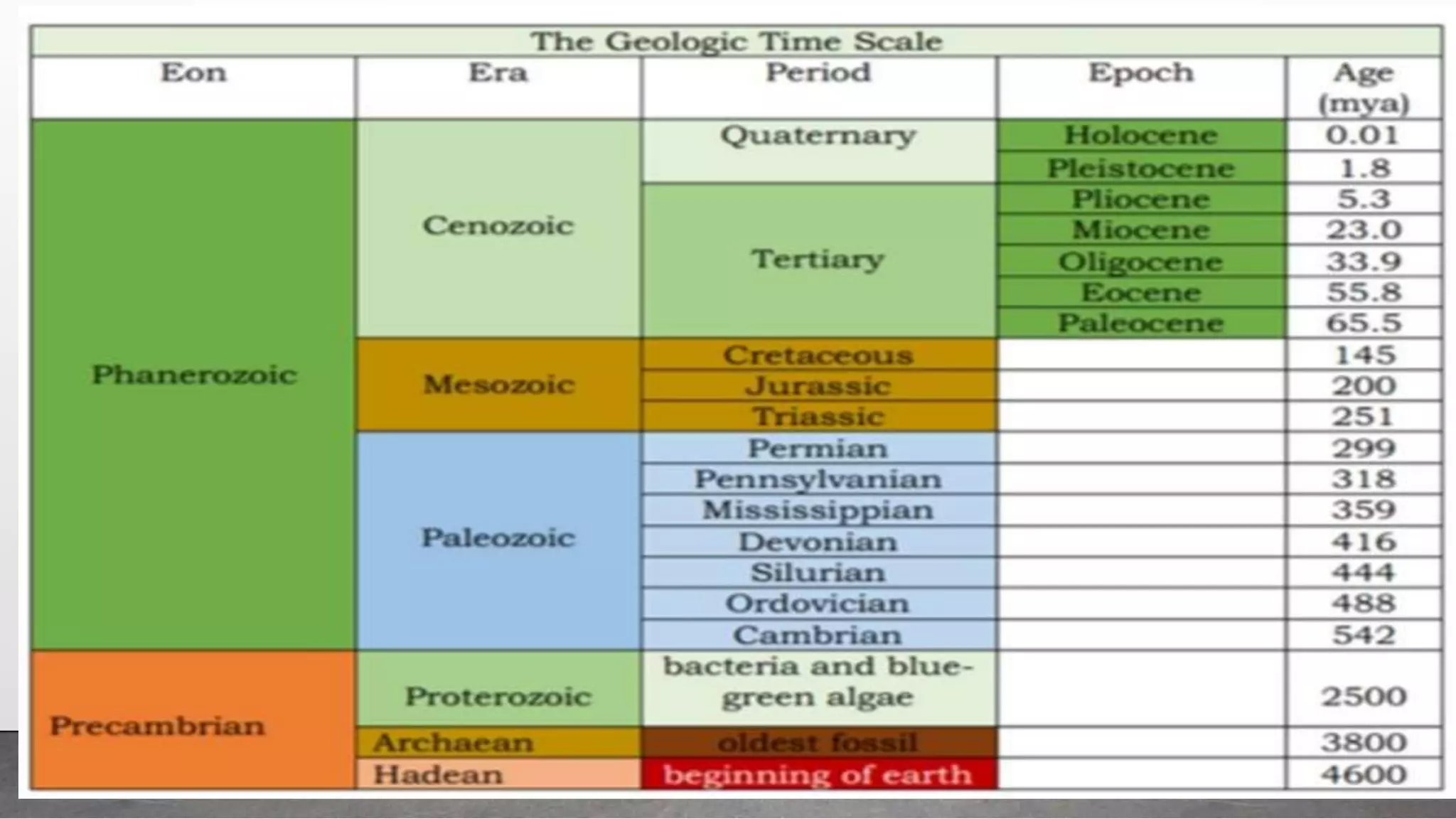
The document discusses the geologic time scale which is used by geologists to relate stratigraphy and time. It describes the major subdivisions of the time scale from largest to smallest as eons, eras, periods, and epochs. It provides details about each eon and era, describing the dominant life forms and major events that occurred during each period of Earth's history.