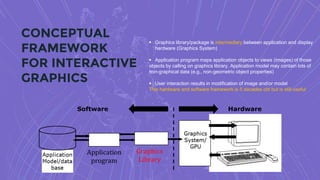
This document provides an introduction to computer graphics, including definitions, history, and modern developments. It defines computer graphics as pictures and films created using computers, usually referring to computer-generated image data. [It then summarizes that graphics programming studies methods for digitally synthesizing and manipulating visual content.] The document goes on to discuss what computer graphics and interactive computer graphics are, provide a brief history of interactive graphics systems including Sketchpad, and outline key enabling technologies for modern computer graphics like GPUs, input devices, display hardware, software improvements, and conceptual frameworks.