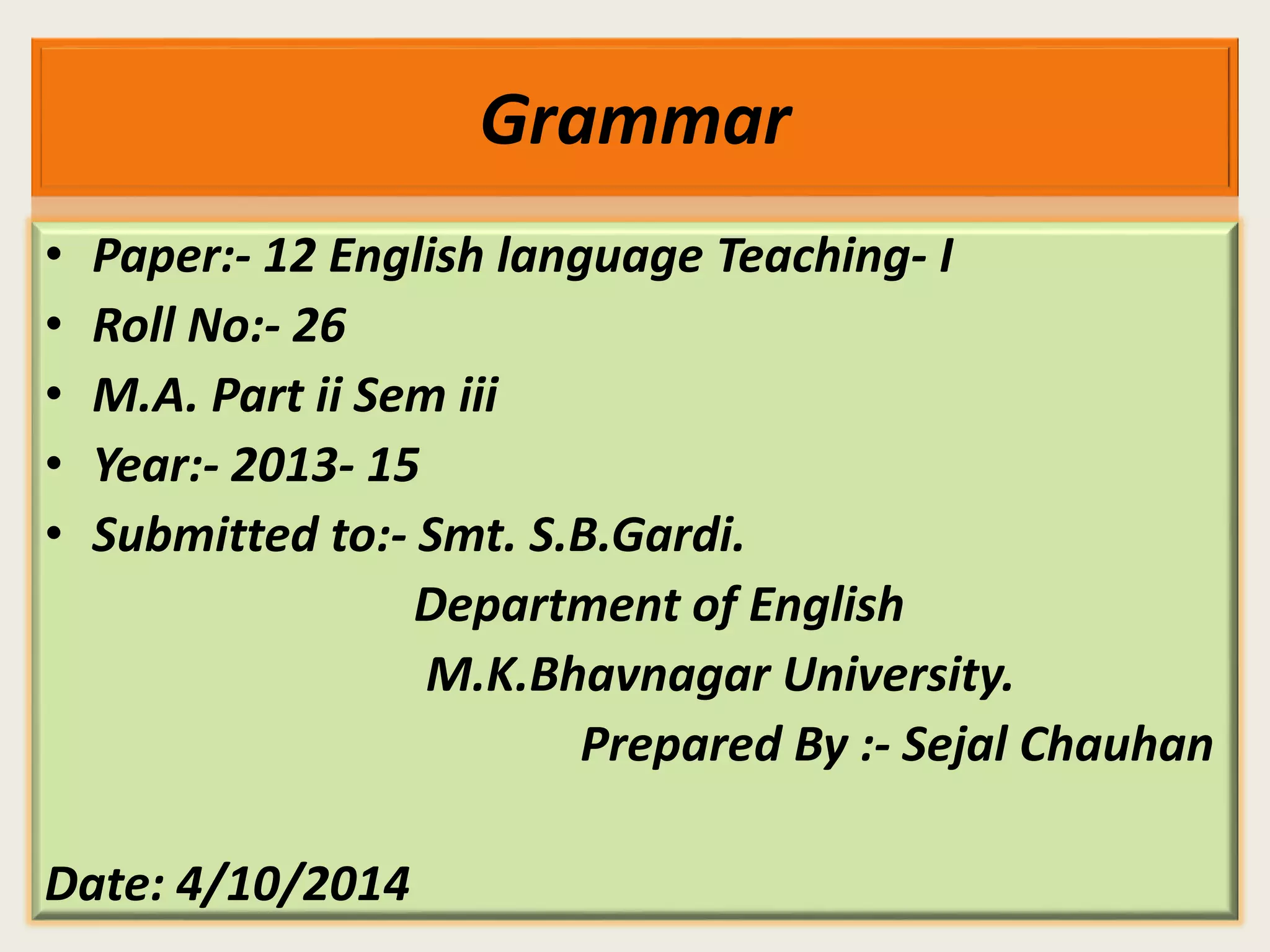
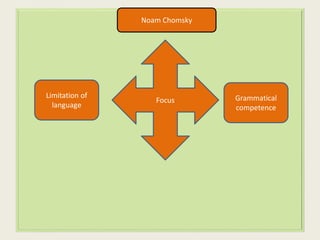
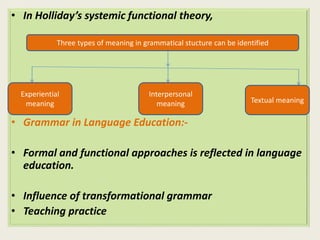
This document discusses different approaches to grammar including formal grammar, functional grammar, and corpus linguistics. It addresses how grammar is studied from the perspectives of morphology, syntax, phonology, semantics and pragmatics. The document also contrasts Chomsky's focus on grammatical competence versus functional grammarians' emphasis on language use and communicative purpose. It notes debates around teaching grammar for communication and the role of focus on form, interaction, and discourse.