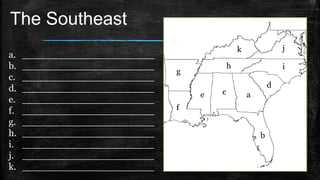
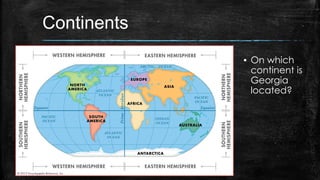
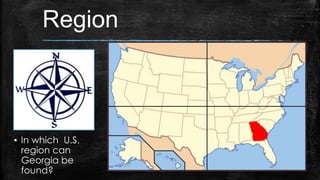
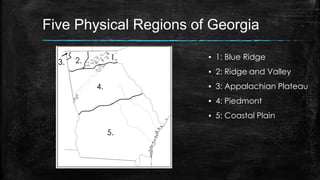
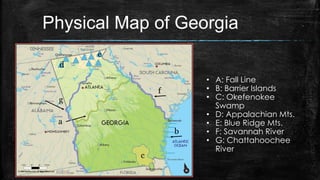
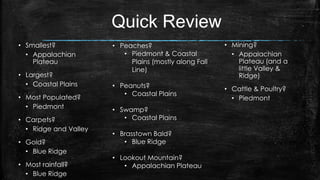
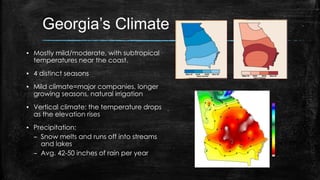
This document provides information about the geography and physical features of Georgia. It begins with an overview of Georgia's location in the northern and western hemispheres on the continent of North America within the nation of the United States in the southeastern region. It then details Georgia's five main physical regions - Blue Ridge, Ridge and Valley, Appalachian Plateau, Piedmont, and Coastal Plain - and notable landforms within each region like the Appalachian Mountains, Fall Line, Savannah River, and Okefenokee Swamp. The document concludes with descriptions of Georgia's climate and how water features influenced the state's development.