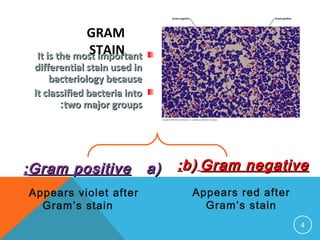
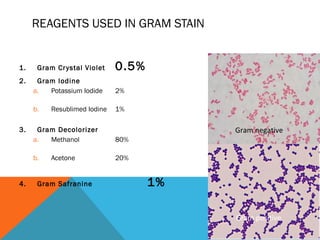
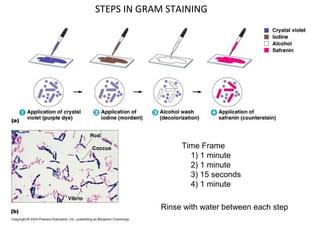
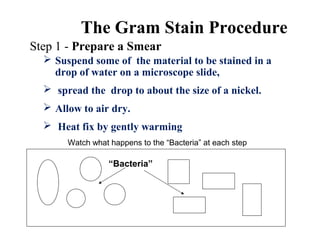
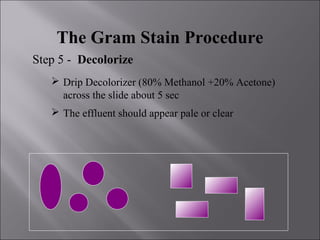
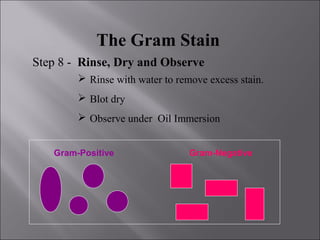
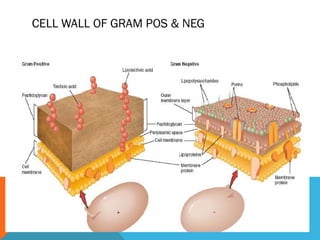
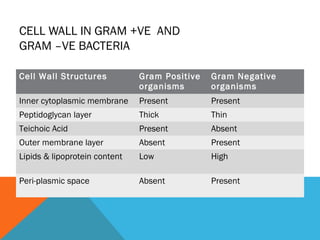
This document discusses Gram staining of bacteria. Gram staining is an important differential staining technique that classifies bacteria into two groups - Gram positive and Gram negative - based on their cell wall structure. Gram positive bacteria appear violet after Gram staining due to their thick peptidoglycan layer retaining the crystal violet dye, while Gram negative bacteria appear red as their thinner peptidoglycan layer is decolorized, revealing the safranin counterstain. The document outlines the reagents, steps, and expected colors of the Gram staining procedure and compares the cell wall structures of Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria.