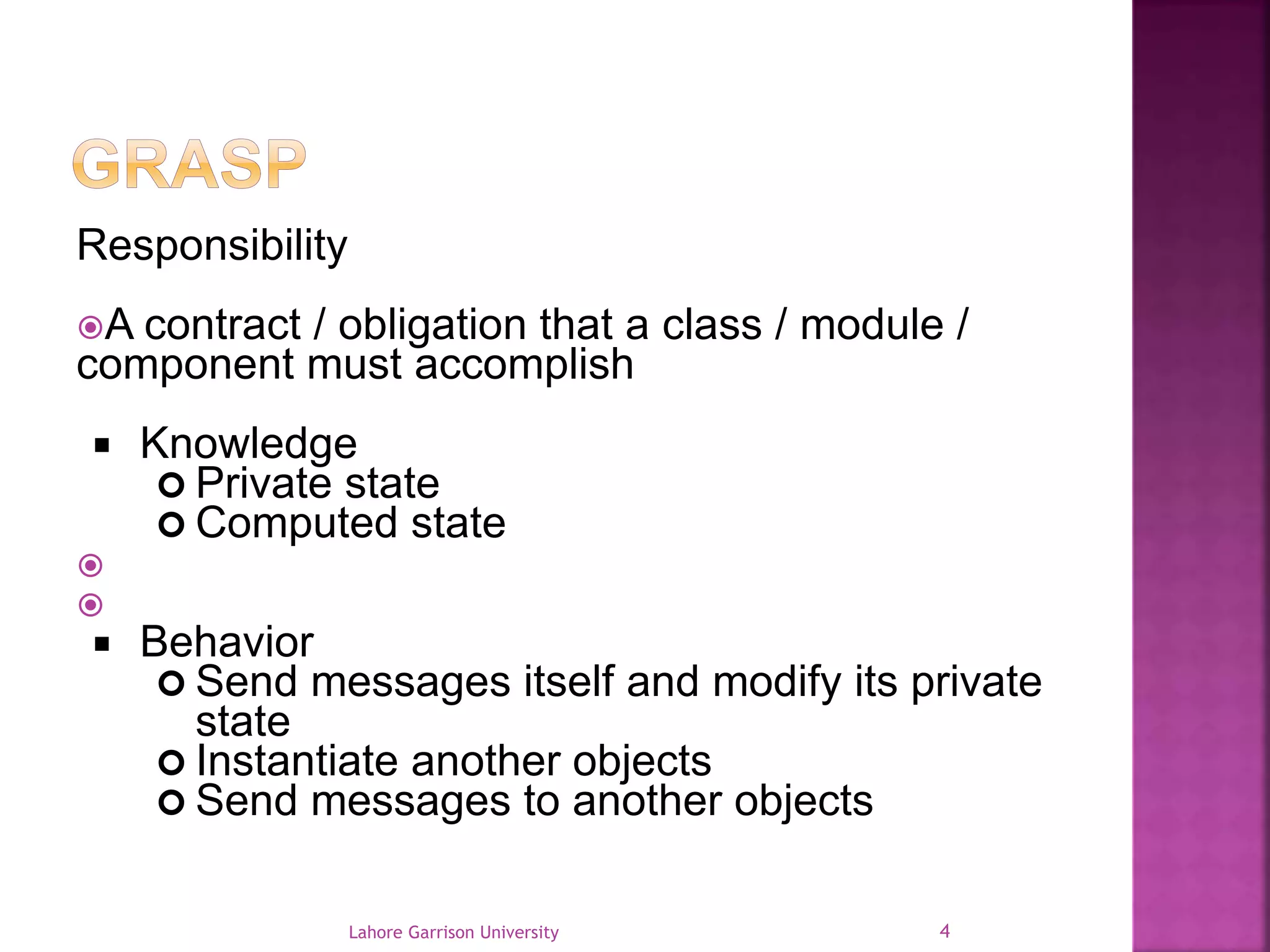
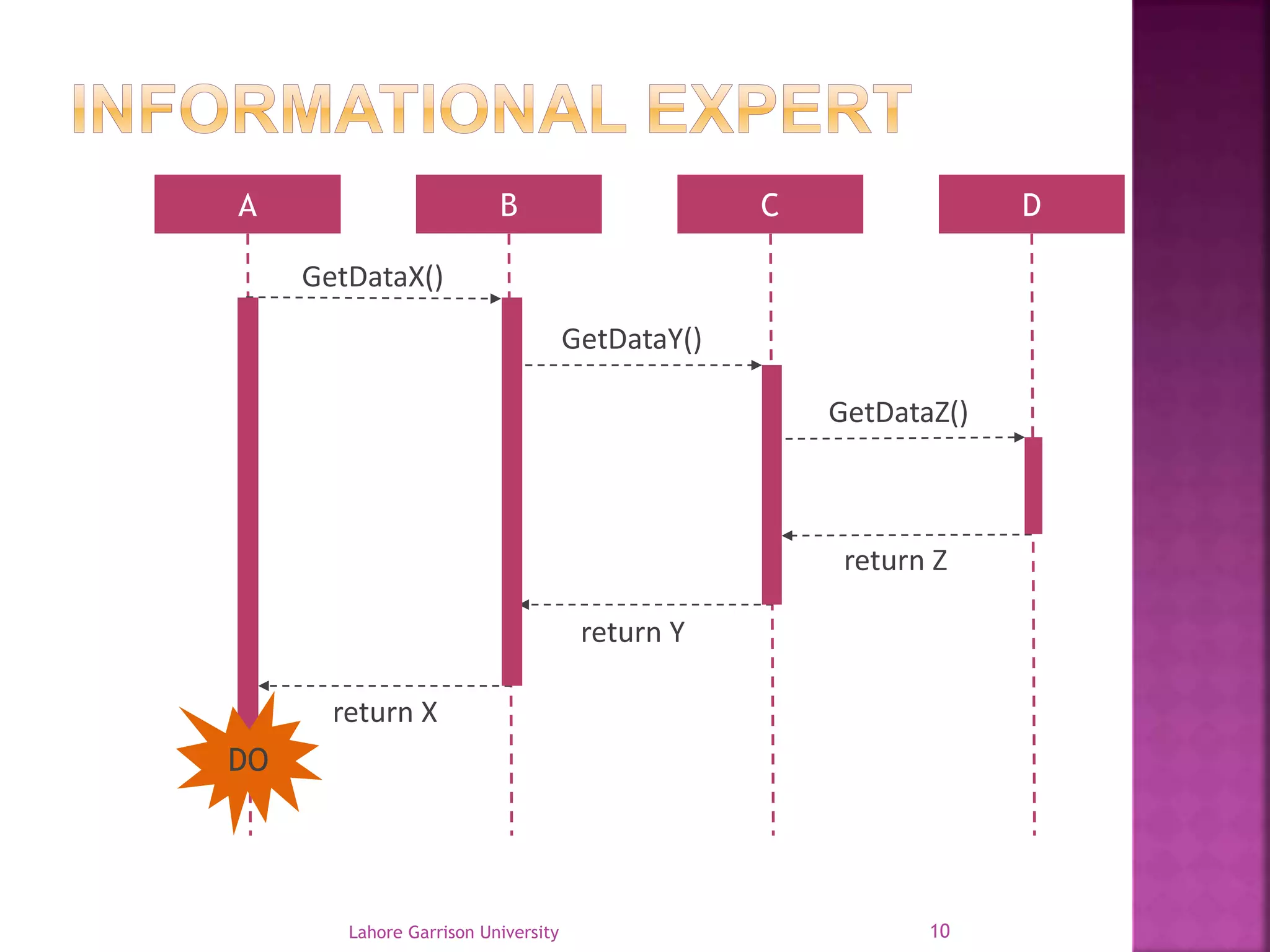
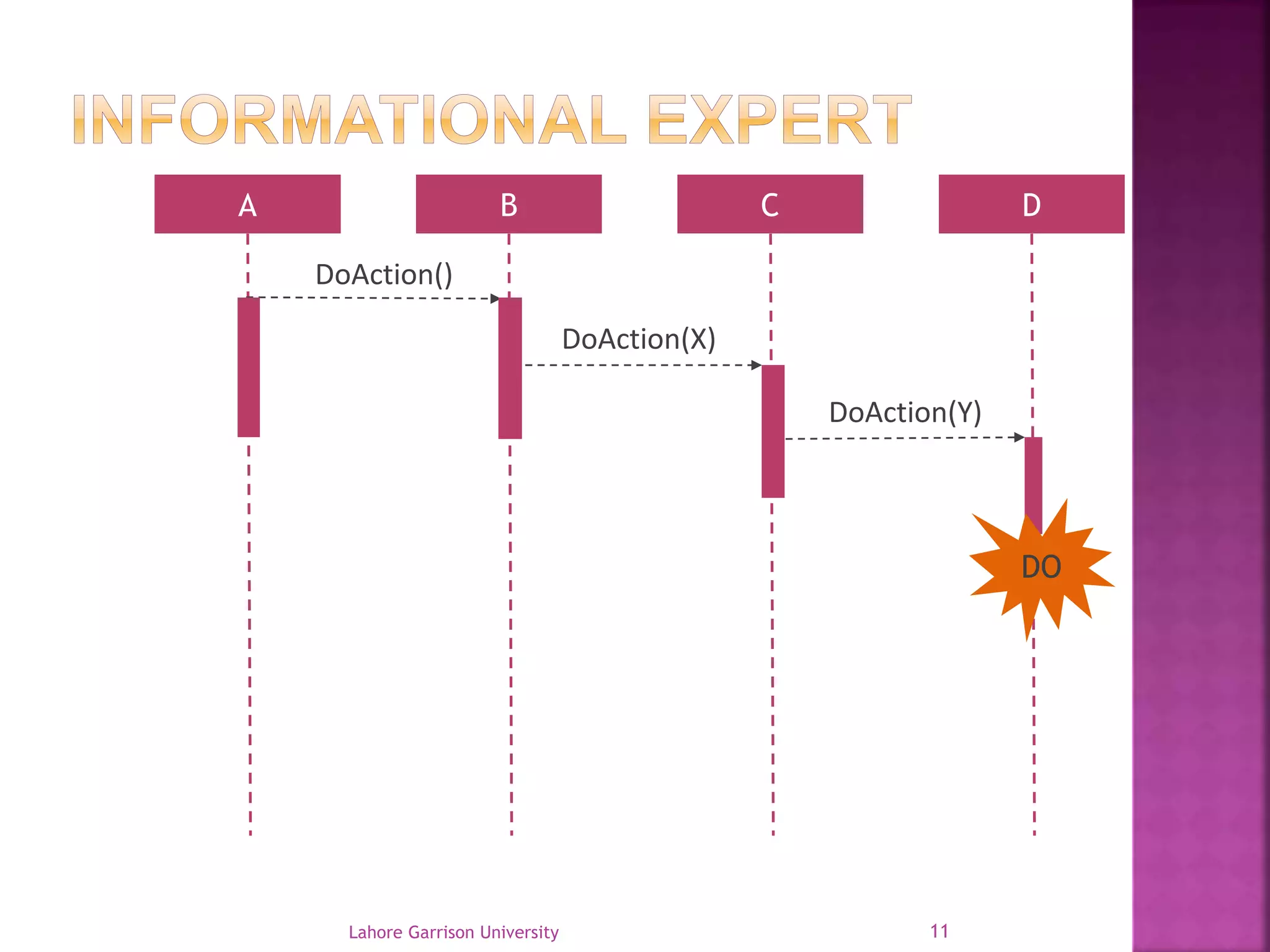
