The document summarizes key aspects of myotatic reflexes and muscle spindles. It describes:
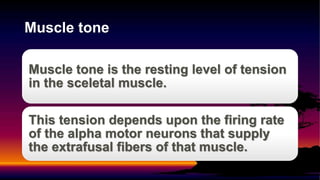
1) Muscle spindles contain intrafusal muscle fibers that are monitored by Ia and II afferent axons. They provide proprioceptive feedback on muscle length and tension.
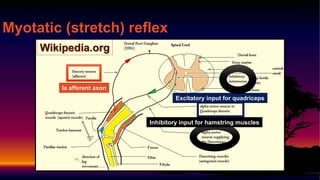
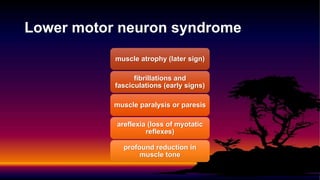
2) The myotatic reflex maintains muscle length through a monosynaptic connection between Ia afferents and motor neurons. It causes muscle contraction when the muscle is stretched.
3) Golgi tendon organs sense muscle tension and inhibit motor neurons through Ib interneurons, reducing muscle tension. They provide feedback different from muscle spindles.