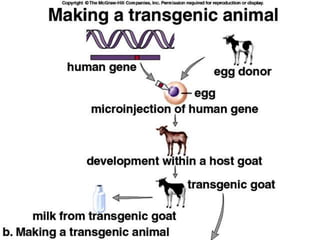
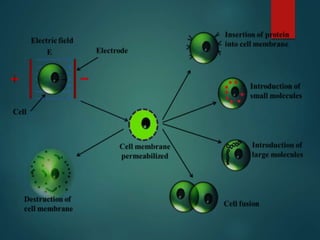
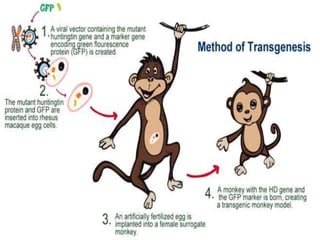
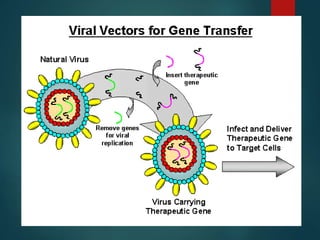
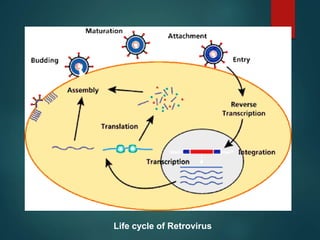
This document discusses genetically modified organisms (GMOs) and transgenic animals. It begins by defining a GMO as an organism whose genetic material has been altered by inserting DNA from another organism. Currently, most GM crops contain bacterial genes for pest or herbicide resistance. The document then discusses three main methods for producing transgenic animals: DNA microinjection, retrovirus-mediated gene transfer, and embryonic stem cell-mediated gene transfer. Transgenic animals have applications in agriculture, medicine, and industry by improving crop yields, providing organs for transplantation, and producing useful proteins.