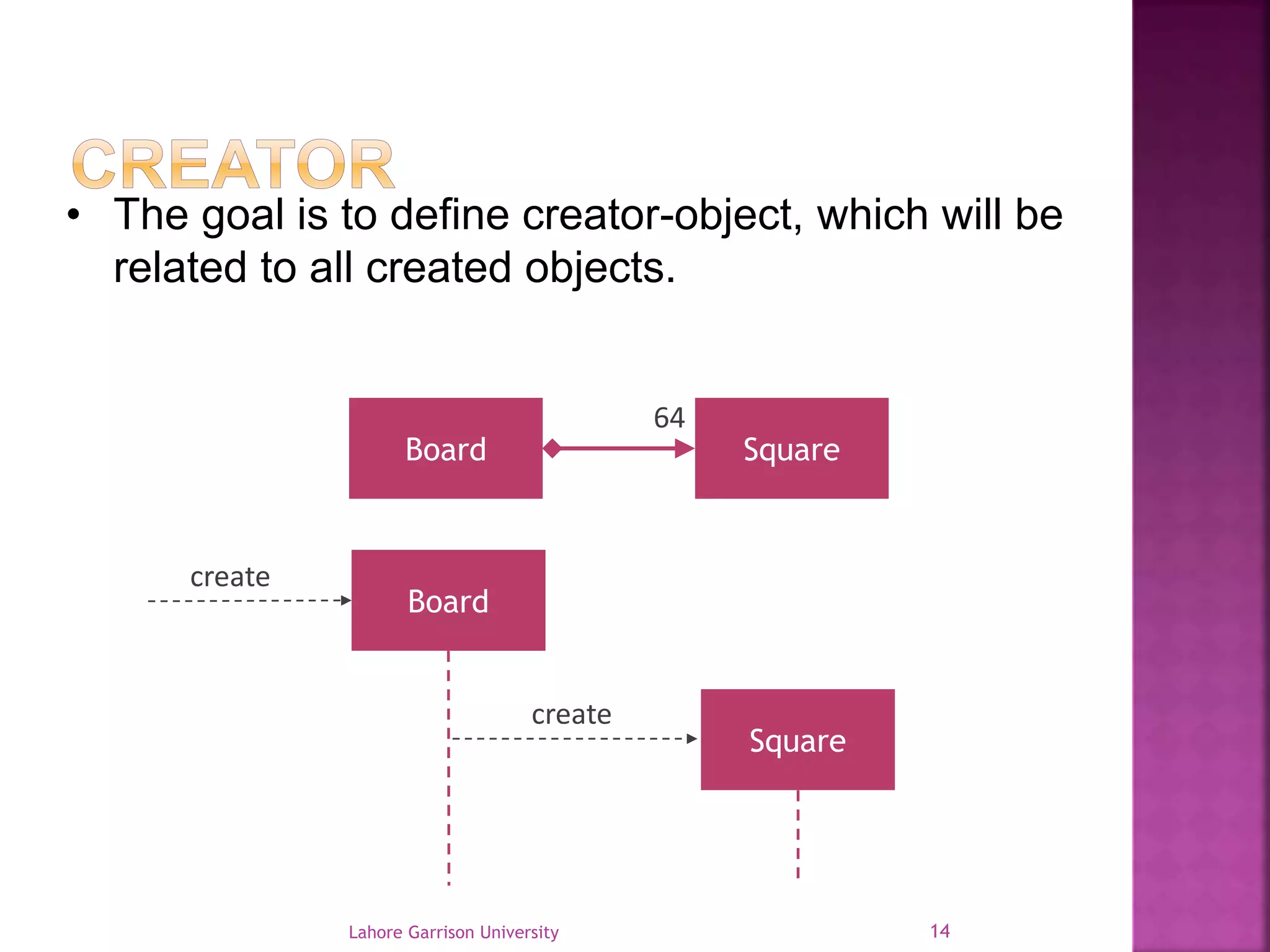
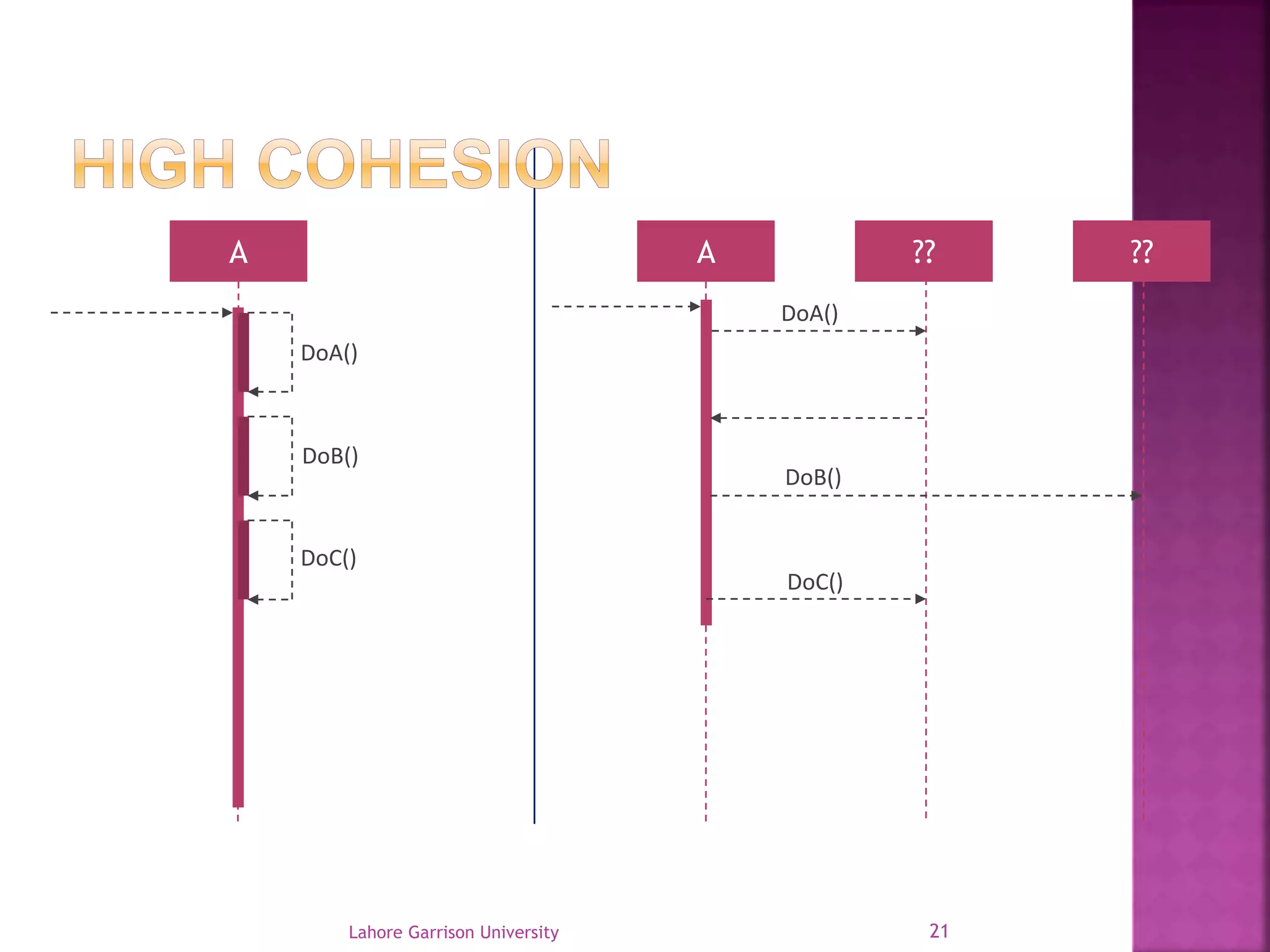
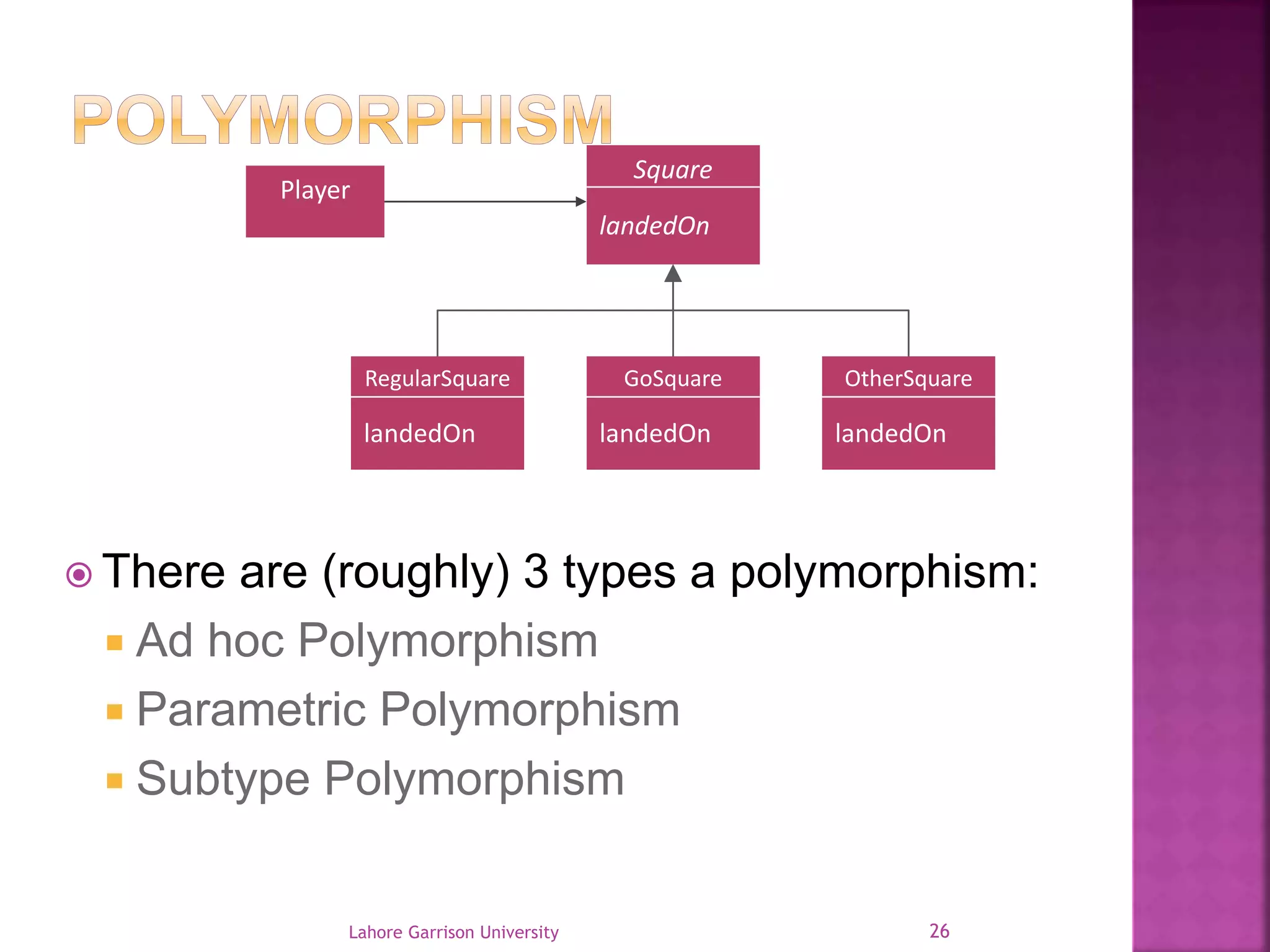
