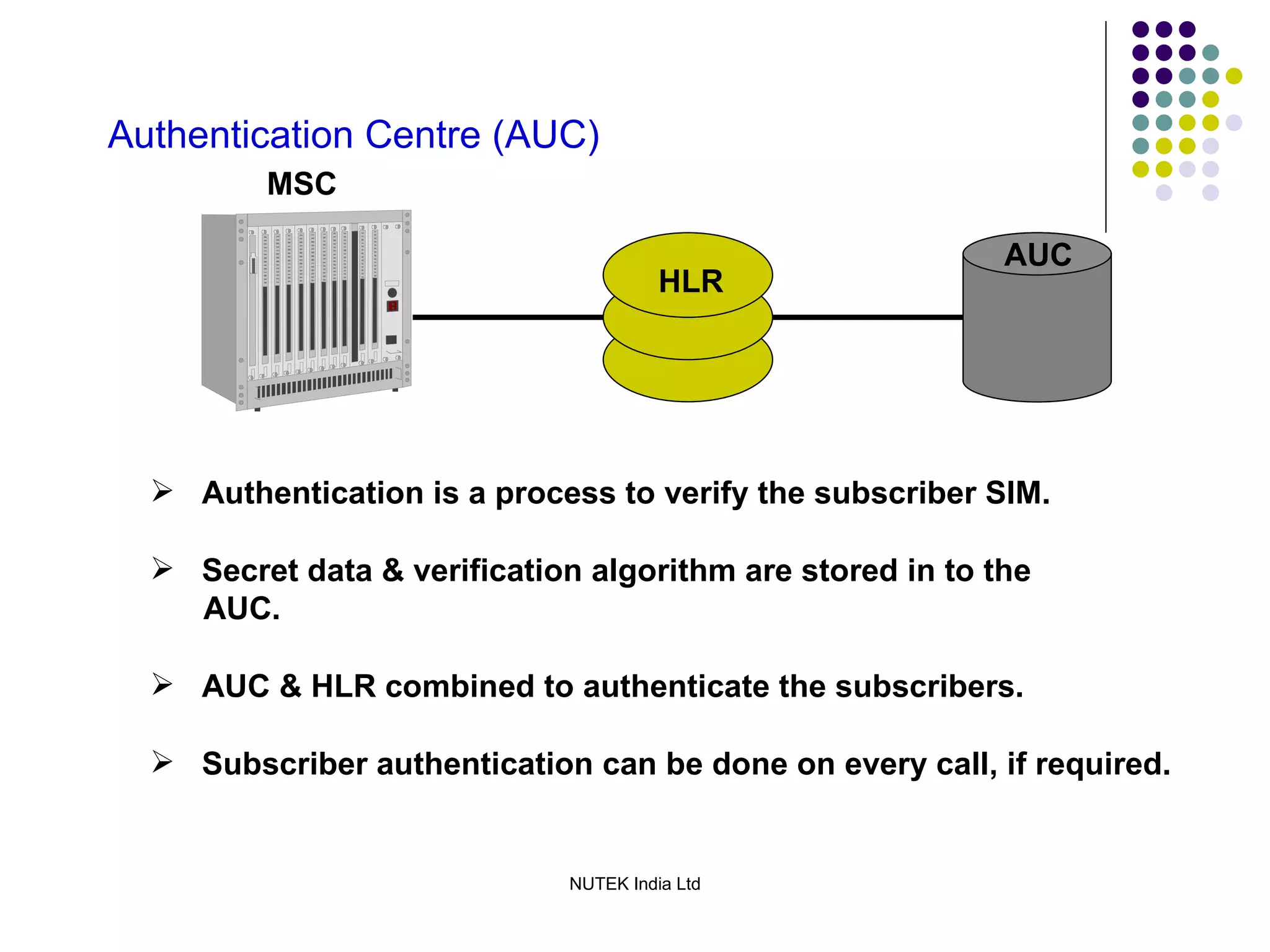
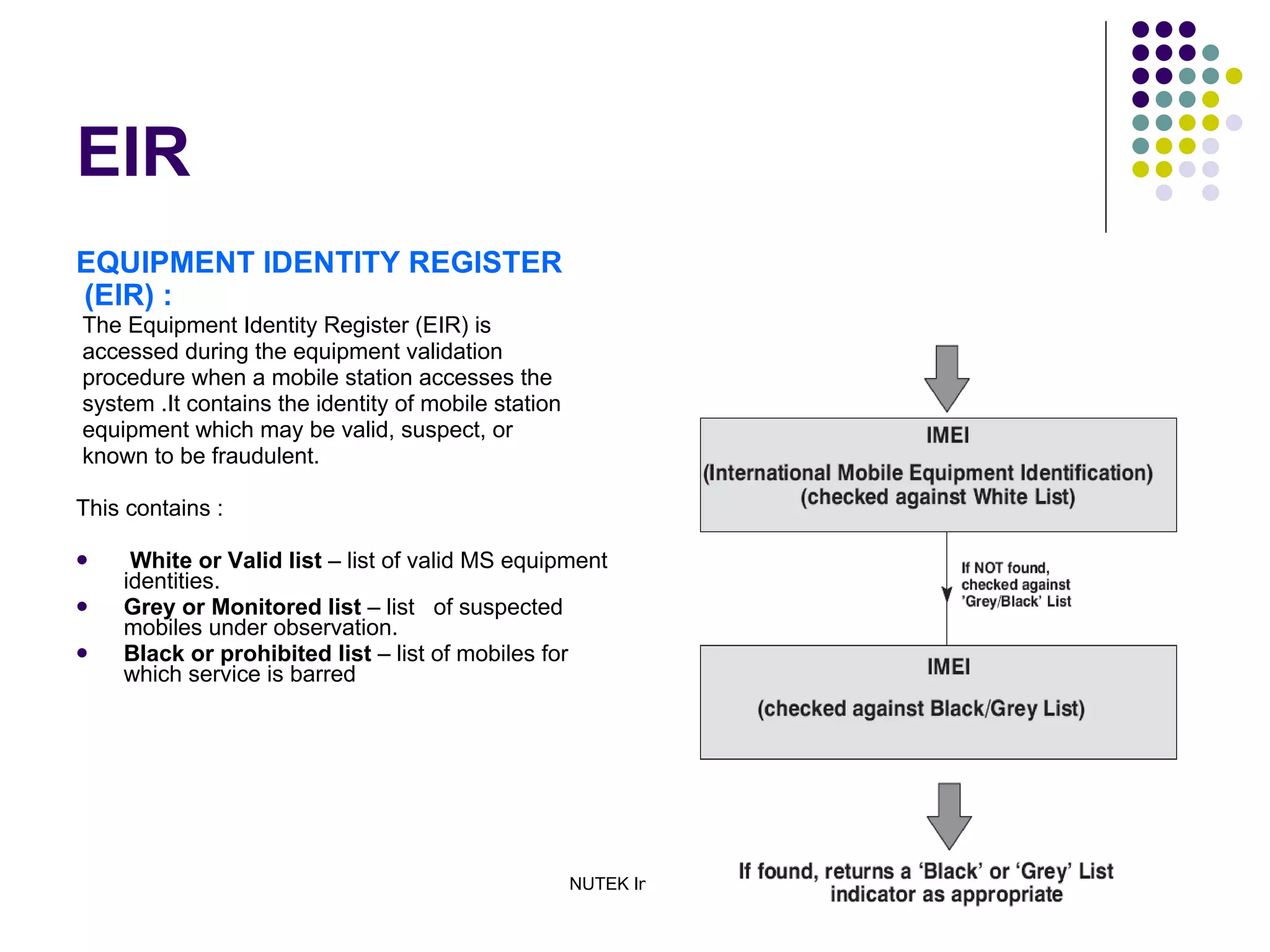
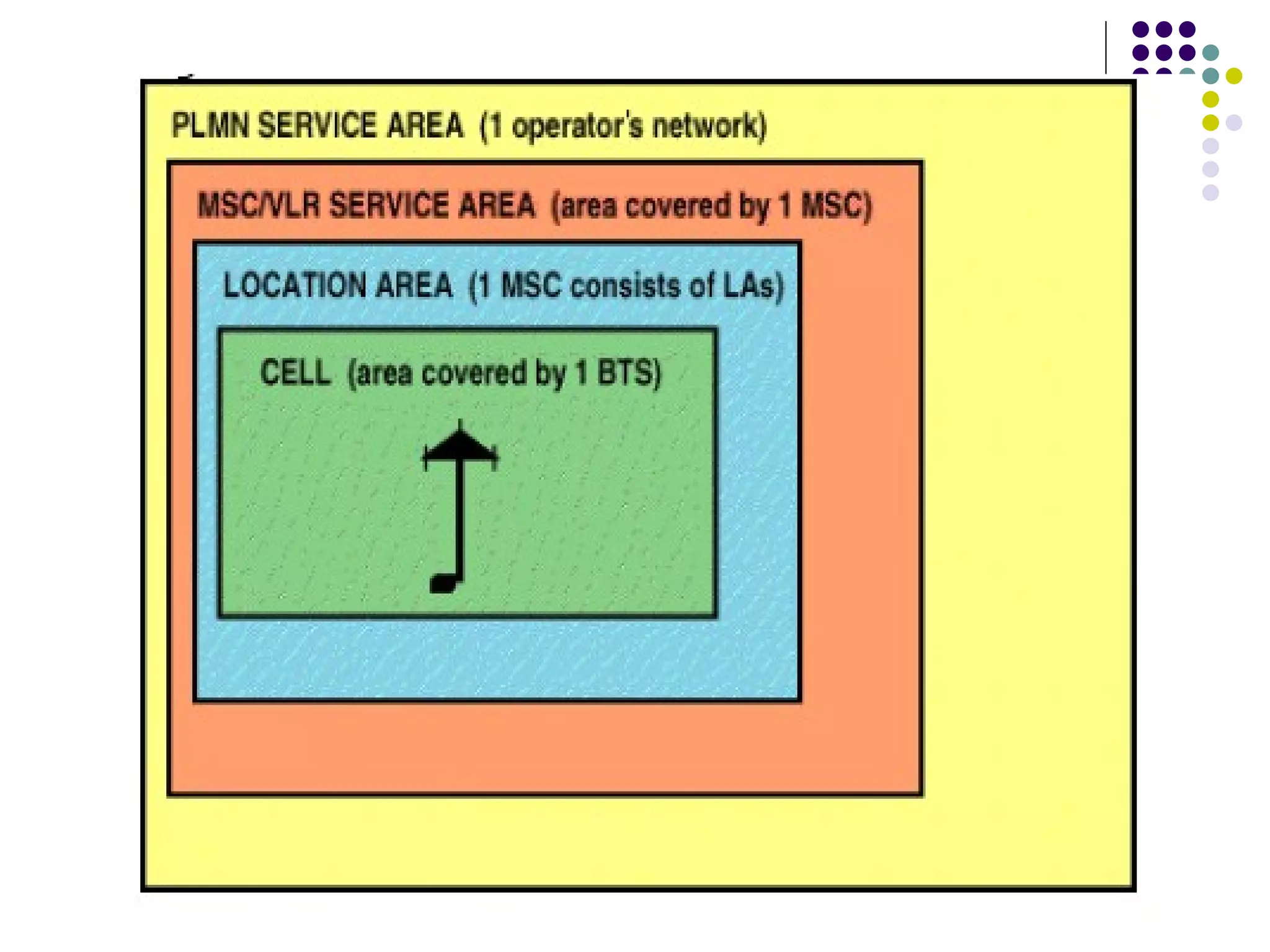
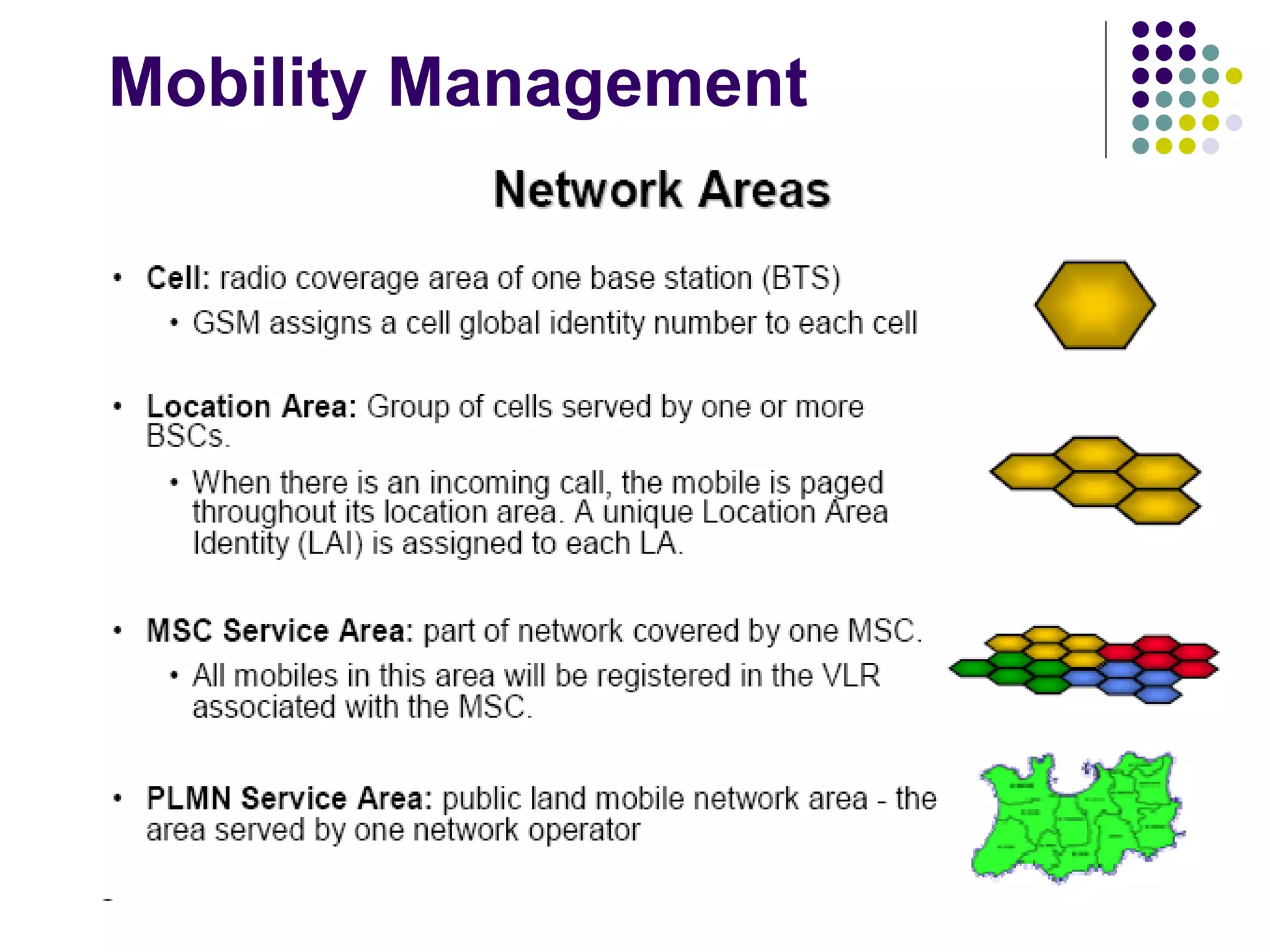
The mobile station consists of the mobile equipment and subscriber identity module (SIM) card, the base station system provides radio connectivity between mobile stations and switching equipment and includes base transceiver stations and base station controllers, and the core network components include the mobile switching center for call routing, home location register for subscriber data, visitor location register for temporary subscriber data, and equipment identity register for validating mobile equipment.