REFLEX ( Physiology)
- 1. REFLEX Dr. Anita Choudhary Professor & HOD Physiology Department R.D.Gardi Medical College Ujjain
- 2. DEFINATION Reflex is an involuntary response to a stimulus Depends on integrity of reflex arc Sensory impulse CNS Motor effect 4/11/2020Dr. Anita Choudhary
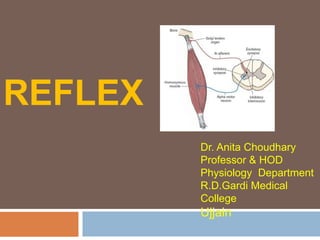
- 3. Components of reflex arc Afferent limb Receptor Sensory nerve Center Efferent Limb Motor nerve Efector organ 4/11/2020Dr. Anita Choudhary
- 4. Afferent limb Carry sensory input from receptor to the centre. The afferent neuron enter CNS via dorsal root or cranial nerves and have their cell bodies in dorsal root ganglia 4/11/2020Dr. Anita Choudhary
- 5. CENTER Part of CNS( spinal cord or brain) Afferent limb ends Synapse directly with efferent limb Or via interneuron 4/11/2020Dr. Anita Choudhary
- 6. EFFERENT LIMB Consist of - Motor nerve – transmit motor impulse from the centre to effector organ Effector organ – in form of muscle or gland which show response to the stimulus 4/11/2020Dr. Anita Choudhary
- 7. Classification of Reflexes Depending upon No. of synapse Anatomical classification Physiological classification Clinical classification Inborn/ acquired 4/11/2020Dr. Anita Choudhary
- 8. Depending upon No. of synapse Asynaptic Monosynaptic Disynaptic Polysynaptic 4/11/2020Dr. Anita Choudhary
- 9. ASYNAPTIC REFLEX No synapse between afferent & efferent neuron Also known as axon reflex arc Not a true reflex arc 4/11/2020Dr. Anita Choudhary
- 10. MONOSYNAPTIC REFLEX One synapse present between afferent & efferent neuron E.g. Stretch reflexes Biceps Triceps knee 4/11/2020Dr. Anita Choudhary
- 11. DISYNAPTIC REFLEXES One interneuron is placed between present between afferent & efferent neuron E.g. Inverse stretch reflex or golgi tendon reflex 4/11/2020Dr. Anita Choudhary
- 12. POLYSYNAPTIC REFLEX More than one interneuron's present E.g. 1. Withdrawal Reflex 2. Crossed flexor reflex 3. Crossed extensor reflex 4/11/2020Dr. Anita Choudhary
- 14. Anatomical Classification Depending upon the location of reflex arc centre .. 1. Cortical reflexes 2. Cerebellar reflexes 3. Midbrain reflexes 4. Bulbar or medullary reflexes 5. Spinal reflexes 4/11/2020Dr. Anita Choudhary
- 15. ANATOMICAL CLASSIFICATION (location of reflex arc center) Cortical reflex: center in cerebral cortex Cerebellar reflexes : in cerebellum Mid brain reflexes : in mid brain Bulbar /medullary reflex: in Medula oblongata Spinal reflexes: in spinal cord 4/11/2020Dr. Anita Choudhary
- 16. Clinical classification Clinically reflexes are classified into- Superficial Deep Visceral Pathological reflexes 4/11/2020Dr. Anita Choudhary
- 17. CLINICAL CLASSIFICATION Superficial reflex – conjuctival, corneal Deep reflex- tendon reflexes Visceral reflex eg.- micturation reflex Pathological reflex eg- Babinski sign, mass reflex, clonus, pendular movement 4/11/2020Dr. Anita Choudhary
- 18. Physiological Classification Flexor reflexes. Extensor reflexes. a. Flexor reflexes occur in response to pain b. Extensor reflexes( antigravity reflexes) – all stretch reflexes are extensor reflexes. These are the basis of muscle tone & posture 4/11/2020Dr. Anita Choudhary
- 19. PHYSIOLOGICAL CLASSIFICATION Flexor Reflexes – Responds to painful stimuli Flexion of joints Also called withdrawal reflex 4/11/2020Dr. Anita Choudhary
- 20. Extensor reflex – Stretch reflex …….(with muscle tone ) Basis of muscle tone and posture Also called anti gravity reflex 4/11/2020Dr. Anita Choudhary
- 21. Spinal cord reflexes According to the receptor from which they originate Muscle reflexes- Stretch reflex - Golgi-tendon reflex Cutaneous reflexes- withdrawal reflex 4/11/2020Dr. Anita Choudhary
- 22. Depending upon the segment involved Segmental Reflexes: efferent neuron begins in the same segment of spinal cord where afferent neuron ends Intersegmental Reflexes: afferent neuron end in one segment and efferent neuron begins in other segment Suprasegmental Reflex: center lies above the spinal cord 4/11/2020Dr. Anita Choudhary
- 23. INBORN/ ACQUIRED CLASSIFICATION INBORN OR UNCONDITIONAL REFLEXES Present since birth No learning/ training required Eg: salivation when object in mouth 4/11/2020Dr. Anita Choudhary
- 24. Acquired or Conditional Reflex Develop after birth Learning & training required Eg- salivation by sight, smell and thought 4/11/2020Dr. Anita Choudhary
- 26. Monosynaptic reflex( Stretch reflex) When a skeletal muscle with intact nerve supply is stretched ,it contracts Stimulus: stretch to the muscle Receptor : Muscle spindle NT: Glutamic acid( at central synapse) Reaction Time: application of stimulus and the response Central delay: 0.6 to 0.9 msec (to traverse the spinal cord) 4/11/2020Dr. Anita Choudhary
