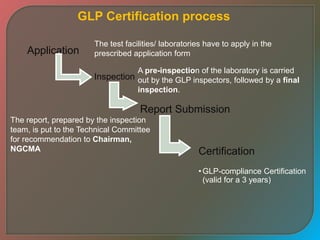
Good Laboratory Practices (GLP) are quality standards for designing, conducting, recording, and reporting non-clinical research studies that generate data as safety and efficacy information for health or environmental regulations. GLP was developed to increase quality and validity of non-clinical safety studies by defining roles, responsibilities, standard operating procedures, and documentation requirements. Key elements of GLP include management and quality assurance systems, personnel qualifications, facility organization and maintenance, test and control article characterization, standard operating procedures, documentation, and reporting.