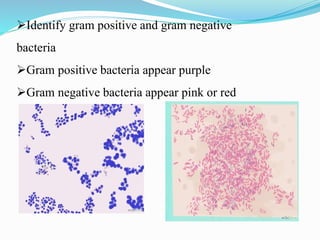
Hans Christian Gram developed a staining technique in 1884 that allows differentiation of bacteria into two types - Gram positive and Gram negative. The Gram staining technique involves staining a bacterial sample with crystal violet, adding iodine to fix the stain, washing with decolorizer such as alcohol or acetone, and counterstaining with safranin. Gram positive bacteria will appear purple due to retention of crystal violet stain, while Gram negative bacteria will appear pink from the counterstain. This simple staining method provides vital information for identifying and diagnosing bacterial infections.