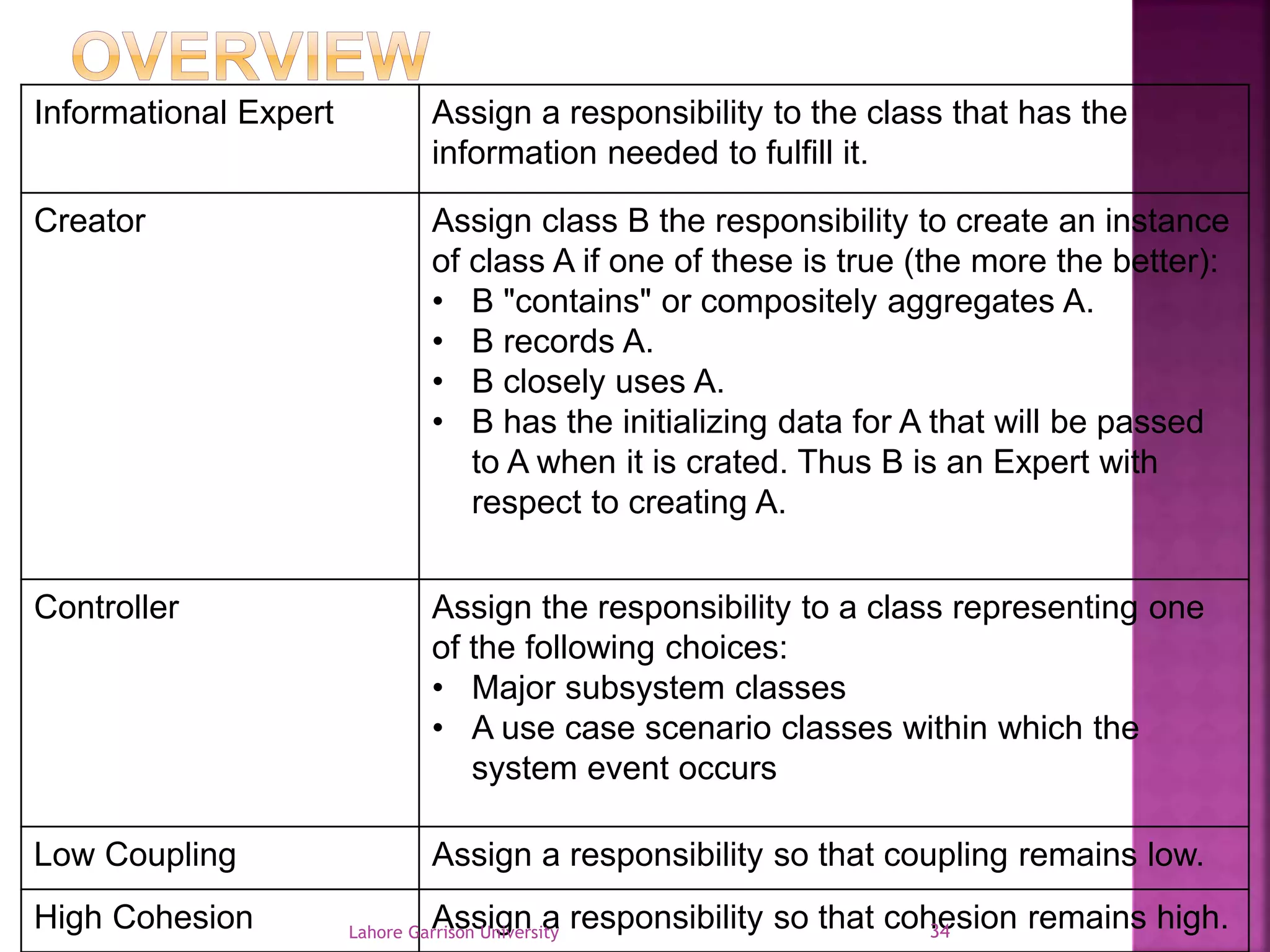
This document discusses the General Responsibility Assignment Software Patterns (GRASP) principles for object-oriented design. It begins with an introduction to GRASP and its goals of being a mental toolset for designing software. It then explains nine key GRASP design patterns - Informational Expert, Creator, Controller, Low Coupling, High Cohesion, Polymorphism, Pure Fabrication, Indirection, and Protected Variations. For each pattern, it provides a definition and example of how and when to apply the pattern when assigning responsibilities to classes. It concludes with references for further reading on GRASP patterns.