The document discusses genetically modified crops (GMCs), including their definition, methods of genetic modification, potential benefits and risks. Some key points:
- GMCs are plants whose genetic characteristics have been altered by inserting genes from other species, conferring traits like pest/disease resistance, herbicide tolerance, drought tolerance, or improved nutrition.
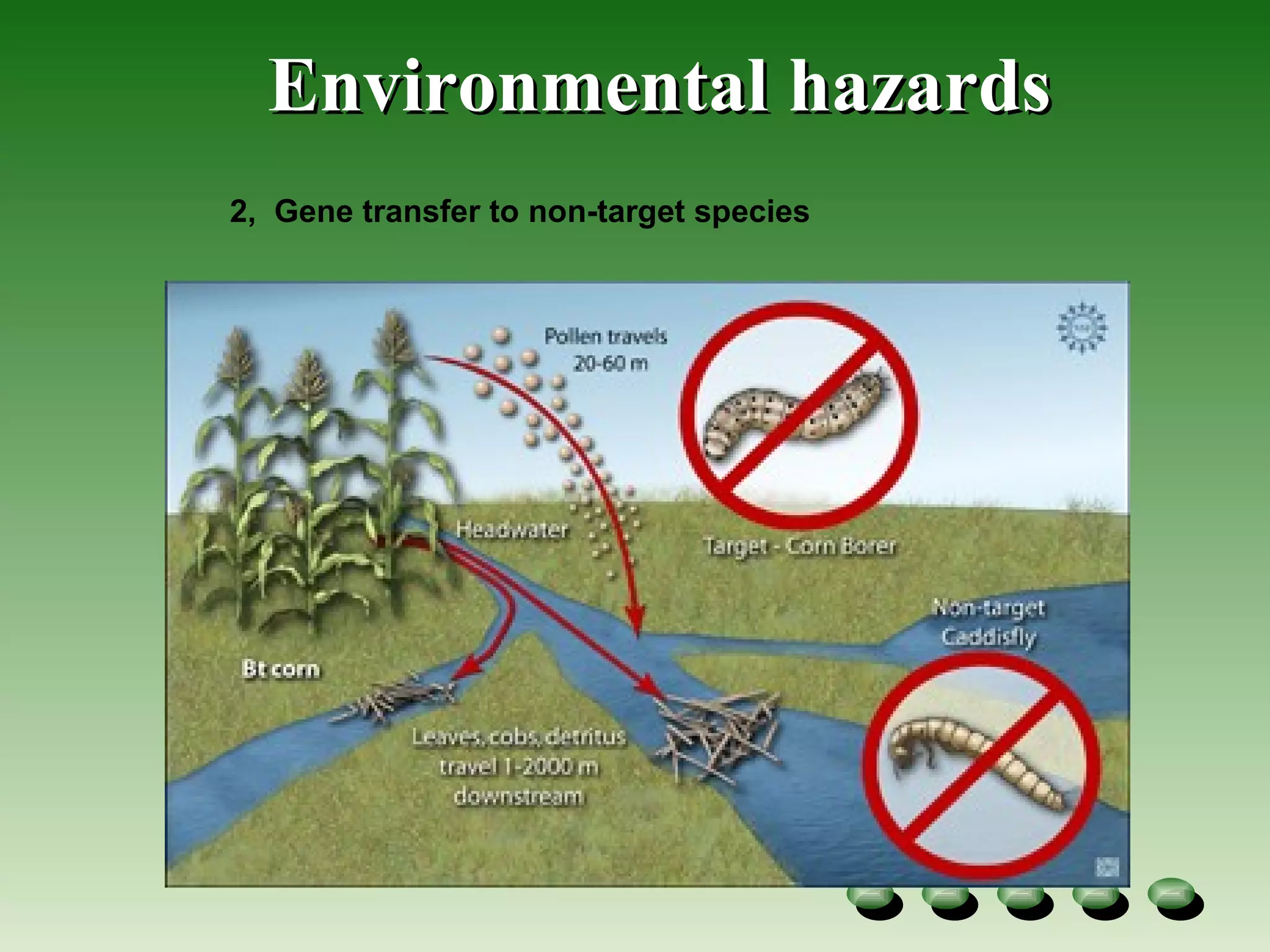
- Potential benefits include increased crop yields and reduced need for pesticides, but risks include possible human health impacts and environmental effects like gene transfer to non-target species.
