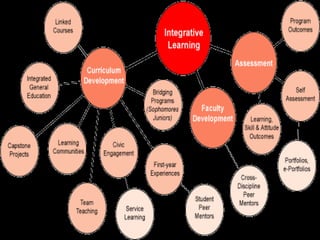
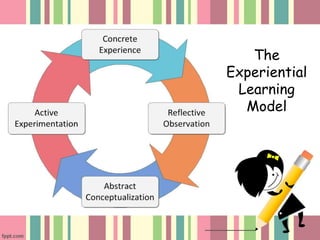
This document discusses principles of learning and techniques for curriculum development and managing learning. It covers three areas of learning principles: subjective principles like self-concept and past experience, and objective principles related to learning situations. Special learning techniques discussed include massed and distributed learning, feedback, and overlearning. Techniques for managing learning addressed include planning learning sequences, using feedback, taking an integrative approach, and using experiential learning. Guidelines are provided for curriculum developers to encourage inquiry, be democratic, accept differences, utilize research, minimize memorization and maximize discovery.