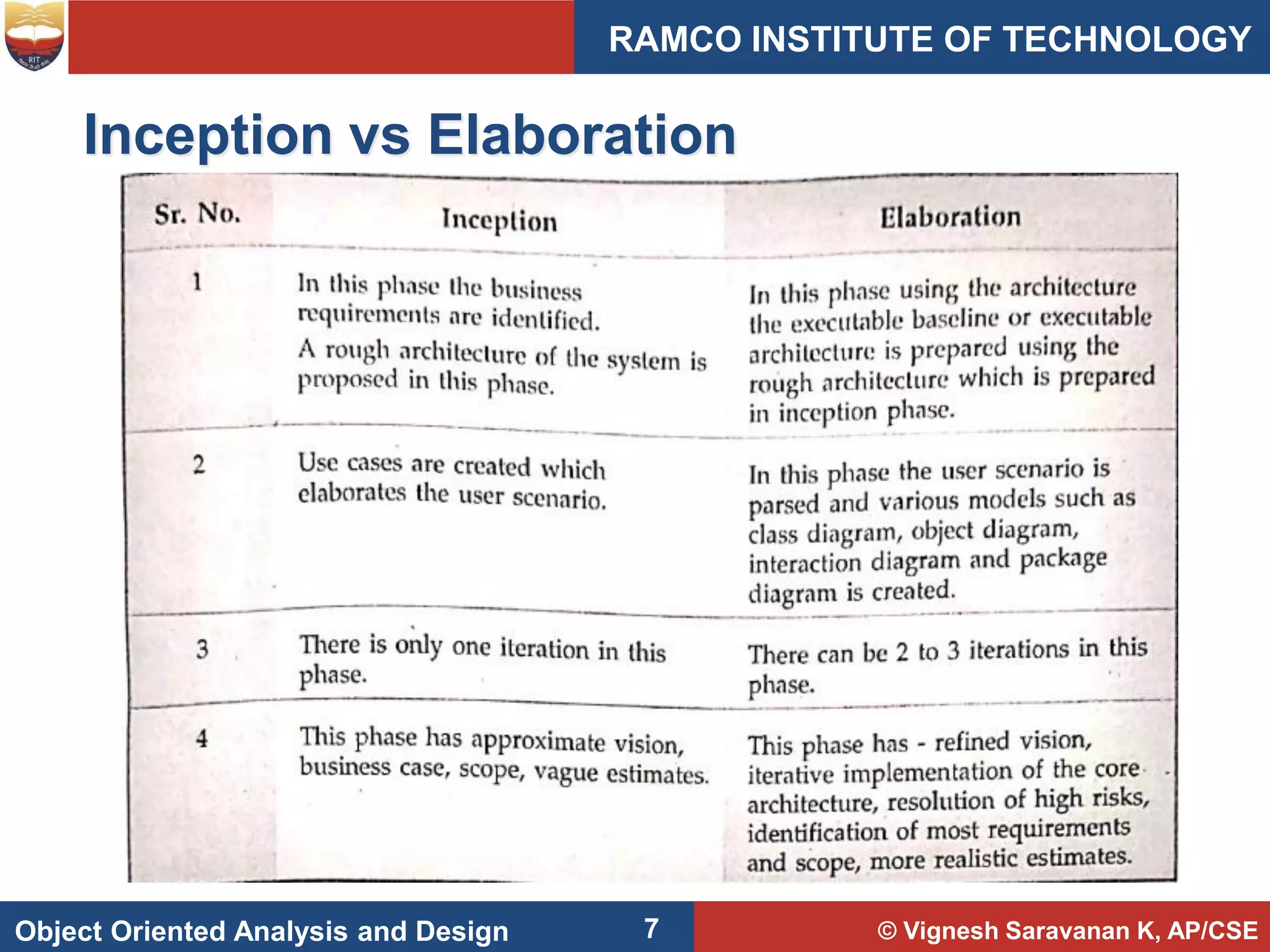
This document discusses object oriented analysis and design concepts including class diagrams, elaboration, and domain modeling. It describes how class diagrams show object types and relationships, and how elaboration refines requirements through iterative modeling. Elaboration builds the core architecture, resolves risks, and clarifies requirements over multiple iterations. A domain model visually represents conceptual classes and relationships in the problem domain.


![© Vignesh Saravanan K, AP/CSE
Object Oriented Analysis and Design
RAMCO INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
9
DOMAIN MODELS (cont.)
Domain models are also called as conceptual models. Domain models are
illustrated with a set of class diagrams
Domain objects or conceptual classes
Association between conceptual classes
Attributes of conceptual classes
A domain model shows real-situation conceptual classes and not software
classes. [such as Java or C++ classes]
So a domain model should probably avoid
Software artifacts like window or database
Methods and responsibilities.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit-2-lecture-11-elaborationanddomainmodel-220106094814/75/Elaboration-and-domain-model-9-2048.jpg)
