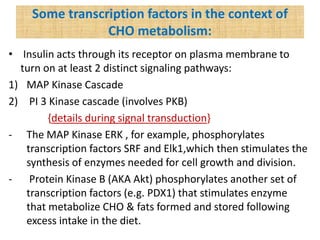
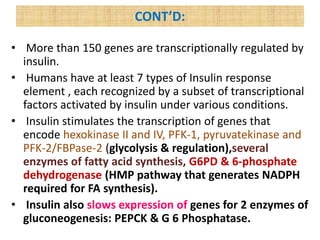
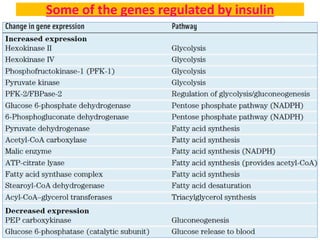
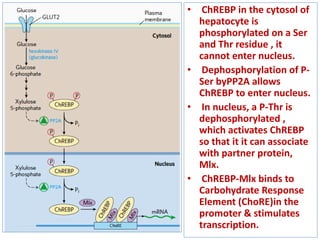
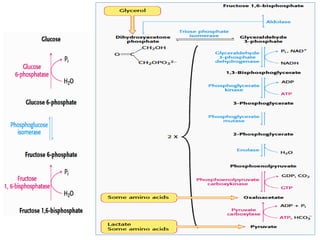
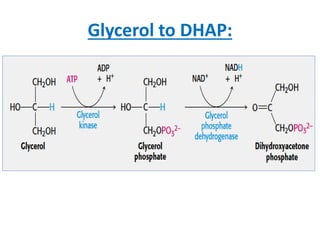
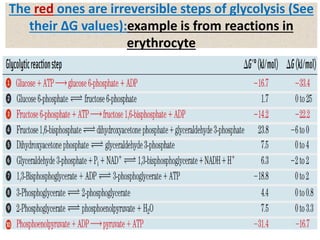
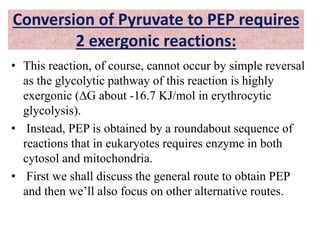
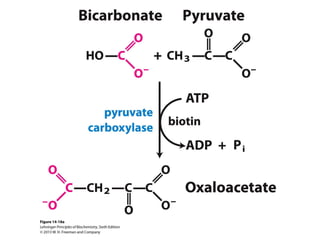
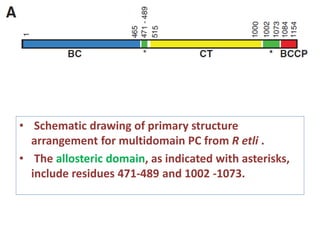
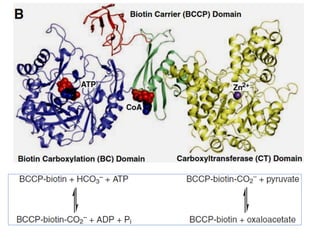
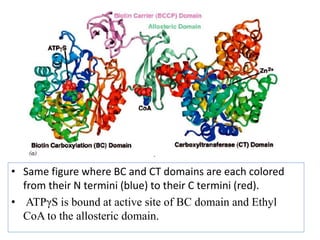
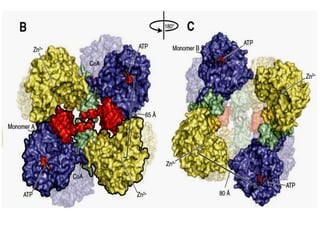
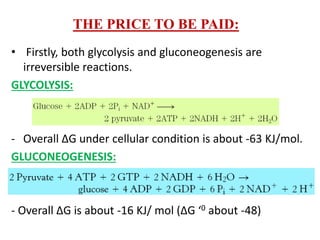
Glucose synthesis from non-carbohydrate precursors, known as gluconeogenesis, is essential for energy supply in mammals, particularly for the brain. The process utilizes various precursors, mainly three-carbon compounds, and occurs primarily in the liver and to a lesser extent in the kidneys and intestines. Notably, gluconeogenesis is not merely a reversal of glycolysis, as it involves specific bypass reactions to circumvent three key irreversible steps of glycolysis.





