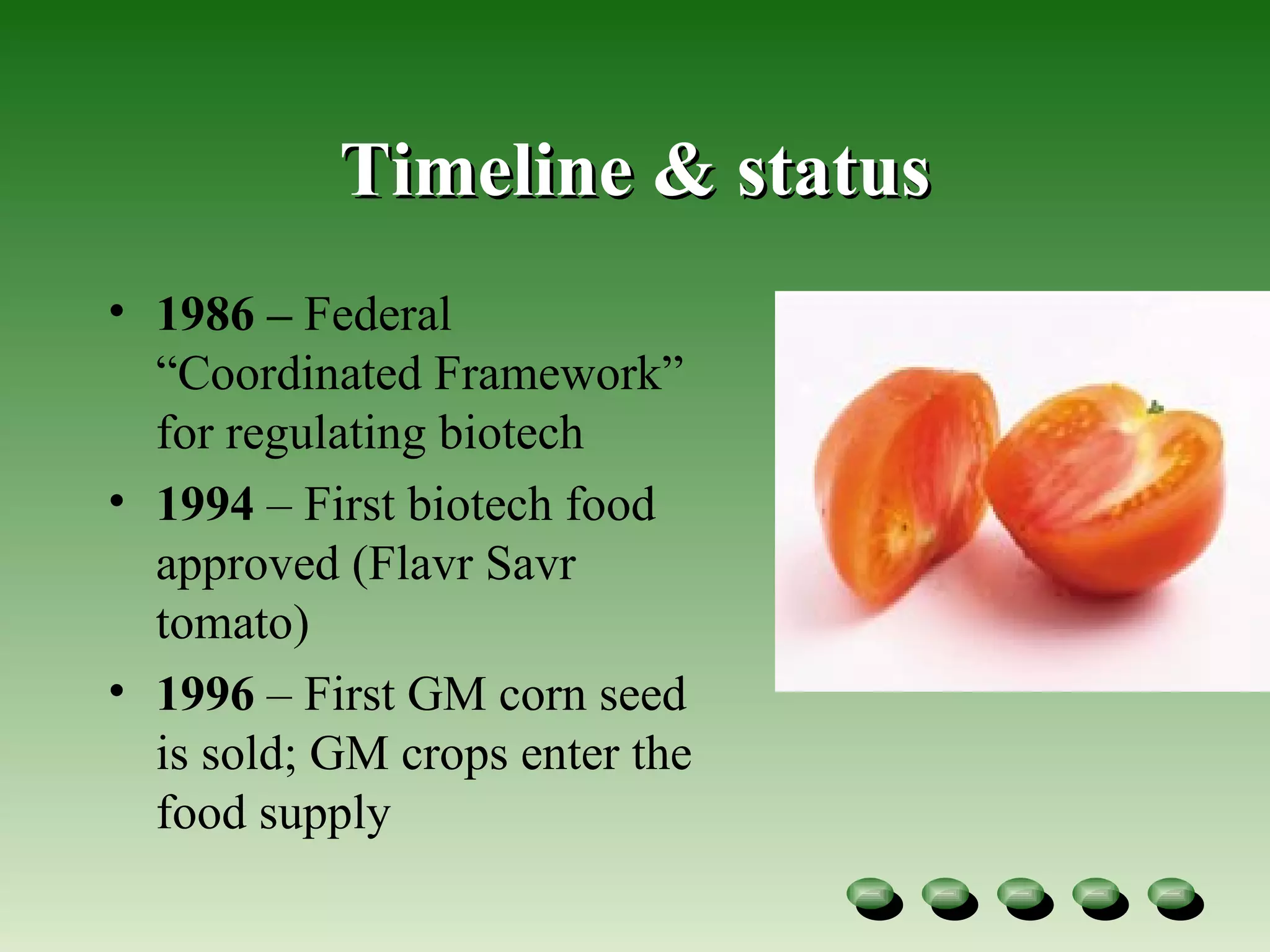
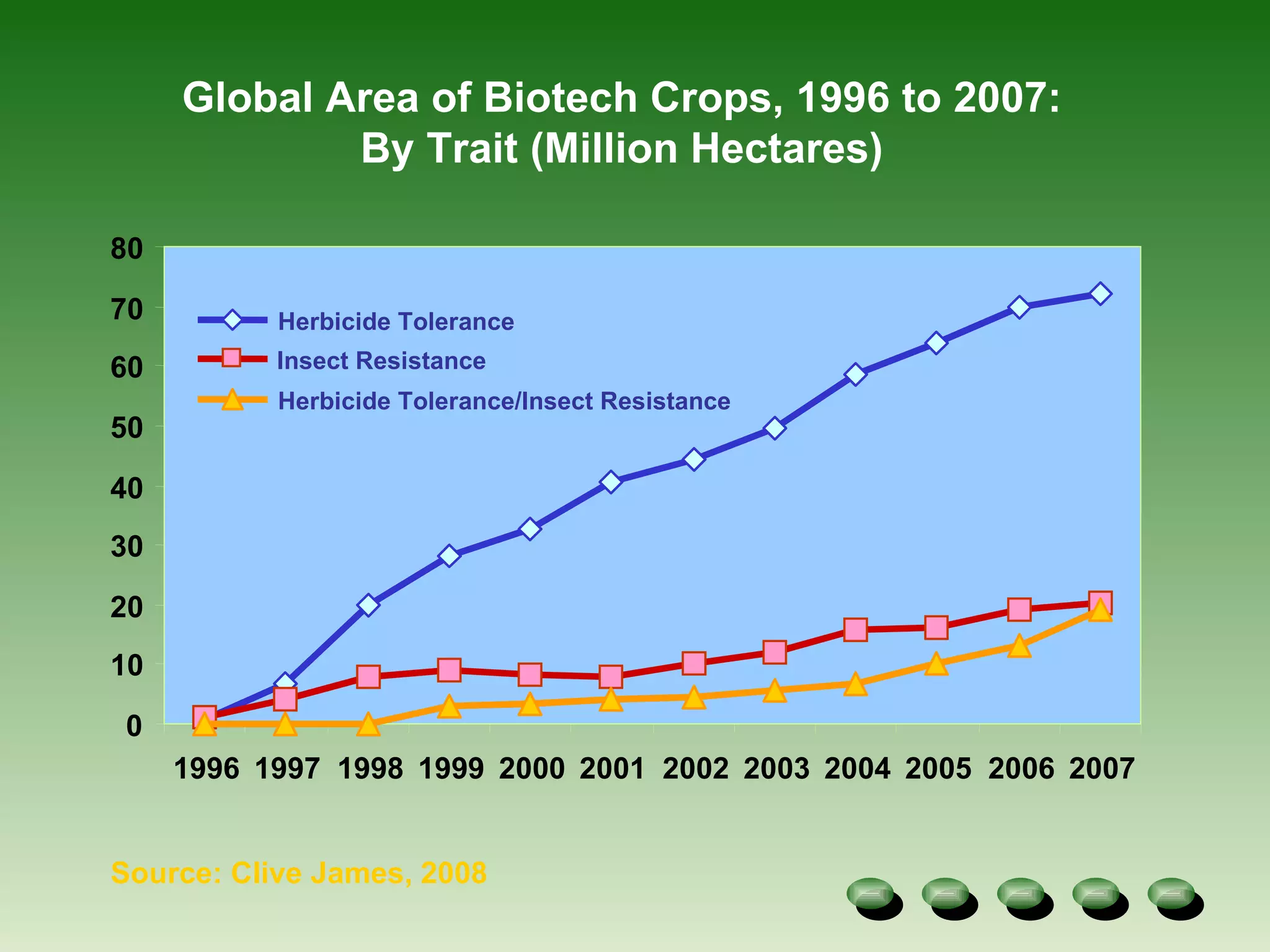
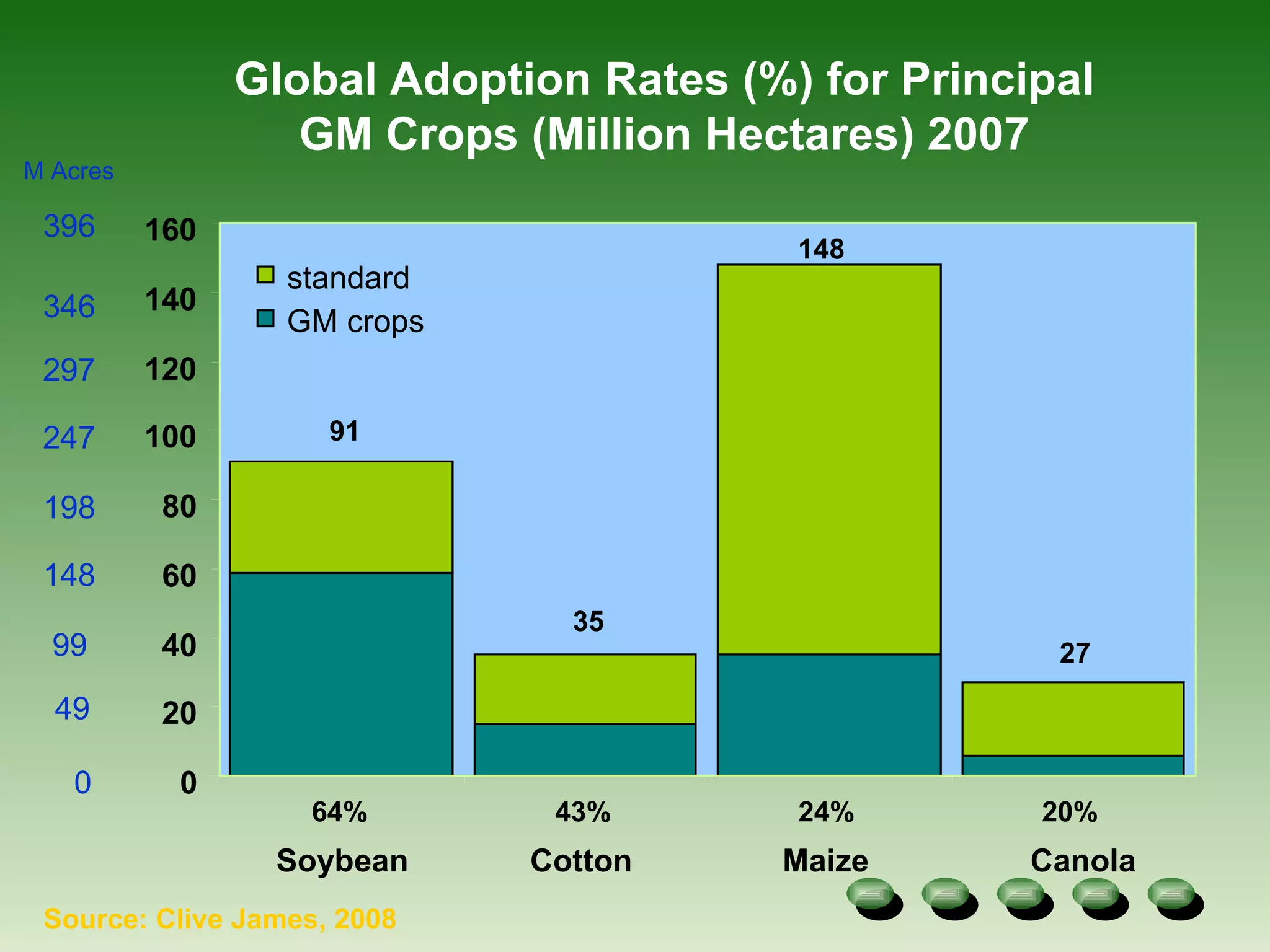
- Global adoption of major GM crops like soybean and maize has increased significantly since their introduction in the late 1990s, though uptake varies by country. Vietnam has conducted research on GM rice,