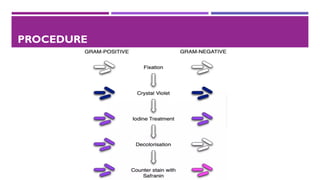
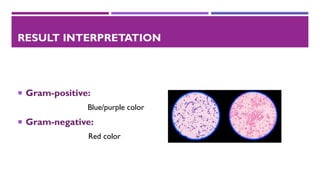
The document outlines the gram staining technique, which differentiates bacteria into gram-positive and gram-negative based on their cell wall composition. Developed by Hans Christian Gram in 1884, the method utilizes specific reagents such as crystal violet, iodine, and safranin to achieve color differentiation. Applications include diagnosing diseases and selecting culture media appropriate for the bacterial type.