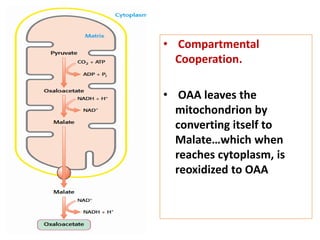
![But first let’s transport OAA to cytosol:
• Mitochondrial membrane has no transporter for
oxaloacetate (OAA).
• Therefore, before export to cytosol, OAA must be
reduced to malate by mitochondrial malate
dehydrogenase, at the expense of NADH.
• The ∆G’0 for this reaction is quite high, but under
physiological conditions (including low [OAA]), ∆G is
approximately 0, and the reaction is readily reversible.
Mitochondrial malate dehydrogenase works for both
gluconeogenesis and TCA cycle, but the flow of
metabolites is in opposite direction.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gluconeogenesis-190213033515/85/Gluconeogenesis-43-320.jpg)
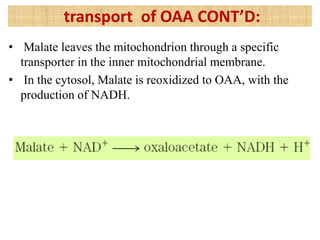
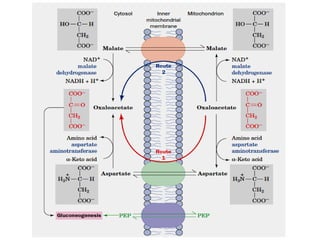
![• The [NADH] / [NAD+] ratio in the cytosol is 8 x 10-4 ,
about 105 times lower than in mitochondria.
• Because cytosolic NADH is consumed during
gluconeogenesis (during conversion of 1,3-
bisphosphoglycerate to glceraldehyde-3-P), glucose
synthesis isn’t possible unless NADH is available.
• The transport of malate, as we saw, utilizes
mitochondrial NADH and produces cytosolic NADH.
• Thus NADH is made available at the site where they
are scarce.
This path thus provides an important balance between
NADH produced and consumed in the cytosol during
gluconeogenesis.
this makes sense:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gluconeogenesis-190213033515/85/Gluconeogenesis-46-320.jpg)


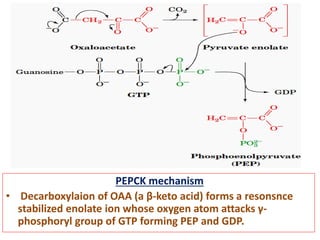




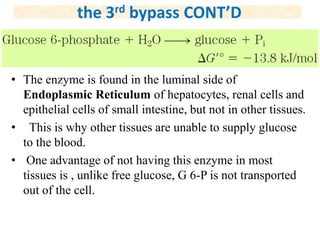
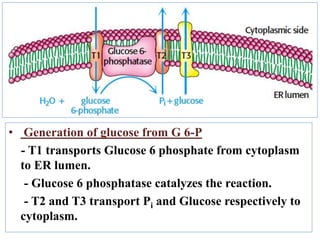
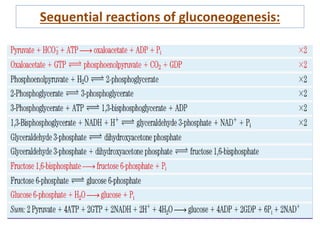

![• Now , the regulation of gluconeogenesis
[ in coordination with glycolysis]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gluconeogenesis-190213033515/85/Gluconeogenesis-62-320.jpg)


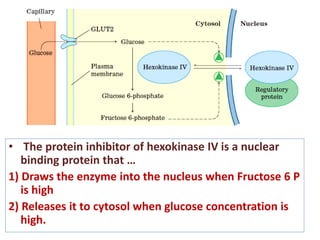

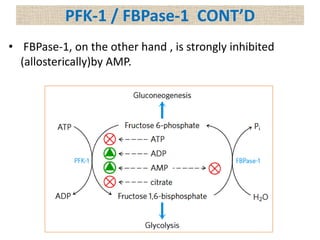
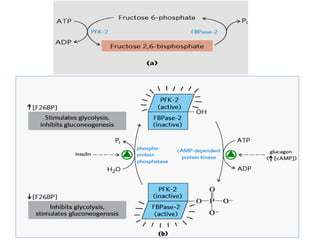
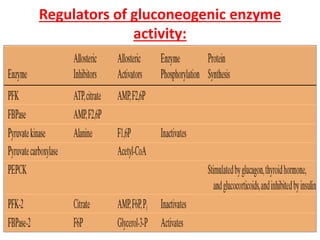
![PFK-1 / FBPase-1
• ATP is not only substrate for PFK-1 but also an end
product of glycolytic pathway.
• When high cellular [ATP]signals that ATP is being
produced faster than it is being consumed, ATP inhibits
PFK-1 by binding to an allosteric site and lowering the
affinity of enzyme for its substrate Fructose 6-P.
• ADP and AMP which increase in concentration as
consumption of ATP outpaces production, act
allosterically to relieve this inhibition by ATP.
• These effects combine to produce higher enzymatic
activity when ADP and AMP accumulates AND lower the
activity when ATP accumulates.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gluconeogenesis-190213033515/85/Gluconeogenesis-68-320.jpg)
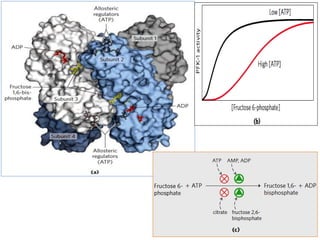
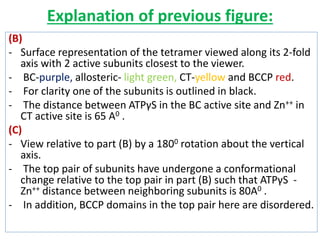
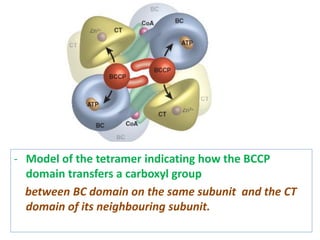
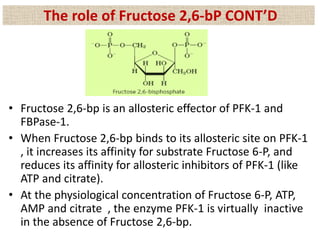
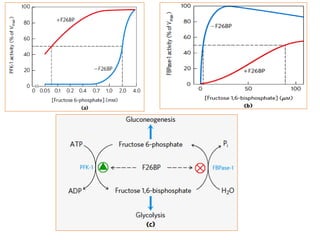
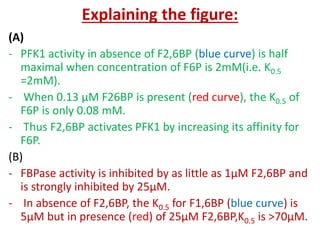
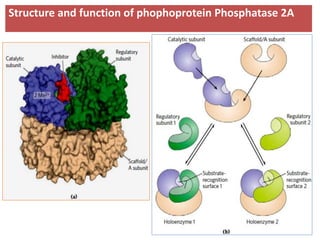
![(A)
- Surface contour image of E. coli PFK-1 showing portions of its
identical subunits…
- Each subunit has own catalytic site, producing ADP(red) and
Fructose 1,6-bp (yellow).
- ATP, the allosteric regulator is buried in the protein as
indicated.
(B)
- Allosteric regulation of muscle PFK-1 shown by substrate
activity curve.
- At low [ATP], the K0.5 (Km for regulatory enzyme) for fructose
6-P is low, enabling enzyme to perform at high rate.
(C) - Summary of the regulators
Explanation of the figure:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gluconeogenesis-190213033515/85/Gluconeogenesis-70-320.jpg)



