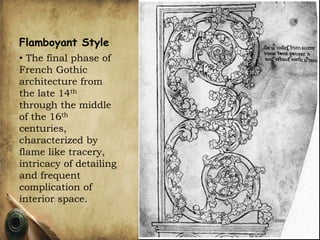
Gothic architecture, originating in 12th-century France, includes three phases: early French, rayonnant, and flamboyant styles, focusing on features like pointed arches and intricate tracery. English gothic architecture has three phases as well: early English, decorated, and perpendicular styles, characterized by different window types and ornate stonework. The Gothic revival movement arose in the late 18th century, emphasizing the revival of Gothic forms, with notable examples like St. Pancras Railway Station showcasing eclectic influences and industrial advances.




![Abbé Suger
(French: [syʒe]; c. 1081 – 13
January 1151)
was one of the
last French abbot-statesmen,
a historian, and the
influential first patron
of Gothic architecture.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gothicstyles-160827110748/85/Gothic-styles-5-320.jpg)