This document summarizes information about genetically modified organisms and foods. It discusses:
- The history of genetic engineering beginning in the 1970s with the first recombinant DNA molecule and transgenic animal.
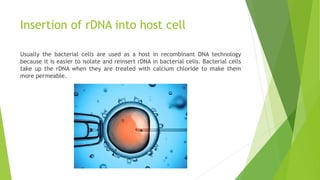
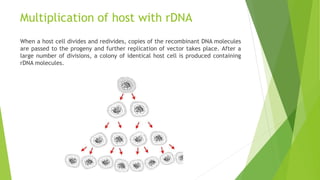
- The multi-stage process of producing GMOs, including identifying genes of interest, creating recombinant DNA, and inserting the DNA into host cells.
- Both the advantages of GMOs, such as increased crop yields and disease resistance, and the disadvantages, which include risks to biodiversity and potential allergic reactions in humans.
- Examples of genetically modified plants, animals, and other applications like producing insulin and vaccines.
- The ongoing controversies around GMOs regarding their ethics, impacts, and whether they should