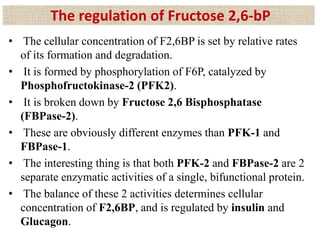
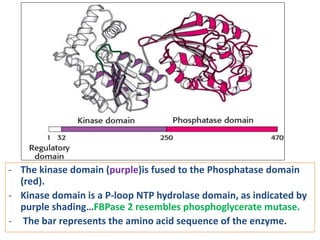
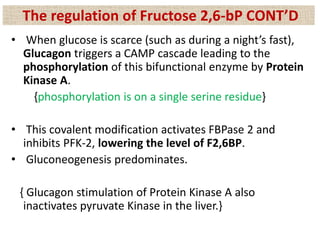


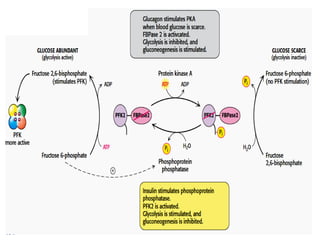




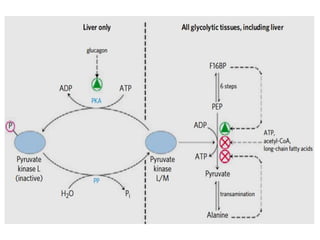

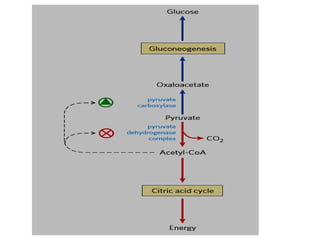
![• When cell’s energy need are being met, oxidative
phosphorylation slows down, [NADH] rises relative to
[NAD+] , and Acetyl CoA accumulates.
• The increased concentration of Acetyl CoA inhibits the
PDH Complex, slowing formation of Acetyl CoA from
Pyruvate, and stimulates gluconeogenesis by activating
Pyruvate Carboxylase.
• OAA is then converted to PEP by PEPCK.
• Regulation of PEPCK in mammals is usually at the level
of transcription.
• Fasting (high Glucagon) increases the transcription rate
through cAMP...Insulin has opposite effect.
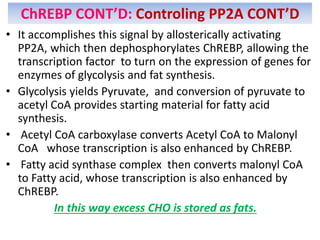
CONT’D](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gluconeogenesis-190213033515/85/Gluconeogenesis-94-320.jpg)
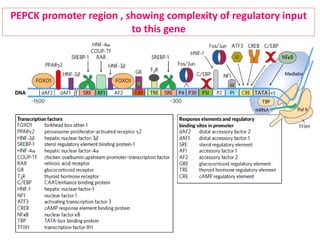
![• Transcriptional Regulation of
Gluconeogenesis
[ In Coordination with Glycolysis]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gluconeogenesis-190213033515/85/Gluconeogenesis-96-320.jpg)