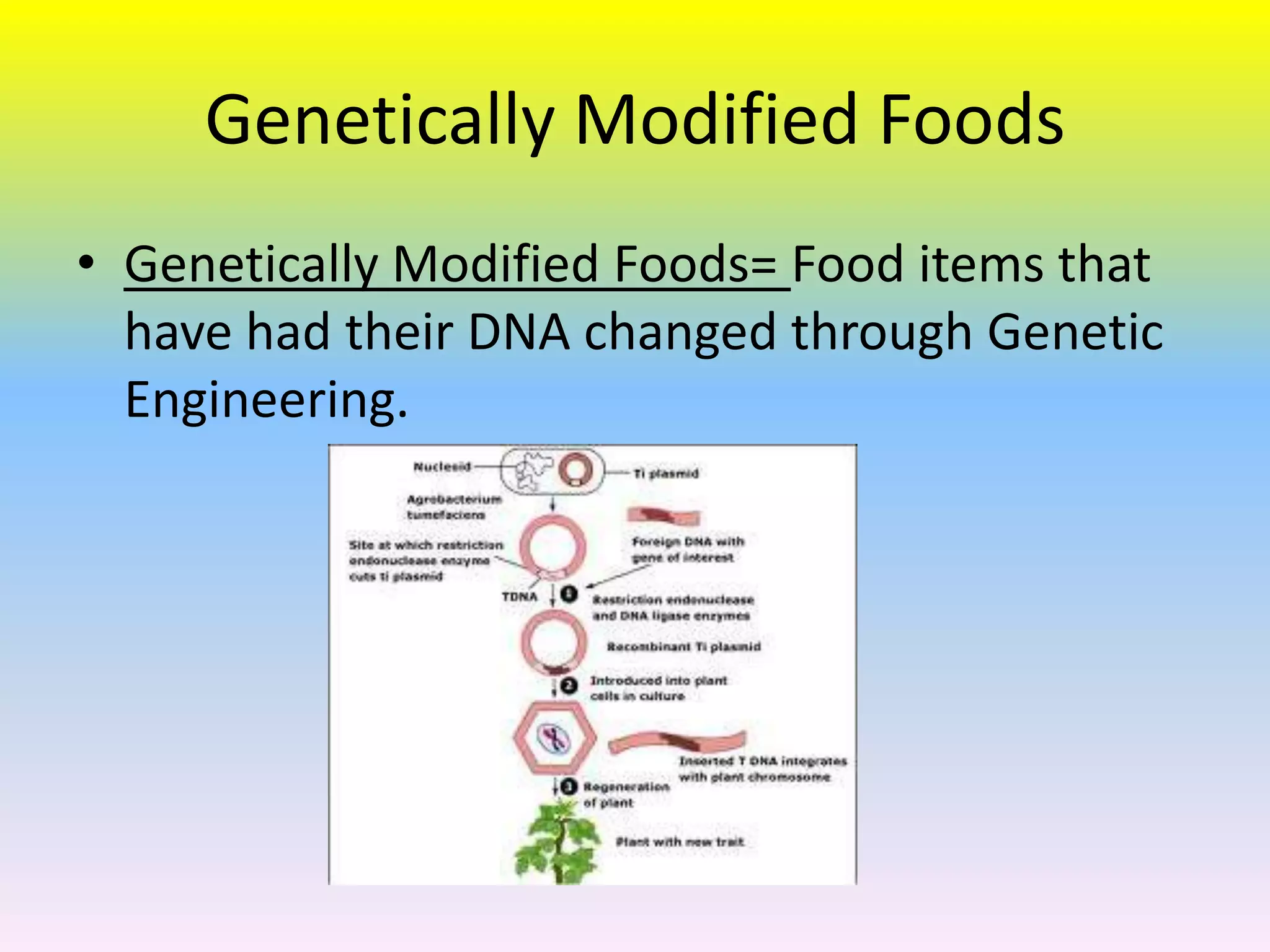
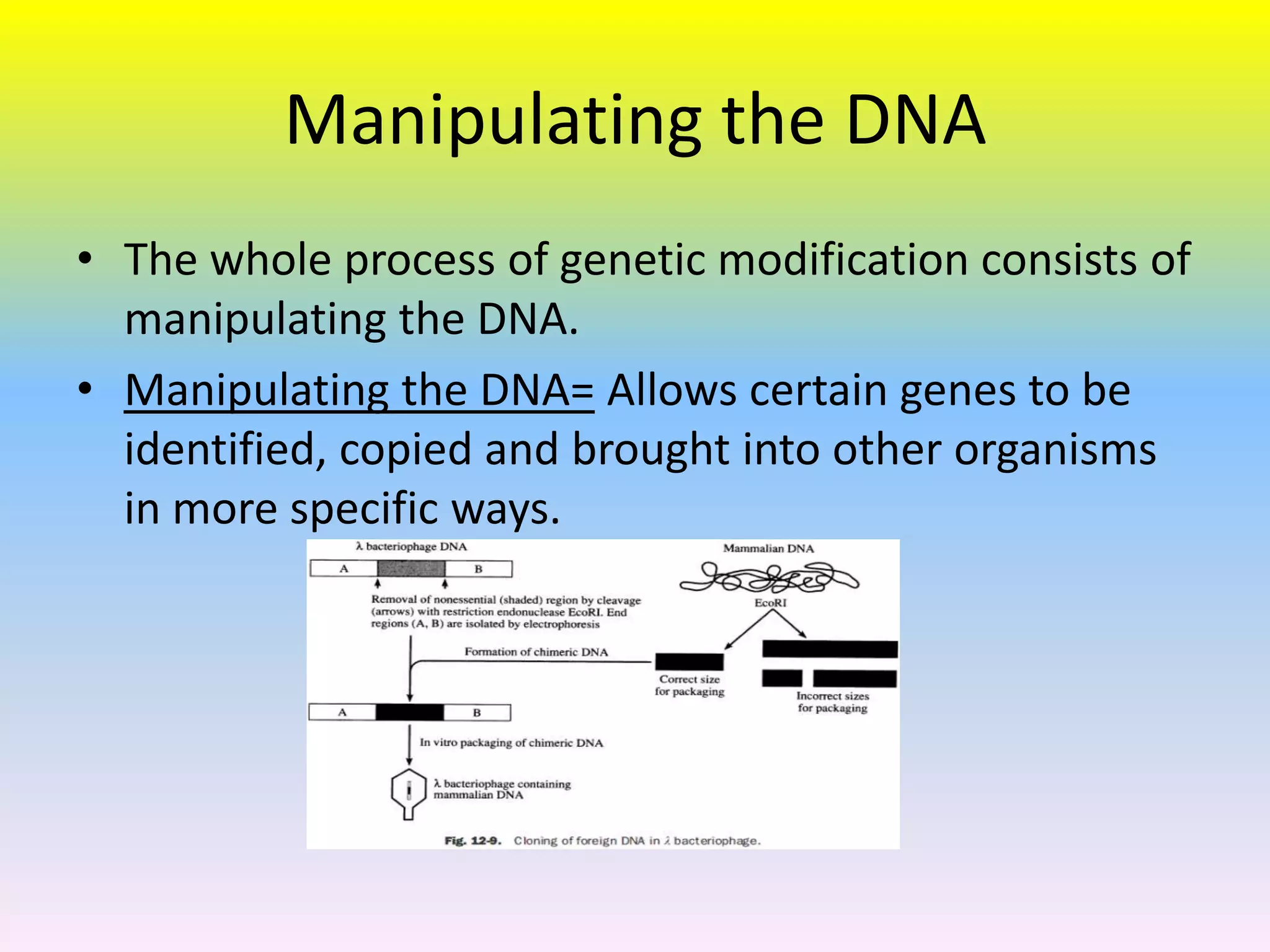
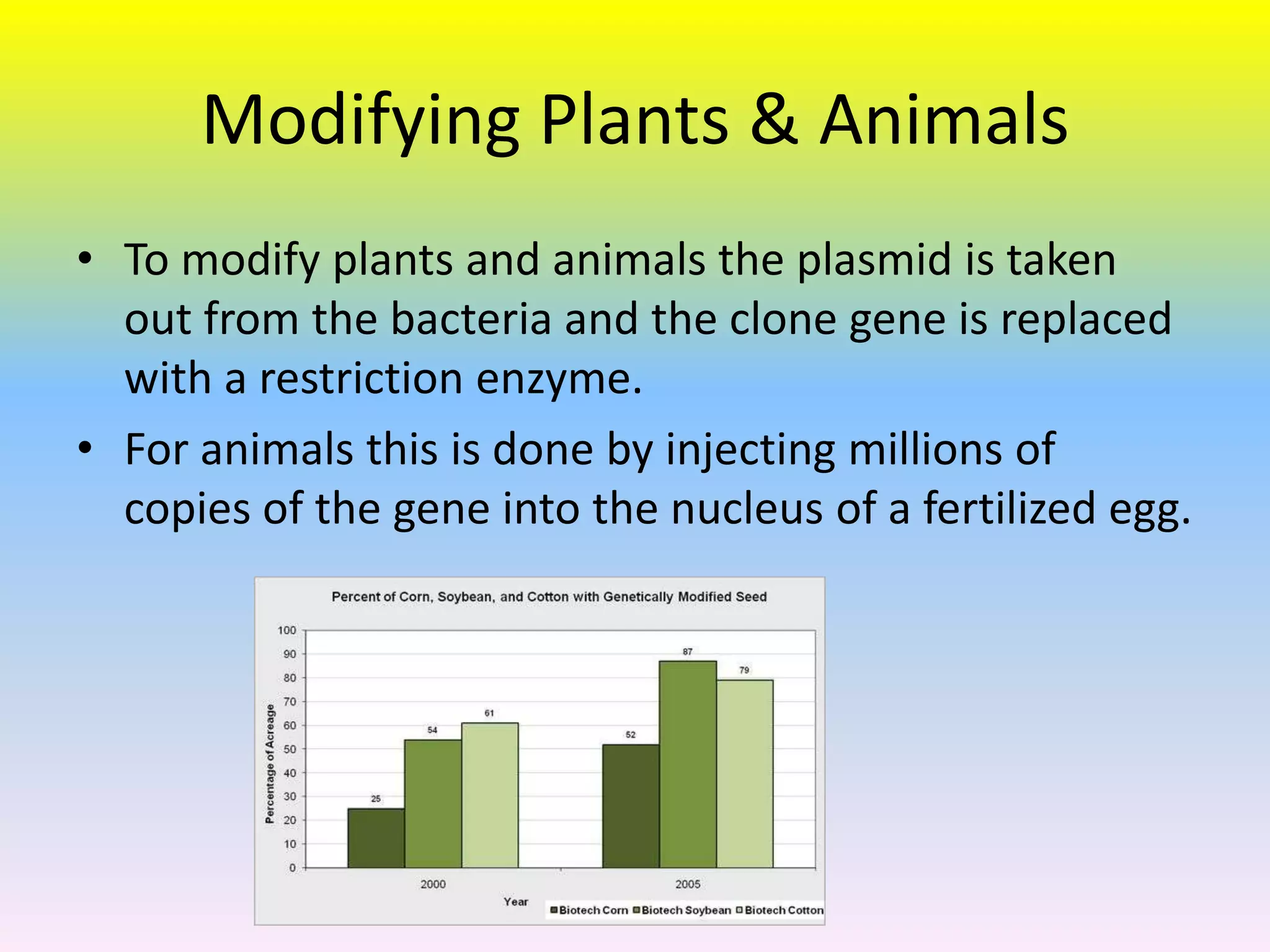
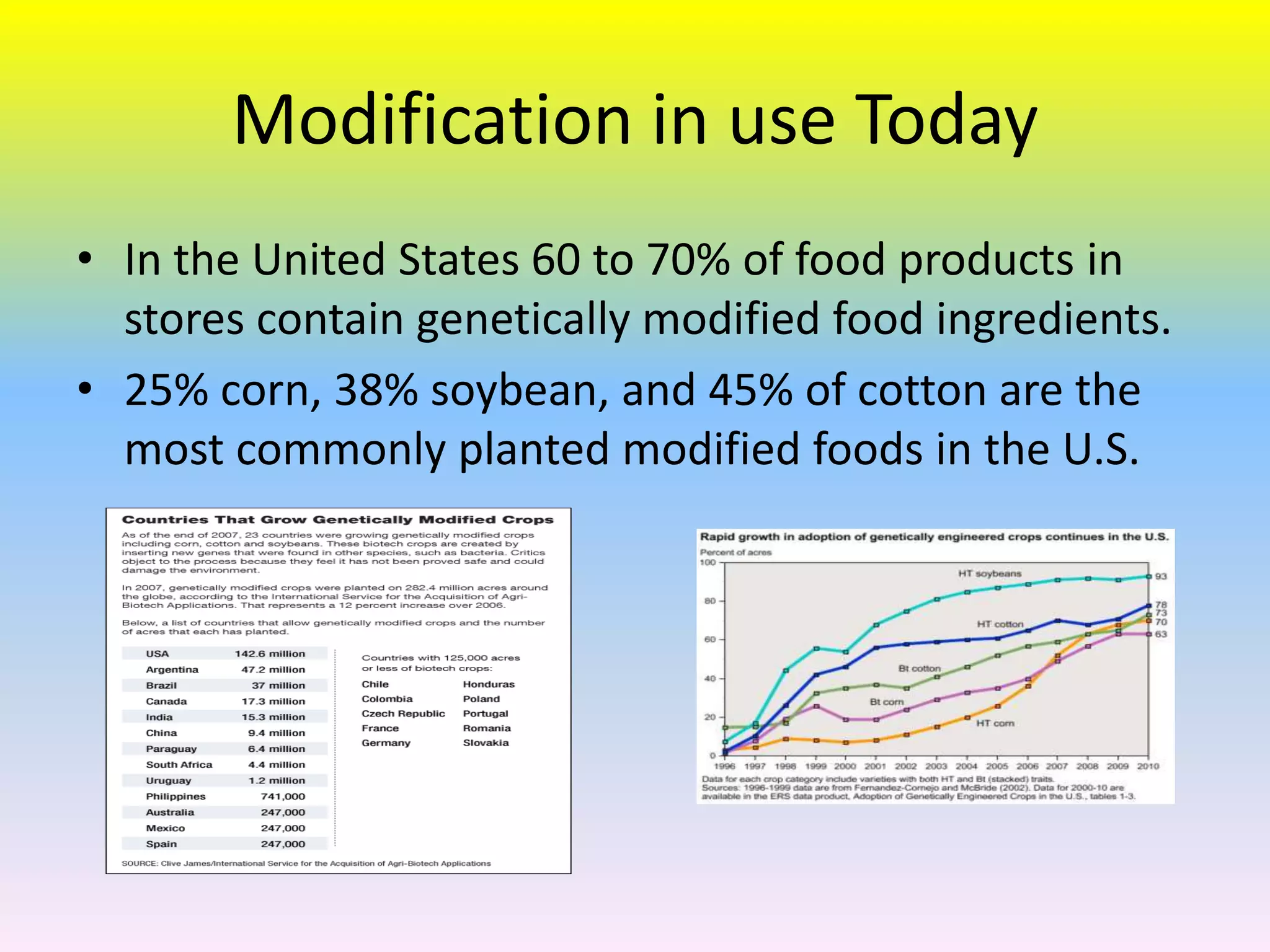
Genetically modified foods are foods that have had their DNA altered through genetic engineering. The process involves manipulating the DNA by identifying specific genes, copying them, and inserting them into other organisms. This is done to plants and animals by removing genes from bacteria and replacing them, or by injecting millions of copies of genes into fertilized eggs. Foods are modified by injecting genes or chemicals to make bananas larger or riper longer. While modification increases crop yields, it can also cause health concerns from potential allergic reactions to new ingredients. Most processed foods in the US contain genetically modified corn, soybeans, or cotton. Researchers are exploring new techniques like MAS to further boost agricultural production.