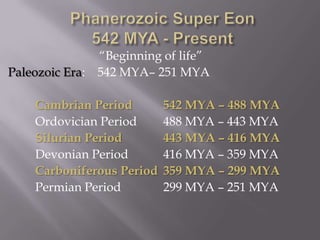
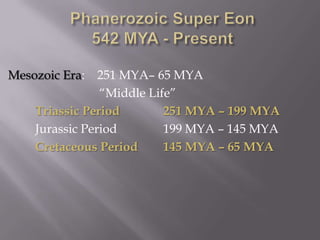
The document summarizes Earth's geologic history from its formation 4.6 billion years ago to the present. It is divided into eons, eras, periods, and epochs. The earliest eons included the Hadean and Archean, when Earth was molten and the first life formed. The Proterozoic saw continued formation of continents and oxygen buildup. The Phanerozoic eon saw the rise of complex life, including during the Paleozoic era of the Cambrian, Ordovician, and other periods. During the Mesozoic era, life included dinosaurs and the breakup of Pangaea. The Cenozoic era is the current one including the C