- 27. 2. INVERSE STRETCH REFLEX (disynaptic reflex) Also called Golgi tendon reflex . Receptor involved – Golgi tendon organs Located in tendons & musculoapeurotic junction Placed in series Supplied by Ib type sensory nerve When muscle contract it stretched 4/11/2020Dr. Anita Choudhary
- 28. Receptor – Golgi tendon organ Afferent – Ib myelinated nerve fibers Centre- spinal cord , end in inhibitory interneuron that in turn end directly on the motor neurons Efferent – alpha motor neurons to muscle fiber 4/11/2020Dr. Anita Choudhary
- 30. Pathway & activity of reflex Contraction of muscle Increase muscle tension Golgi tendon detect tension Send impulse through Ib fibre Enter spinal cord through dorsal root 4/11/2020Dr. Anita Choudhary
- 31. Cont…. In spinal cord stimulate inhibitory interneuron Release inhibitory mediator glycine(IPSP) Inhibit ᾳ motor neuron Relaxation of muscle that was originally contracted 4/11/2020Dr. Anita Choudhary
- 32. Function of Golgi tendon reflex Protective function: reflexily inhibit muscle contraction Regulation of tension during normal muscle activity: 4/11/2020Dr. Anita Choudhary
- 33. Role of gamma motor neuron Stretching of muscle Increase firing rate of Ia fibres Increase ᾳ motor neuron activity Reflex contraction of muscle 4/11/2020Dr. Anita Choudhary
- 34. Cont… Contraction of extrafusal fiber Makes muscle spindle slack Decrease firing rate of Ia fibers (Unloading of muscle spindle) Once it occur CNS will not receiving the rate & extend of muscle shortening 4/11/2020Dr. Anita Choudhary
- 35. Higher control of stretch reflex Facilitator y ↑ϒ-motor neuron discharge Inhibitory ↓ ϒ motor neuron discharge 4/11/2020Dr. Anita Choudhary
- 36. 3. Withdrawal reflex ( polysynaptic) Definition :Also known as flexers reflex, Is an cutaneous reflex in response to painful stimuli Receptors: nociceptors in free nerve endings of Aδ & C fibres Pathway : As it is poly synaptic reflex consisting of following pathway: 4/11/2020Dr. Anita Choudhary
- 37. Withdrawal reflex Also known as flexor reflex Cutaneous reflex Occur in response of painful stimuli Characterized by removal of body parts from the region 4/11/2020Dr. Anita Choudhary
- 38. Reflex arc of withdrawal reflex Pain fibers carry impulse Enter spinal cord Synapse with many interneuron's A B C 4/11/2020Dr. Anita Choudhary
- 39. A : projects on ᾳ- motor neuron on same side , that stimulate the flexers cause withdrawal of limb. B: forms inhibitory pathway & : projects on ᾳ- motor neuron supplying the extensors on same side brings their relaxation. 4/11/2020Dr. Anita Choudhary
- 40. C : some of IN cross to opposite side of spinal cord end on ᾳ- motor neuron supplying the extensors of contralateral side – extension of opposite limb Crossed Extensor Response(2 limb response) 4/11/2020Dr. Anita Choudhary
- 41. Flexor Response Painful stimuli Contraction of flexors & Inhibition of extensors Leading to Flexion of stimulated limb & its withdrawal from painful stimuli 4/11/2020Dr. Anita Choudhary
- 42. FUNCTION OF WITHDRAWAL REFLEX When associated with crossed extensor reflex it helps to support the body and regulate the posture 4/11/2020Dr. Anita Choudhary
- 43. Properties of reflexes 1.Adequate stimulus 2.Delay - Synaptic delay, minimum in mono synaptic reflexes 3 .One way conduction - Bell Magendie law 4/11/2020Dr. Anita Choudhary
- 44. 4. Bell Magendie law Impulse Receptor Center Effector organ 4/11/2020Dr. Anita Choudhary
- 45. 5.Recruitment Stimulus of constant strength applied for long time Progressive increase in response Increase activation of motor neurons 4/11/2020Dr. Anita Choudhary
- 46. Application of strong stimulus Impulse spread to neighboring neurons through collaterals or interneurons Gives wider response 4/11/2020Dr. Anita Choudhary
- 47. 6.After discharge Reflex action is elicited continuously Stop stimulation Even then reflex response may continue ( internucial neuron continue to transmit signals to center) 4/11/2020Dr. Anita Choudhary
- 48. 7.Final Common Pathway All excitatory / Inhibitory neuronal influences Funnel through ᾳ Motor neuron Affect muscular contraction + stimulation of ᾳ Motor neuron – contraction - ve stimulation of ᾳ Motor neuron – relaxation 4/11/2020Dr. Anita Choudhary
- 49. 8.Rebound Phenomenon Inhibition of reflex activity for some time Once inhibition is over Reflex activity reappear and become more powerful 4/11/2020Dr. Anita Choudhary
- 50. cont… 4/11/2020Dr. Anita Choudhary 9.Summation 10. Inhibition 11. Occlusion 12. Habituation : reflex response is stereotyped but with experience it can be modified this is habi… 13. Senstization : when stimulted repeatedly decrease response of target neuron
- 51. THANK YOU 4/11/2020Dr. Anita Choudhary